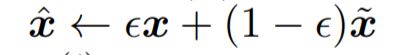WGAN-GP 简介与代码实战
1.介绍
WGAN虽然理论证明很完美,但真正的效果并没有很好,主要原因在于lipschitz连续性条件,本文所讲的WGAN-GP就是针对lipschitz连续性条件而做的改进,更加详细的内容可参见论文:Improved Training of Wasserstein GANs
2.模型结构
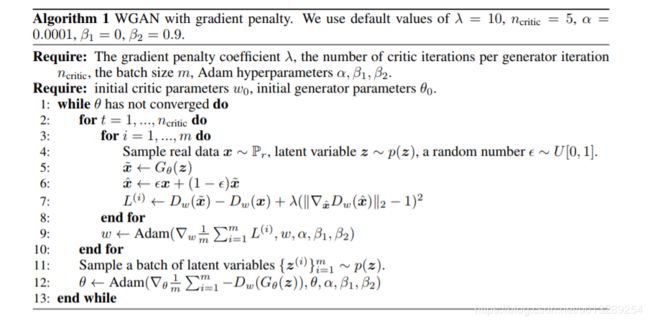
整个算法流程,我们注意这两点就行:
1. 利用随机数,在生成数据和真实数据上做一个插值
2. 梯度惩罚
3.模型特点
WGAN-GP相比WGAN的算法实现流程却只改了两点:
1. WGAN在权值剪切(比如剪切到[-0.01,+0.01]会导致,权重分散不均匀)的时候,而WGAN-GP利用梯度惩罚,可以很好的使得权重分布均匀,充分发挥神经网络的学习力。
2. D的梯度是整个空间(包括生成图片和真实图片),如果直接计算,会导致运行速度很慢,作者的方式很巧妙:利用随机数,在生成数据和真实数据上做一个插值(是不是有点像batch size操作,以部分代替全部)
3. D不能用batch norm, 因为每个样本是被独立的添加梯度惩罚,而batch norm会引入同一batch样本之间的依赖关系
4.代码实现 keras
class WGANGP():
def __init__(self):
self.img_rows = 28
self.img_cols = 28
self.channels = 1
self.img_shape = (self.img_rows, self.img_cols, self.channels)
self.latent_dim = 100
# Following parameter and optimizer set as recommended in paper
self.n_critic = 5
optimizer = RMSprop(lr=0.00005)
# Build the generator and critic
self.generator = self.build_generator()
self.critic = self.build_critic()
#-------------------------------
# Construct Computational Graph
# for the Critic
#-------------------------------
# Freeze generator's layers while training critic
self.generator.trainable = False
# Image input (real sample)
real_img = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
# Noise input
z_disc = Input(shape=(self.latent_dim,))
# Generate image based of noise (fake sample)
fake_img = self.generator(z_disc)
# Discriminator determines validity of the real and fake images
fake = self.critic(fake_img)
valid = self.critic(real_img)
# Construct weighted average between real and fake images
interpolated_img = RandomWeightedAverage()([real_img, fake_img])
# Determine validity of weighted sample
validity_interpolated = self.critic(interpolated_img)
# Use Python partial to provide loss function with additional
# 'averaged_samples' argument
partial_gp_loss = partial(self.gradient_penalty_loss,
averaged_samples=interpolated_img)
partial_gp_loss.__name__ = 'gradient_penalty' # Keras requires function names
self.critic_model = Model(inputs=[real_img, z_disc],
outputs=[valid, fake, validity_interpolated])
self.critic_model.compile(loss=[self.wasserstein_loss,
self.wasserstein_loss,
partial_gp_loss],
optimizer=optimizer,
loss_weights=[1, 1, 10])
#-------------------------------
# Construct Computational Graph
# for Generator
#-------------------------------
# For the generator we freeze the critic's layers
self.critic.trainable = False
self.generator.trainable = True
# Sampled noise for input to generator
z_gen = Input(shape=(100,))
# Generate images based of noise
img = self.generator(z_gen)
# Discriminator determines validity
valid = self.critic(img)
# Defines generator model
self.generator_model = Model(z_gen, valid)
self.generator_model.compile(loss=self.wasserstein_loss, optimizer=optimizer)
def gradient_penalty_loss(self, y_true, y_pred, averaged_samples):
"""
Computes gradient penalty based on prediction and weighted real / fake samples
"""
gradients = K.gradients(y_pred, averaged_samples)[0]
