HBase学习之六: hbase的预分区设计
背景
HBase默认建表时有一个region,这个region的rowkey是没有边界的,即没有startkey和endkey,在数据写入时,所有数据都会写入这个默认的region,随着数据量的不断 增加,此region已经不能承受不断增长的数据量,会进行split,分成2个region。在此过程中,会产生两个问题:
1.数据往一个region上写,会有写热点问题。
2.region split会消耗宝贵的集群I/O资源。
基于此我们可以控制在建表的时候,创建多个空region,并确定每个region的起始和终止rowky,这样只要我们的rowkey设计能均匀的命中各个region,就不会存在写热点问题。自然split的几率也会大大降低。当然随着数据量的不断增长,该split的还是要进行split。像这样预先创建hbase表分区的方式,称之为预分区,下面给出一种预分区的实现方式:
首先看没有进行预分区的表,startkey和endkey为空。
![]()
要进行预分区,首先要明确rowkey的取值范围或构成逻辑,以我的rowkey组成为例:
两位随机数+时间戳+客户号,两位随机数的范围从00-99,于是我划分了10个region来存储数据,每个region对应的rowkey范围如下:
-10,10-20,20-30,30-40,40-50,50-60,60-70,70-80,80-90,90-在使用HBase API建表的时候,需要产生splitkeys二维数组,这个数组存储的rowkey的边界值。下面是java 代码实现:
private byte[][] getSplitKeys() {
String[] keys = new String[] { "10|", "20|", "30|", "40|", "50|",
"60|", "70|", "80|", "90|" };
byte[][] splitKeys = new byte[keys.length][];
TreeSet rows = new TreeSet(Bytes.BYTES_COMPARATOR);//升序排序
for (int i = 0; i < keys.length; i++) {
rows.add(Bytes.toBytes(keys[i]));
}
Iterator rowKeyIter = rows.iterator();
int i=0;
while (rowKeyIter.hasNext()) {
byte[] tempRow = rowKeyIter.next();
rowKeyIter.remove();
splitKeys[i] = tempRow;
i++;
}
return splitKeys;
} 需要注意的是,在上面的代码中用treeset对rowkey进行排序,必须要对rowkey排序,否则在调用admin.createTable(tableDescriptor,splitKeys)的时候会出错。创建表的代码如下:
/**
* 创建预分区hbase表
* @param tableName 表名
* @param columnFamily 列簇
* @return
*/
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public boolean createTableBySplitKeys(String tableName, List columnFamily) {
try {
if (StringUtils.isBlank(tableName) || columnFamily == null
|| columnFamily.size() < 0) {
log.error("===Parameters tableName|columnFamily should not be null,Please check!===");
}
HBaseAdmin admin = new HBaseAdmin(conf);
if (admin.tableExists(tableName)) {
return true;
} else {
HTableDescriptor tableDescriptor = new HTableDescriptor(
TableName.valueOf(tableName));
for (String cf : columnFamily) {
tableDescriptor.addFamily(new HColumnDescriptor(cf));
}
byte[][] splitKeys = getSplitKeys();
admin.createTable(tableDescriptor,splitKeys);//指定splitkeys
log.info("===Create Table " + tableName
+ " Success!columnFamily:" + columnFamily.toString()
+ "===");
}
} catch (MasterNotRunningException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
log.error(e);
return false;
} catch (ZooKeeperConnectionException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
log.error(e);
return false;
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
log.error(e);
return false;
}
return true;
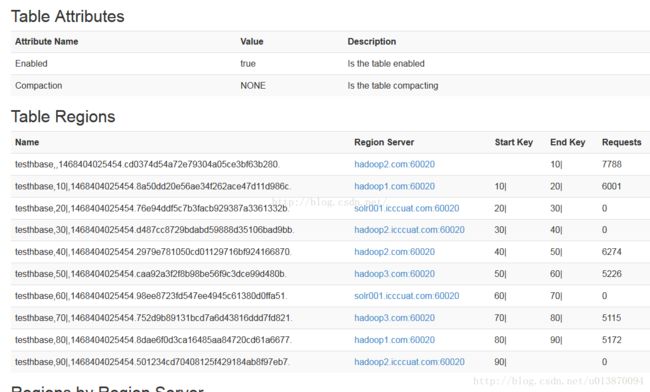
} 在hbase shell中输入命令san 'hbase:meta'查看建表结果:
从上图可看出10个region均匀的分布在了3台regionserver上(集群就3台机器regionserver),达到预期效果。还可以在hbase的web UI界面中更加直观的查看建表的预分区信息。
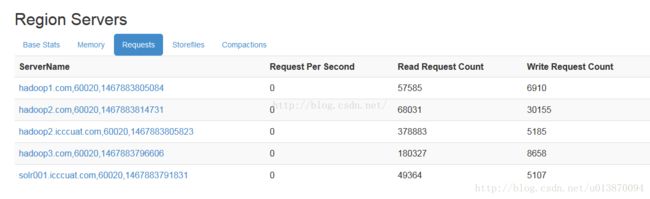
再看看写数据是否均匀的命中各个region,是否能够做到对写请求的负载均衡:
public class TestHBasePartition {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
HBaseAdmin admin = new HBaseAdmin(conf);
HTable table = new HTable(conf, "testhbase");
table.put(batchPut());
}
private static String getRandomNumber(){
String ranStr = Math.random()+"";
int pointIndex = ranStr.indexOf(".");
return ranStr.substring(pointIndex+1, pointIndex+3);
}
private static List batchPut(){
List list = new ArrayList();
for(int i=1;i<=10000;i++){
byte[] rowkey = Bytes.toBytes(getRandomNumber()+"-"+System.currentTimeMillis()+"-"+i);
Put put = new Put(rowkey);
put.add(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("name"), Bytes.toBytes("zs"+i));
list.add(put);
}
return list;
}
} 我写了1万条数据,从Write Request Count一栏可以查看写请求是否均匀的分布到3台机器上,实测我的达到目标,完成。参考文章:
http://www.cnblogs.com/bdifn/p/3801737.html
http://blog.csdn.net/chaolovejia/article/details/46375849
http://www.cnblogs.com/panfeng412/archive/2012/03/08/hbase-performance-tuning-section1.html