分享篇 - 基于 Android 图解 ReactNative 原理
基于 Android 图解 ReactNative 原理,深度好文。(编写中...)
目录:
- RN 的优点和缺陷
- RN 的启动流程
- Java、Js 的调用流程
1. RN 的优点和缺陷
优点:
- 最大的优点是合理简单不具备黑科技的热更新能力和媲美 Native 般的 UI 体验;
- 对比原生开发更为灵活,对比 H5 体验更为高效;
- 多个版本迭代后的今天,它已经拥有了丰富的第三方插件支持。
缺点:
- 底层需要大量的 Native(Android & Ios) 开发工作量来做封装和定制,并且涉及到接口方面的修改仍然需要 Native 发版;
- 相对增大了 App 的体积;
- Android 上的兼容性问题;
- 整体体验还是不如原生,特别是依赖于 JsBridge 的频繁交互;
- 转输大数据慢:如图像的 base64 字符串信息;
- 无线同步通信:通信都是异步;
- Js Thread 帧率低:Js 解释执行,同时需要执行业务逻辑与 diff 操作,在低端手机里,快速滑动时,掉帧严重。
2. RN 的启动流程
使用 RN 有两种方式:
继承 ReactActivity 或者通过 ReactRootView 进行处理,这两种方式最终都会触发 ReactRootView 的 startReactApplication(), 所以可以从这个函数作为 RN 启动流程的切入点。
先来看段 ReactActivity 使用的代码片段:
public class MainActivity extends ReactActivity {
@Override
protected ReactActivityDelegate createReactActivityDelegate() {
return new MyReactDelegate(this, getMainComponentName());
}
class MyReactDelegate extends ReactActivityDelegate {
MyReactDelegate(Activity activity, @javax.annotation.Nullable String mainComponentName) {
super(activity, mainComponentName);
}
//...
}
}为了方便统一,我们从 ReactActivityDelegate 开始入手。
2.1 ReactActivityDelegate
ReactActivityDelegate 中有几个角色:
再来看看 ReactActivityDelegate 的代码:
public class ReactActivityDelegate {
public ReactActivityDelegate(Activity activity, @Nullable String mainComponentName) {
// 构造器,传入 Activity 与 mainComponentName 名称
}
public ReactActivityDelegate(FragmentActivity fragmentActivity, @Nullable String mainComponentName) {
// 构造器,传入 FragmentActivity 与 mainComponentName 名称
}
@Nullable
protected Bundle getLaunchOptions() {
return null;
}
protected ReactRootView createRootView() {
// 构建 ReactRootView
return new ReactRootView(this.getContext());
}
protected ReactNativeHost getReactNativeHost() {
// 获取 ReactNativeHost
return ((ReactApplication)this.getPlainActivity().getApplication()).getReactNativeHost();
}
public ReactInstanceManager getReactInstanceManager() {
// 获取 ReactInstanceManager
return this.getReactNativeHost().getReactInstanceManager();
}
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
if (this.mMainComponentName != null) {
this.loadApp(this.mMainComponentName);
}
// ...
}
protected void loadApp(String appKey) {
if (this.mReactRootView != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot loadApp while app is already running.");
} else {
// 创建 ReactRootView
this.mReactRootView = this.createRootView();
// ReactRootView.startReactApplication
this.mReactRootView.startReactApplication(this.getReactNativeHost().getReactInstanceManager(), appKey, this.getLaunchOptions());
// 将 ReactRootView 设置为 Activity 的 contentView
this.getPlainActivity().setContentView(this.mReactRootView);
}
}
protected void onPause() {
if (this.getReactNativeHost().hasInstance()) {
// 将 onPause 交给 ReactInstanceManager 去管理
this.getReactNativeHost().getReactInstanceManager().onHostPause(this.getPlainActivity());
}
}
protected void onResume() {
// 将 onPause 交给 ReactInstanceManager 去管理
}
protected void onDestroy() {
// 将 onDestroy 交给 ReactInstanceManager 去管理
}
public void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, Intent data) {
// 将 onActivityResult 交给 ReactInstanceManager 去管理
}
public boolean onKeyDown(int keyCode, KeyEvent event) {
// 将 onKeyDown 交给 ReactInstanceManager 去管理
}
public boolean onKeyUp(int keyCode, KeyEvent event) {
// 将 onKeyUp 交给 ReactInstanceManager 去管理
}
public boolean onKeyLongPress(int keyCode, KeyEvent event) {
// 将 onKeyLongPress 交给 ReactInstanceManager 去管理
}
public boolean onNewIntent(Intent intent) {
// 将 onNewIntent 交给 ReactInstanceManager 去管理
}
}
从上述代码可以看的,ReactActivityDelegate 其实做的事情很简单:
2.2 ReactRootView
ReactRootView 的真身为 FrameLayout, 我们着重来看下上面的 startReactApplication().