# compute the euclidean norm by squaring ...
gradients_sqr = K.square(gradients)
# ... summing over the rows ...
gradients_sqr_sum = K.sum(gradients_sqr,
axis=np.arange(1, len(gradients_sqr.shape)))
# ... and sqrt
gradient_l2_norm = K.sqrt(gradients_sqr_sum)
# compute lambda * (1 - ||grad||)^2 still for each single sample
gradient_penalty = K.square(1 - gradient_l2_norm)
# return the mean as loss over all the batch samples
return K.mean(gradient_penalty)
def wasserstein_loss(self, y_true, y_pred):
return K.mean(y_true * y_pred)
def build_generator(self):
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(128 * 7 * 7, activation="relu", input_dim=self.latent_dim))
model.add(Reshape((7, 7, 128)))
model.add(UpSampling2D())
model.add(Conv2D(128, kernel_size=4, padding="same"))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Activation("relu"))
model.add(UpSampling2D())
model.add(Conv2D(64, kernel_size=4, padding="same"))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Activation("relu"))
model.add(Conv2D(self.channels, kernel_size=4, padding="same"))
model.add(Activation("tanh"))
model.summary()
noise = Input(shape=(self.latent_dim,))
img = model(noise)
return Model(noise, img)
def build_critic(self):
model = Sequential()
model.add(Conv2D(16, kernel_size=3, strides=2, input_shape=self.img_shape, padding="same"))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(Conv2D(32, kernel_size=3, strides=2, padding="same"))
model.add(ZeroPadding2D(padding=((0,1),(0,1))))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(Conv2D(64, kernel_size=3, strides=2, padding="same"))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(Conv2D(128, kernel_size=3, strides=1, padding="same"))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(Flatten())
model.add(Dense(1))
model.summary()
img = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
validity = model(img)
return Model(img, validity)
def train(self, epochs, batch_size, sample_interval=50):
# Load the dataset
(X_train, _), (_, _) = mnist.load_data()
# Rescale -1 to 1
X_train = (X_train.astype(np.float32) - 127.5) / 127.5
X_train = np.expand_dims(X_train, axis=3)
# Adversarial ground truths
valid = -np.ones((batch_size, 1))
fake = np.ones((batch_size, 1))
dummy = np.zeros((batch_size, 1)) # Dummy gt for gradient penalty
for epoch in range(epochs):
for _ in range(self.n_critic):
# ---------------------
# Train Discriminator
# ---------------------
# Select a random batch of images
idx = np.random.randint(0, X_train.shape[0], batch_size)
imgs = X_train[idx]
# Sample generator input
noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (batch_size, self.latent_dim))
# Train the critic
d_loss = self.critic_model.train_on_batch([imgs, noise],
[valid, fake, dummy])
# ---------------------
# Train Generator
# ---------------------
g_loss = self.generator_model.train_on_batch(noise, valid)
# Plot the progress
print ("%d [D loss: %f] [G loss: %f]" % (epoch, d_loss[0], g_loss))
# If at save interval => save generated image samples
if epoch % sample_interval == 0:
self.sample_images(epoch)
def sample_images(self, epoch):
r, c = 5, 5
noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (r * c, self.latent_dim))
gen_imgs = self.generator.predict(noise)
# Rescale images 0 - 1
gen_imgs = 0.5 * gen_imgs + 0.5
fig, axs = plt.subplots(r, c)
cnt = 0
for i in range(r):
for j in range(c):
axs[i,j].imshow(gen_imgs[cnt, :,:,0], cmap='gray')
axs[i,j].axis('off')
cnt += 1
fig.savefig("images/mnist_%d.png" % epoch)
plt.close()