目录
- 哪些状态是要放到Vuex里进行状态管理呢?
- State
- Mutation
- Action
- Getters
- Module
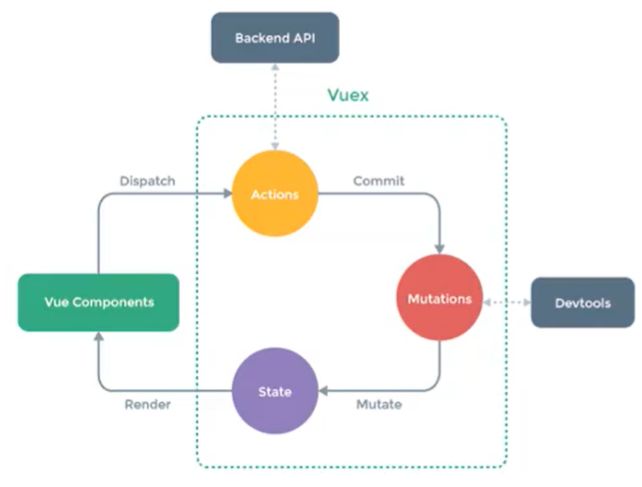
Vuex-多个组件之间共享状态,并且这些状态是响应式的
哪些状态是要放到Vuex里进行状态管理呢?
- 用户的登录状态(token,用户的个人信息)
- 商品的收藏,购物车中的物品
State
- 里用于存放一些需要共享的状态相关信息(对象类型)
- 单一状态树(Single Source of Truth),也可翻译成单一数据源,官方推荐一个项目只使用一个$store对象,方便管理和维护
- state里定义的属性会加入到vue的响应式系统中,响应式系统会监听属性的变化,当属性发生变化时,会通知所有界面中用到该属性的地方,让界面刷新
const store=new Vuex.store(
state:{
counter:100,
students:[
{id:110,name:"why",age:18},
{id:111,name:"kobe",age:24},
{id:112,name:"james",age:30},
{id:113,name:"curry",age:10}
],
info:{name:"bill",age:40,height:180}
}
)
Mutation
- Mutation里定义的函数都必须是同步操作,如果有异步操作,会导致Devtools跟踪不到修改;如果有异步操作放到action里执行
- Mutation 官方建议对State的修改要通过提交Mutations,这样可以通过Devtools工具跟踪修改的步骤
- 字符串的事件类型(type)
- 一个回调函数(handler),该回调函数的第一个参数为state
- mutation的定义方式:
mutations:{
increment(state){
state.count++
}
}
- 通过mutation更新
increment:function(){
this.$store.commit('increment');
}
- 如果需要传入参数,则放在第2个参数,参数被称为mutation的载荷(Payload)
mutations:{
incrementCount(state,count){ //第1个参数固定为state
state.count+=count
}
}
//使用的时候
this.$store.commit('incrementCount',10);
- 如果需要对state里的属性增加属性或删除属性
updateInfo(state){
//state.info["address"]="洛城" //这样加不是响应式的,不会更新界面
Vue.set(state.info,'address','洛城') //响应式的增加属性
// delete state.info.age //删除age属性,这样不是响应式的,不会更新界面
Vue.delete(state.info,'age') //响应式的删除属性
}
- Mutation常量类型-代码
mution-types.js
export const INCREMENT_COUNT
mution定义,用常量定义这一个函数(官方推荐)
import * as types from './mution-types'
mutions:{
[types.INCREMENT_COUNT](state,count){
state.count+=count
}
}
提交时也用这一个常量
import {INCREMENT_COUNT} from './store/mution-types'
this.$store.commt(INCREMENT_COUNT,10)
Action
- Action 主是一些异步操作(调用后端API)要放在actions里提交
- 定义,第1个参数是context,这里就不是state了,context有commit方法,进行提交mution;
第2个参数payload为传入的参数
actions:{
aUpdateInfo(context,payload){
setTimeout(()=>{
context.commit('updateInfo') //这里去提交mution,调用mution里的函数
console.log(payload) //我是传入的参数
},1000)
}
}
通过dispatch进行调用action
this.$store.dispatch('aUpdateInfo','我是传入的参数')
- 异步操作完成后,如果我要回调通知一下界面,怎么办?
1.在payload加一个函数 (此方法不够优雅,官方推荐用Promise)
actions:{
aUpdateInfo(context,payload){
setTimeout(()=>{
context.commit('updateInfo') //这里去提交mution,调用mution里的函数
console.log(payload.message) //我是传入的参数
payload.success("成功了") //回调
},1000)
}
}
通过dispatch进行调用action
this.$store.dispatch('aUpdateInfo',{
message:'我是传入的参数'
success:(txt)=>{
console.log(txt) //成功了
}
})
2.通过Promise进行回调
actions:{
aUpdateInfo(context,payload){
return new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{
setTimeout(()=>{
context.commit('updateInfo') //这里去提交mution,调用mution里的函数
console.log(payload) //我是传入的参数
resolve("成功了")
},1000)
})
}
}
this.$store.dispatch('aUpdateInfo','我是传入的参数')
.then((data)=>{
console.log(data) //成功了
})
Getters
- 类似于计算属性,里面定义为函数,一般我们需要在store中获取一些state经过计算或转换后的状态
getters:{
//count的平方
powerCounter(state){
return state.count*state.count
},
//年龄大于20的学生
more20stu(state){
return state.students.filter(s=>s.age>20)
},
//年龄大于20的人数
more20stuLength(state,getters){ //这里第2个参数是getters
return getters.more20stu.length
},
//年龄大于age的人数,age为传进来的一个参数
moreAgeStu(state){
return function(age){
return state.students.filter(s=>s.age>age)
}
},
//简写
moreAgeStu(state){
return age=>{
return state.students.filter(s=>s.age>age)
}
}
}
//使用
{{$store.getters.powerCounter}}
{{$store.getters.more20stu}}
{{$store.getters.more20stuLength}}
{{$store.getters.moreAgeStu(12)}}
Module
- Vue使用单一状态树,意味着很多状态都会交给Vuex来管理
- 当应用变得非常复杂时,store对象就有可能变得相当臃肿
- 为了解决这个问题,Vuex允许我们将store分割成模块(Module),而每个模块拥有自己的state,mutations,actions,getters等
const moduleA={
state:{},
mutations:{},
actions:{},
getters:{}
}
const moduleB={
state:{},
mutations:{},
actions:{},
getters:{}
}
const store=new Vuex.Store({
modules:{
a:moduleA,
b:moduleB
}
})
store.state.a //->moduleA的状态
store.state.b //->moduleB的状态