public void startReactApplication(ReactInstanceManager reactInstanceManager, String moduleName, @Nullable Bundle initialProperties) {
try {
// 必须运行在主线程
UiThreadUtil.assertOnUiThread();
this.mReactInstanceManager = reactInstanceManager;
this.mJSModuleName = moduleName;
this.mAppProperties = initialProperties;
// 如果没有初始化 ReactContext,则异步创建 ReactContext
if (!this.mReactInstanceManager.hasStartedCreatingInitialContext()) {
this.mReactInstanceManager.createReactContextInBackground();
}
// 和 ReactRootView 绑定在一起
this.attachToReactInstanceManager();
} finally {
Systrace.endSection(0L);
}
}- ReactInstanceManager: 大内总管接口类,提供一个构造者模式的初始化 Builder,实现类是 XReactInstanceManagerImpl,这类也是我们在集成 RN 时 new ReactRootView 的之前自己创建的。
- moduleName: 与 JS 代码约定的 String 类型识别 name,JS 端通过 AppRegistry.registerComponent 方法设置这个 name,Java 端重写基类的 getMainComponentName 方法设置这个 name,这样两边入口就对上了。
- launchOptions: 这里默认是 null 的,如果自己不继承 ReactActivity 而自己实现的话可以通过这个参数在 startActivity 时传入一些参数到 JS 代码,用来依据参数初始化 JS 端代码。
startReactApplication 中主要做了两件事:
# ReactInstanceManager.createReactContextInBackground()
@ThreadConfined("UI")
private void recreateReactContextInBackgroundInner() {
UiThreadUtil.assertOnUiThread();
// ...
final DeveloperSettings devSettings = this.mDevSupportManager.getDevSettings();
// 如果是 dev 模式,BuildConfig.DEBUG=true 就走这里,在线更新 bundle,手机晃动出现调试菜单等
if (this.mDevSupportManager.hasUpToDateJSBundleInCache() && !devSettings.isRemoteJSDebugEnabled()) {
this.onJSBundleLoadedFromServer((NativeDeltaClient)null);
} else if (this.mBundleLoader == null) {
this.mDevSupportManager.handleReloadJS();
} else {
this.mDevSupportManager.isPackagerRunning(new PackagerStatusCallback() {
public void onPackagerStatusFetched(final boolean packagerIsRunning) {
UiThreadUtil.runOnUiThread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
if (packagerIsRunning) {
ReactInstanceManager.this.mDevSupportManager.handleReloadJS();
} else {
devSettings.setRemoteJSDebugEnabled(false);
// recreateReactContextInBackgroundFromBundleLoader
ReactInstanceManager.this.recreateReactContextInBackgroundFromBundleLoader();
}
}
});
}
});
}
} @ThreadConfined("UI")
private void recreateReactContextInBackgroundFromBundleLoader() {
Log.d("ReactNative", "ReactInstanceManager.recreateReactContextInBackgroundFromBundleLoader()");
PrinterHolder.getPrinter().logMessage(ReactDebugOverlayTags.RN_CORE, "RNCore: load from BundleLoader");
this.recreateReactContextInBackground(this.mJavaScriptExecutorFactory, this.mBundleLoader);
}注意这个 mBundleLoader: 自定义热更新时 setJSBundleFile 方法参数就是巧妙的利用这里是 JSBundleLoader.createAssetLoader还是 JSBundleLoader.createFileLoader.
