算法----LFU缓存
实现最不经常使用(LFU)缓存算法设计并实现数据结构。
它应该支持以下操作:get 和 put。
get(key) - 如果键存在于缓存中,则获取键的值(总是正数),否则返回 -1。
put(key, value) - 如果键不存在,请设置或插入值。当缓存达到其容量时,则应该在插入新项之前,使最不经常使用的项无效。在此问题中,当存在平局(即两个或更多个键具有相同使用频率)时,应该去除 最近 最少使用的键。
「项的使用次数」就是自插入该项以来对其调用 get 和 put 函数的次数之和。使用次数会在对应项被移除后置为 0 。
进阶:
你是否可以在 O(1) 时间复杂度内执行两项操作?
示例:
LFUCache cache = new LFUCache( 2 /* capacity (缓存容量) */ );
cache.put(1, 1);
cache.put(2, 2);
cache.get(1); // 返回 1
cache.put(3, 3); // 去除 key 2
cache.get(2); // 返回 -1 (未找到key 2)
cache.get(3); // 返回 3
cache.put(4, 4); // 去除 key 1
cache.get(1); // 返回 -1 (未找到 key 1)
cache.get(3); // 返回 3
cache.get(4); // 返回 4
解法一 :哈希表HashMap+红黑树TreeSet
实现一个缓存,当执行put操作时,如果当前元素个数已经到达容量最大值则应该首先删除最近最不经常使用的元素,然后执行插入操作。
对于缓存的每一项构建一个Node来存储,其中包含属性key value count time
count表示该Node节点被使用的次数 time表示该缓存创建以来经过的时间 即最近最不经常使用的元素即为count最小 time最小的元素,即需要对于一系列Node节点进行count time的二重排序,这里定义compare方法,代码如下:
class Node implements Comparable{
int key, value;
int count;
int time; // 这里count time要保证元素的唯一性
int freq;
// 注意TreeSet在判断元素是否重复以及排序顺序时均使用该方法
@Override
public int compareTo(Node o) {
return this.count == o.count ?
Integer.compare(this.time, o.time) :
Integer.compare(this.count, o.count);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node{" + "key=" + key + ", value=" + value + ", count=" + count + ", time=" + time + '}';
}
} 这里使用TreeSet来实现logN时间内的Node节点的排序相关功能 也可以使用优先级队列来实现
当执行插入操作时 往哈希表中插入key-Node对应关系 往TreeSet中插入Node节点 由于Node实现compare方法,因此TreeSet会对于所有Node进行排序 此时第一项即为最近最不经常使用的元素,如果容量已满 删除该元素即可。
public class LFUCache {
Map map;
TreeSet tree;
int capacity;
int time; // 用来计算缓存时间
int size;
public LFUCache(int capacity) {
this.map = new HashMap<>();
this.tree = new TreeSet<>();
this.capacity = capacity;
this.time = 0;
this.size = 0;
}
public int get(int key) {
if(capacity == 0) {
return -1;
}
Node n = map.get(key);
if(n == null) {
return -1;
}
tree.remove(n);
n.time = ++time;
n.count = ++n.count;
tree.add(n);
System.out.println("get first " + tree.first().key);
for(Node t: tree){
System.out.println(t.toString());
}
return n.value;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
if(capacity == 0) {
return;
}
Node n = map.get(key);
// 如果key已经存在 则更新value
if(n != null){
tree.remove(n);
n.time = ++time;
n.count = ++n.count;
n.value = value;
tree.add(n);
System.out.println("put update first " + tree.first().key);
return;
}
// 如果key不存在 容量已经溢出 则删除最近最不访问的元素 即红黑树的最左节点
if(size >= capacity){
