图像边框实现
Use the OpenCV function :copy_make_border:`copyMakeBorder <>` to set the borders (extra padding to your image). The explanation below belongs to the bookLearning OpenCV by Bradski and Kaehler.
- In our previous tutorial we learned to use convolution to operate on images. One problem that naturally arises is how to handle the boundaries. How can we convolve them if the evaluated points are at the edge of the image?
- What most of OpenCV functions do is to copy a given image onto another slightly larger image and then automatically pads the boundary (by any of the methods explained in the sample code just below). This way, the convolution can be performed over the needed pixels without problems (the extra padding is cut after the operation is done).
- In this tutorial, we will briefly explore two ways of defining the extra padding (border) for an image:
- BORDER_CONSTANT: Pad the image with a constant value (i.e. black or0)
- BORDER_REPLICATE: The row or column at the very edge of the original is replicated to the extra border.
This will be seen more clearly in the Code section.
What does this program do?
- Load an image
- Let the user choose what kind of padding use in the input image. There are two options:
- Constant value border: Applies a padding of a constant value for the whole border. This value will be updated randomly each 0.5 seconds.
- Replicated border: The border will be replicated from the pixel values at the edges of the original image.
- The user chooses either option by pressing 'c' (constant) or 'r' (replicate)
- The program finishes when the user presses 'ESC'
The tutorial code's is shown lines below.
''' file name : border.py
Description : This sample shows how to add border to an image'''
import cv2
import numpy as np
print " Press r to replicate the border with a random color "
print " Press c to replicate the border "
print " Press Esc to exit "
img = cv2.imread('../boldt.jpg')
rows,cols = img.shape[:2]
dst = img.copy()
top = int (0.05*rows)
bottom = int (0.05*rows)
left = int (0.05*cols)
right = int (0.05*cols)
while(True):
cv2.imshow('border',dst)
k = cv2.waitKey(500)
if k==27:
break
elif k == ord('c'):
value = np.random.randint(0,255,(3,)).tolist()
dst = cv2.copyMakeBorder(img,top,bottom,left,right,
cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT,value = value)
elif k == ord('r'):
dst = cv2.copyMakeBorder(img,top,bottom,left,right,cv2.BORDER_REPLICATE)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
Explanation
1. Now we initialize the argument that defines the size of the borders (top,bottom,left andright). We give them a value of 5% the size of src.
top = int (0.05*rows)
bottom = int (0.05*rows)
left = int (0.05*cols)
right = int (0.05*cols)while(True):
cv2.imshow('border',dst)
k = cv2.waitKey(500)
if k==27:
break
elif k == ord('c'):
value = np.random.randint(0,255,(3,)).tolist()
dst = cv2.copyMakeBorder(img,top,bottom,left,right,cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT,value = value)
elif k == ord('r'):
dst = cv2.copyMakeBorder(img,top,bottom,left,right,cv2.BORDER_REPLICATE)
copyMakeBorder( src, dst, top, bottom, left, right, borderType, value );The arguments are:
- src: Source image
- dst: Destination image
- top, bottom, left,right: Length in pixels of the borders at each side of the image. We define them as being 5% of the original size of the image.
- borderType: Define what type of border is applied. It can be constant or replicate for this example.
- value: If borderType isBORDER_CONSTANT, this is the value used to fill the border pixels.
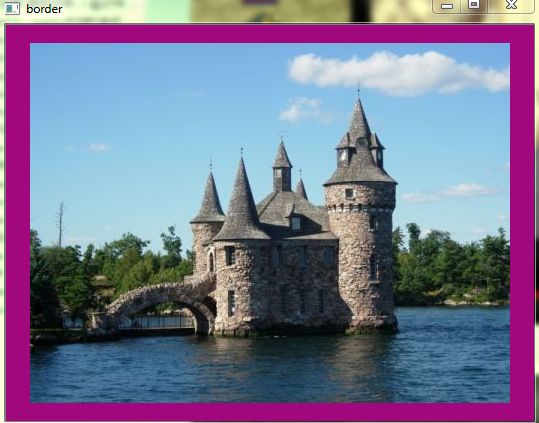
输出结果
After compiling the code above, you can execute it giving as argument the path of an image. The result should be:
- By default, it begins with the border set to BORDER_CONSTANT. Hence, a succession of random colored borders will be shown.
- If you press 'r', the border will become a replica of the edge pixels.
- If you press 'c', the random colored borders will appear again
- If you press 'ESC' the program will exit.
Below some screenshot showing how the border changes color and how theBORDER_REPLICATE option looks:
关于Image Engineering & Computer Vision的更多讨论与交流,敬请关注本博客和新浪微博songzi_tea.