最终调用到 runCreateReactContextOnNewThread(),在子线程中创建 ReactContext(继承于 Context):
@ThreadConfined("UI")
private void runCreateReactContextOnNewThread(final ReactInstanceManager.ReactContextInitParams initParams) {
UiThreadUtil.assertOnUiThread();
synchronized(this.mReactContextLock) {
if (this.mCurrentReactContext != null) {
this.tearDownReactContext(this.mCurrentReactContext);
this.mCurrentReactContext = null;
}
}
this.mCreateReactContextThread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
// ...
ReactInstanceManager.this.mHasStartedCreatingInitialContext = true;
try {
// 调用 createReactContext()
final ReactApplicationContext reactApplicationContext = ReactInstanceManager.this.createReactContext(initParams.getJsExecutorFactory().create(), initParams.getJsBundleLoader());
// ...
Runnable setupReactContextRunnable = new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
// 调用 setupReactContext()
ReactInstanceManager.this.setupReactContext(reactApplicationContext);
} catch (Exception var2) {
ReactInstanceManager.this.mDevSupportManager.handleException(var2);
}
}
};
reactApplicationContext.runOnNativeModulesQueueThread(setupReactContextRunnable);
} catch (Exception var4) {
}
}
});
this.mCreateReactContextThread.start();
}runCreateReactContextOnNewThread() 中的两个重点:
- createReactContext()
- setupReactContext()
private ReactApplicationContext createReactContext(JavaScriptExecutor jsExecutor, JSBundleLoader jsBundleLoader) {
// ......
// 默认不就是上面刚刚分析的 "assets://" + bundleAssetName 么
mSourceUrl = jsBundleLoader.getSourceUrl();
List moduleSpecs = new ArrayList<>();
Map reactModuleInfoMap = new HashMap<>();
// Js 层模块注册表,通过它把所有的 JavaScriptModule 注册到 CatalystInstance。我们自定义的继承 JavaScriptModule 接口的 Java 端也是通过它来管理。
JavaScriptModuleRegistry.Builder jsModulesBuilder = new JavaScriptModuleRegistry.Builder();
// ContextWrapper 封装类,其实就是 getApplicationContext 的封装,用在 ReactContext 中
final ReactApplicationContext reactContext = new ReactApplicationContext(mApplicationContext);
// 如果是开发模式下 ReactApplicationContext 中有崩溃就捕获后交给 mDevSupportManager 处理(出错时弹个红框啥玩意的都是这货捕获的功劳)
if (mUseDeveloperSupport) {
// mDevSupportManager 实例对象来源于 XReactInstanceManagerImpl 构造方法中一个工厂方法,实质由 useDeveloperSupport 决定 DevSupportManager 是哪个实例
// 非开发模式情况下 mDevSupportManager 为 DisabledDevSupportManager 实例,开发模式下为 DevSupportManagerImpl 实例
reactContext.setNativeModuleCallExceptionHandler(mDevSupportManager);
}
// ......
try {
// 创建 CoreModulesPackage(ReactPackage),RN framework 的核心 Module Package,主要通过 createNativeModules、createJSModules 和 createViewManagers 等方法创建本地模块,JS 模块及视图组件等
//CoreModulesPackage封装了通信、调试等核心类。
CoreModulesPackage coreModulesPackage = new CoreModulesPackage(this, mBackBtnHandler, mUIImplementationProvider);
// 拼装来自 coreModulesPackage 的各种 module 了,JS 的直接 add 进了 jsModulesBuilder 映射表、Native 的直接保存在了 moduleSpecs、reactModuleInfoMap 中
processPackage(
coreModulesPackage,
reactContext,
moduleSpecs,
reactModuleInfoMap,
jsModulesBuilder);
} finally {
Systrace.endSection(TRACE_TAG_REACT_JAVA_BRIDGE);
}
// 加载我们自定义的 ReactPackage,譬如自己封装的和 MainReactPackage 等,mPackages 就来源于我们自己定义的;整个过程同上 CoreModulesPackage,进行各种拼装 module
for (ReactPackage reactPackage : mPackages) {
Systrace.beginSection(
TRACE_TAG_REACT_JAVA_BRIDGE,
"createAndProcessCustomReactPackage");
try {
processPackage(
reactPackage,
reactContext,
moduleSpecs,
reactModuleInfoMap,
jsModulesBuilder);
} finally {
Systrace.endSection(TRACE_TAG_REACT_JAVA_BRIDGE);
}
}
// Java 层模块注册表,通过它把所有的 NativeModule 注册到 CatalystInstance。我们自定义的继承 NativeModule 接口的 Java 端也是通过它来管理