Node theLeftMost = tree.first();
tree.remove(theLeftMost);
map.remove(theLeftMost.key);
size--;
theLeftMost = null;
}
// 插入新节点
Node newNode = new Node();
newNode.key = key;
newNode.value = value;
newNode.count = 0;
newNode.time = ++time;
map.put(key, newNode);
tree.add(newNode);
size++;
System.out.println("put add first " + tree.first().key + " size= " + size);
for(Node t: tree){
System.out.println(t.toString());
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LFUCache obj = new LFUCache(2);
obj.put(1, 1);
obj.put(2, 2);
obj.get(1);
obj.put(3, 3);
System.out.println(obj.get(2));
}
} 其中get put操作时间复杂度均为logN
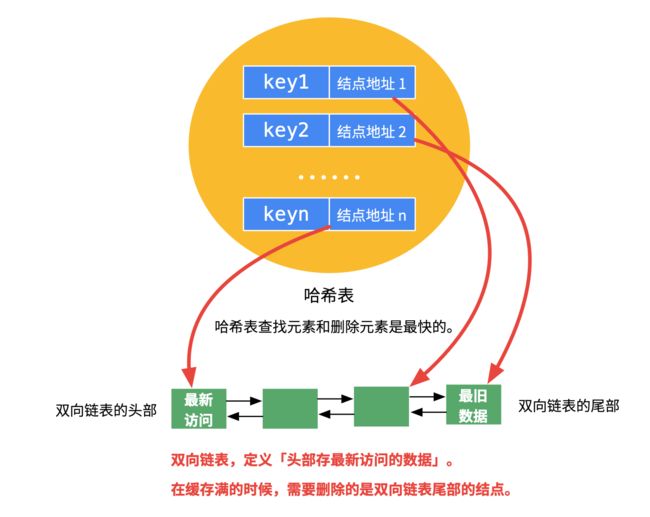
解法二:哈希表HashMap+双向链表LinkedHashSet
Node节点包含 key value freq属性
定义一个minFreq来保存当前全局最小的使用频率 当删除元素时该值要相应更新
使用哈希表来存储key-Node
另一个哈希表来存储freq-List 其中freq为使用频率 List为所有相同使用频率的Node列表 这里使用LinkedHashSet对于相同频率的元素最近最不经常使用的Node位于链表首元素 实际上也是对于一系列Node元素的使用频率和访问时间的二重排序。
对于get 根据key-Node来查询相应的Node,得到freq,进而根据freq-List得到freq列表 由于Node被访问一次 因此应该将Node从freq列表中删除放入到freq+1列表中
对于put 查询key-Node 如果Node存在 则执行相应更新操作即可 如果Node不存在 则判断容量是否溢出 如果已满则首先将最小频率minFeq对应的List首元素删除,然后新建Node节点来执行插入操作。
public class LFUCache2 {
// key 使用频率fre LinkedHashSet 具有相同使用频率fre的双向Node列表
Map> freqMap;
// key 缓存键值对key value 该key对应的Node
Map keyMap;
// 最小使用频率
// 最小频率更新时机
// 当有删除操作时 如果当前freq==minFreq并且删除元素之后链表为空则应该更新minFreq
int minFreq;
int size;
int capacity;
public LFUCache2(int capacity) {
this.freqMap = new HashMap<>();
this.keyMap = new HashMap<>();
this.minFreq = 0;
this.size = 0;
this.capacity = capacity;
}
public int get(int key) {
if(capacity == 0) return -1;
Node n = keyMap.get(key);
if(null == n) return -1;
int freq = n.freq;
// 从freq链表中删除
freqMap.get(freq).remove(n);
if(freq == minFreq && freqMap.get(freq).size() == 0){
minFreq = freq + 1;
}
n.freq = ++n.freq;
if(freqMap.get(freq+1) == null){
freqMap.put(freq+1, new LinkedHashSet<>());
}
// 添加到freq+1链表中
freqMap.get(freq+1).add(n);
return n.value;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
if(capacity == 0) return;
Node n = keyMap.get(key);
// 更新操作
if(null != n){
n.value = value;
freqMap.get(n.freq).remove(n);
if(n.freq == minFreq && freqMap.get(n.freq).size() == 0){
minFreq = n.freq + 1;
}
n.freq = ++n.freq;
if(freqMap.get(n.freq) == null){
freqMap.put(n.freq, new LinkedHashSet<>());
}
// 添加到freq+1链表中
freqMap.get(n.freq).add(n);
return;
}
// 超出容量 则删除使用频率最小的Node
if(size>=capacity){
// 对应最小使用频率下标链表的首元素即为应该删除元素
LinkedHashSet theMinOldList = freqMap.get(minFreq);
Node minOld = theMinOldList.iterator().next();
freqMap.get(minFreq).remove(minOld);
keyMap.remove(minOld.key);
size--;
// 如果最小值索引链表为空 则更新最小值索引
if(theMinOldList.size() == 0){
minFreq = minFreq + 1;
}
}
Node newNode = new Node();
newNode.freq = 0;
newNode.key = key;
newNode.value = value;
keyMap.put(key, newNode);
if(freqMap.get(newNode.freq) == null){
freqMap.put(newNode.freq, new LinkedHashSet<>());
}
freqMap.get(newNode.freq).add(newNode);
size++;
minFreq = 0;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LFUCache2 obj = new LFUCache2(2);
obj.put(1, 1);
obj.put(2, 2);
obj.get(1);
obj.put(3, 3);
System.out.println(obj.get(2));
}
}
时间复杂度为O(1)
基本思想 利用哈希表来保存key-Node对应关系 利用其它数据结构来保存Node 并且实现Node高效的排序 增加 删除 查询功能。核心在于HashMap TreeSet LinkedHashSet数据结构。
LFU与LRU
LRU (Least Recently Used)缓存机制(看时间)
在缓存满的时候,删除缓存里最久未使用的数据,然后再放入新元素;
数据的访问时间很重要,访问时间距离现在越近,就越不容易被删除;
就是喜新厌旧,淘汰在缓存里呆的时间最久的元素。在删除元素的时候,只看「时间」这一个维度。
LFU (Least Frequently Used)缓存机制(看访问次数)
在缓存满的时候,删除缓存里使用次数最少的元素,然后在缓存中放入新元素;
数据的访问次数很重要,访问次数越多,就越不容易被删除;
根据题意,「当存在平局(即两个或更多个键具有相同使用频率)时,最近最少使用的键将被去除」,即在「访问次数」相同的情况下,按照时间顺序,先删除在缓存里时间最久的数据。
核心思想:先考虑访问次数,在访问次数相同的情况下,再考虑缓存的时间。
顺带搞一下LRUCache 实际上就是对于Node节点的排序规则仅考虑时间这一因素 当然该实现方法不是最优的。
可以参考HashMap+LinkedList
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/lru-cache/solution/ha-xi-biao-shuang-xiang-lian-biao-java-by-liweiw-2/
基于HashMap+TreeSet来实现LRUCache
public class LRUCache {
Map map;
TreeSet tree;
int capacity;
int time; // 用来计算缓存时间
int size;
public LRUCache(int capacity) {
this.map = new HashMap<>();
this.tree = new TreeSet<>(Comparator.comparingInt(o -> o.time));
this.capacity = capacity;
this.time = 0;
this.size = 0;
}
public int get(int key) {
if(capacity == 0) {
return -1;
}
Node n = map.get(key);
if(n == null) {
return -1;
}
tree.remove(n);
n.time = ++time;
tree.add(n);
return n.value;
}
public void put(int key, int value) {
if(capacity == 0) {
return;
}
Node n = map.get(key);
// 如果key已经存在 则更新value
if(n != null){
tree.remove(n);
n.time = ++time;
n.value = value;
tree.add(n);
return;
}
// 如果key不存在 容量已经溢出 则删除最近最不访问的元素 即红黑树的最左节点
if(size >= capacity){
Node theLeftMost = tree.first();
tree.remove(theLeftMost);
map.remove(theLeftMost.key);
size--;
theLeftMost = null;
}
// 插入新节点
Node newNode = new Node();
newNode.key = key;
newNode.value = value;
newNode.time = ++time;
map.put(key, newNode);
tree.add(newNode);
size++;
}
}