NativeModuleRegistry nativeModuleRegistry;
try {
// new 一 个NativeModuleRegistry,其管理了 NativeModule 和 OnBatchCompleteListener 列表(JS 调用 Java 结束时的回调管理)
nativeModuleRegistry = new NativeModuleRegistry(moduleSpecs, reactModuleInfoMap);
} finally {
Systrace.endSection(TRACE_TAG_REACT_JAVA_BRIDGE);
ReactMarker.logMarker(BUILD_NATIVE_MODULE_REGISTRY_END);
}
// 依据外面是否设置 mNativeModuleCallExceptionHandler 异常捕获实现来决定 exceptionHandler 是使用外面的还是DevSupportManager
NativeModuleCallExceptionHandler exceptionHandler = mNativeModuleCallExceptionHandler != null
? mNativeModuleCallExceptionHandler
: mDevSupportManager;
// 重点创建 CatalystInstance 的 CatalystInstanceImpl 实现实例
CatalystInstanceImpl.Builder catalystInstanceBuilder = new CatalystInstanceImpl.Builder()
.setReactQueueConfigurationSpec(ReactQueueConfigurationSpec.createDefault())
.setJSExecutor(jsExecutor)
.setRegistry(nativeModuleRegistry)
.setJSModuleRegistry(jsModulesBuilder.build())
.setJSBundleLoader(jsBundleLoader)
.setNativeModuleCallExceptionHandler(exceptionHandler);
final CatalystInstance catalystInstance;
try {
catalystInstance = catalystInstanceBuilder.build();
} finally {
Systrace.endSection(TRACE_TAG_REACT_JAVA_BRIDGE);
ReactMarker.logMarker(CREATE_CATALYST_INSTANCE_END);
}
if (mBridgeIdleDebugListener != null) {
catalystInstance.addBridgeIdleDebugListener(mBridgeIdleDebugListener);
}
// 关联 reactContext 与 catalystInstance
reactContext.initializeWithInstance(catalystInstance);
// 通过 catalystInstance 加载 js bundle 文件
catalystInstance.runJSBundle();
return reactContext;
} 总的来说 createReactContext() 方法做的都是一些取数据组表放表的过程,核心就是通过 ReactPackage 实现类的 createNativeModules()、createJSModules() 等方法把所有 NativeModule 包装后放入 NativeModuleRegistry 及 JavaScriptModule 包装后放入 JavaScriptModuleRegistry,然后把这两张映射表交给 CatalystInstanceImpl,同时包装创建 ReactContext 对象,然后通过 CatalystInstanceImpl 的 runJSBundle() 方法把 JS bundle 文件的 JS 代码加载进来等待 Task 结束以后调用 JS 入口进行渲染 RN.
既然上面涉及到了 CatalystInstanceImpl, 我们来简单看一下 CatalystInstanceImpl:
public class CatalystInstanceImpl implements CatalystInstance {
// C++ 部分
private final HybridData mHybridData;
private native static HybridData initHybrid();
private CatalystInstanceImpl(
final ReactQueueConfigurationSpec ReactQueueConfigurationSpec,
final JavaScriptExecutor jsExecutor,
final NativeModuleRegistry registry,
final JavaScriptModuleRegistry jsModuleRegistry,
final JSBundleLoader jsBundleLoader,
NativeModuleCallExceptionHandler nativeModuleCallExceptionHandler) {
// native C++ 方法,用来初始化 JNI 相关状态然后返回 mHybridData。
mHybridData = initHybrid();
// 创建 ReactNative 的三个线程 nativeModulesThread 和 jsThread、uiThread,都是通过 Handler 来管理的
mReactQueueConfiguration = ReactQueueConfigurationImpl.create(ReactQueueConfigurationSpec, new NativeExceptionHandler());
mBridgeIdleListeners = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
mJavaRegistry = registry;
mJSModuleRegistry = jsModuleRegistry;
mJSBundleLoader = jsBundleLoader;
mNativeModuleCallExceptionHandler = nativeModuleCallExceptionHandler;
// native C++ 方法,用来初始化 Bridge
initializeBridge(new BridgeCallback(this), jsExecutor,
mReactQueueConfiguration.getJSQueueThread(),
mReactQueueConfiguration.getNativeModulesQueueThread(),
mJavaRegistry.getModuleRegistryHolder(this));
mMainExecutorToken = getMainExecutorToken();
}
private native void initializeBridge(ReactCallback callback,
JavaScriptExecutor jsExecutor,
MessageQueueThread jsQueue,
MessageQueueThread moduleQueue,
ModuleRegistryHolder registryHolder);
// ...
}
// initializeBridge 建立了 Bridge 连接
private native void initializeBridge(ReactCallback var1, JavaScriptExecutor var2, MessageQueueThread var3, MessageQueueThread var4, Collection var5, Collection var6);
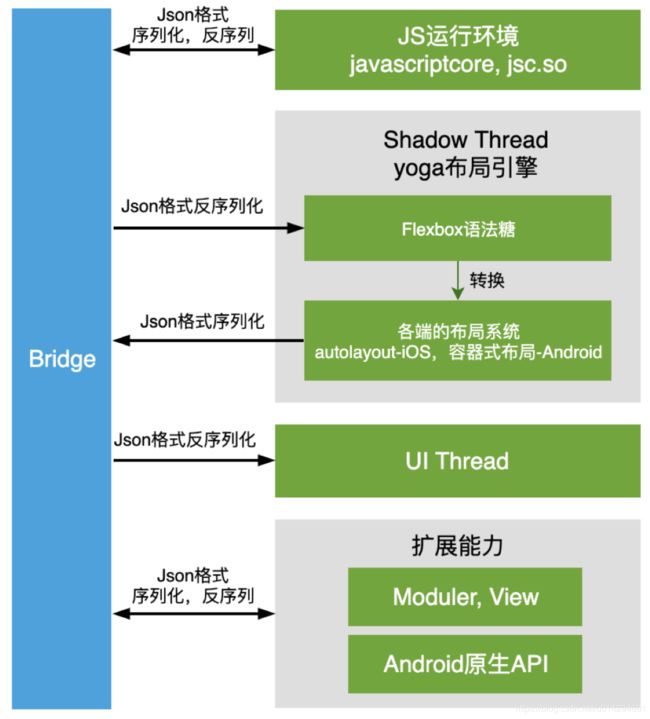
} CatalystInstanceImpl 就是个封装总管,负责了 Java 层代码到 JNI 封装初始化的任务和 Java 与 JS 调用的 Java 端控制中心,initializeBridge 与 JsBridge 建立了连接。注意里面创建了 ReactNative 的三个线程 nativeModulesThread 和 jsThread、uiThread,这边来简单说下 RN 的三个线程:
- UI Thread:Native 的 UI 渲染。
- Shadow Thread:yoga 引擎,基于 flexbox 的语法糖转换为各端的扁平化框架。
- Javascript Thread:React 执行环境,业务逻辑与 diff 操作执行环境。
再来看下 setupReactContext():
private void setupReactContext(ReactApplicationContext reactContext) {
......
CatalystInstance catalystInstance =
Assertions.assertNotNull(reactContext.getCatalystInstance());
// 执行 Native Java Module 的 initialize
catalystInstance.initialize();
// 重置 DevSupportManager 实现类的 reactContext 相关
mDevSupportManager.onNewReactContextCreated(reactContext);
// 内存状态回调设置
mMemoryPressureRouter.addMemoryPressureListener(catalystInstance);
// 置位生命周期
moveReactContextToCurrentLifecycleState();
// 核心方法
for (ReactRootView rootView : mAttachedRootViews) {
attachMeasuredRootViewToInstance(rootView, catalystInstance);
}
......
}最后,我们来总结一下 RN 的启动流程:
3. Java、Js 的调用流程
参考链接:
https://blog.csdn.net/yanbober/article/details/53157456