C++中详解调用dll的方法
第1节 动态调用(显示链接)
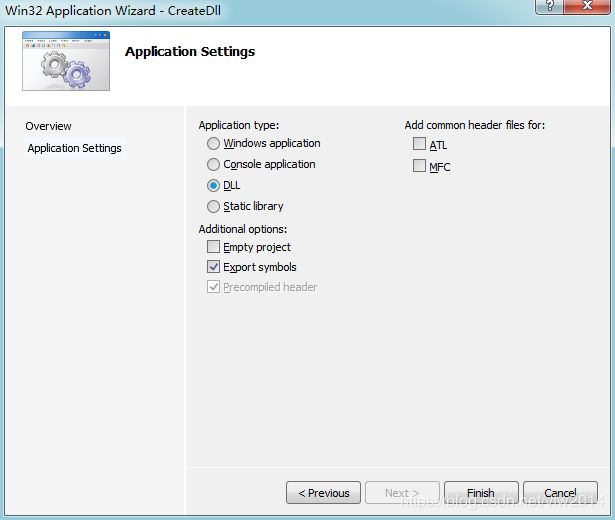
1、创建dll(被调用者)
创建工程注意事项
勾选DLL 和Export symbols
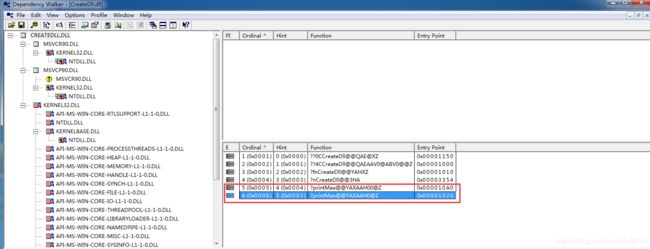
2、调用着调用过程发现问题
运行调用者程序GetProcAddress返回为空,未找到函数。用depends查看dll调用函数名称为如图所示。
结论:创建过程中,函数的名称发生改变而非创建时被调用者dll中函数名称
3、导出函数名称修饰问题解决方法
1)笨方法,按照上述方式,在调用者调用时,先查看(depends或者附带工具dumpbin)被调用者dll函数名称,然后调用
2)导出函数名规范化处理。常用两种方法:一是运用extern "C"修饰printMax;二是运用模块定义文件.def。后者的效果更好。
下面分别说明:
第一种:定义.def
1.在被调用者模块中添加.def文件,根据期望的函数名称,修改函数名称
LIBRARY "CreateDll"
EXPORTS
pMaxA2 = ?printMax@@YAXAAH0@Z
pMaxA3 = ?printMax@@YAXAAH00@Z2.修改被调用者.h文件
修改前
修改后
3.调用者用修改后的名称调用被调用者函数
//原始创建时函数名称
//const char* funName1 = "printMax";
//const char* funName2 = "printMax";
//用depend查看器看到CreateDLL.dll导出函数名为?printMax@@YAXAAH00@Z和?printMax@@YAXAAH0@Z
//const char* funName1 = "?printMax@@YAXAAH0@Z";
//const char* funName2 = "?printMax@@YAXAAH00@Z";
//被调用者.def修改后的期望函数名称
const char* funName1 = "pMaxA2";
const char* funName2 = "pMaxA3";4.完整代码示例
注:本代码及上述大部分逻辑均来自博客:https://blog.csdn.net/ixsea/article/details/6676802
1)被调者
CreateDll.h
// The following ifdef block is the standard way of creating macros which make exporting
// from a DLL simpler. All files within this DLL are compiled with the CREATEDLL_EXPORTS
// symbol defined on the command line. this symbol should not be defined on any project
// that uses this DLL. This way any other project whose source files include this file see
// CREATEDLL_API functions as being imported from a DLL, whereas this DLL sees symbols
// defined with this macro as being exported.
#ifdef CREATEDLL_EXPORTS
#define CREATEDLL_API __declspec(dllexport)
#else
#define CREATEDLL_API __declspec(dllimport)
#endif
// This class is exported from the CreateDll.dll
class CREATEDLL_API CCreateDll {
public:
CCreateDll(void);
// TODO: add your methods here.
};
extern CREATEDLL_API int nCreateDll;
CREATEDLL_API int fnCreateDll(void);
CREATEDLL_API void printMax(int&,int&);
CREATEDLL_API void printMax(int&,int&,int&);
CreateDll.cpp
// CreateDll.cpp : Defines the exported functions for the DLL application.
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "CreateDll.h"
#include
using namespace std;
// This is an example of an exported variable
CREATEDLL_API int nCreateDll=0;//导出变量
// This is an example of an exported function.
CREATEDLL_API int fnCreateDll(void)//导出函数
{
return 42;
}
CREATEDLL_API void printMax(int& a,int& b)
{
std::cout<<"Among ("<b?a:b)<<"\n";
}
CREATEDLL_API void printMax(int& a,int&b,int&c)
{
std::cout<<"Among ("<b?a:b)>c)?(a>b?a:b):c)<<"\n";
}
// This is the constructor of a class that has been exported.
// see CreateDll.h for the class definition
CCreateDll::CCreateDll()//导出类
{
return;
}
CreateDLL.def
LIBRARY "CreateDll"
EXPORTS
pMaxA2 = ?printMax@@YAXAAH0@Z
pMaxA3 = ?printMax@@YAXAAH00@Z
2)调用者
UseDLL.cpp
#include//包含头文件Windows.h,原因在于程序中用到了LoadLibrary、FreeLibrary、GetProcAddress等Win32 API函数。
#include
//FUNA和FUNB是函数指针类型的声明。
typedef void(*FUNA)(int&,int&);
typedef void(*FUNB)(int&,int&,int&);
int main()
{
const char* dllName = "CreateDLL.dll";
//原始创建时函数名称
//const char* funName1 = "printMax";
//const char* funName2 = "printMax";
//用depend查看器看到CreateDLL.dll导出函数名为?printMax@@YAXAAH00@Z和?printMax@@YAXAAH0@Z
//const char* funName1 = "?printMax@@YAXAAH0@Z";
//const char* funName2 = "?printMax@@YAXAAH00@Z";
//被调用者.def修改后的期望函数名称
const char* funName1 = "pMaxA2";
const char* funName2 = "pMaxA3";
int x(100), y(100), z(100);
HMODULE hDLL = LoadLibrary(dllName);
if(hDLL != NULL)
{
FUNA fp1 = FUNA(GetProcAddress(hDLL,funName1));
if(fp1 != NULL)
{
std::cout<<"Input 2 Numbers:";
std::cin>>x>>y;
fp1(x,y);
}
else
{
std::cout<<"Cannot Find Function "<>x>>y>>z;
fp2(x,y,z);
}
else
{
std::cout<<"Cannot Find Function "< 第二种 使用extern "C"
1、使用depends查看使用exrern "C"编译的被调用者的函数名称和代码中定义的名称一致
2.完整代码
1)被调用者
1.CreateDll.h
// The following ifdef block is the standard way of creating macros which make exporting
// from a DLL simpler. All files within this DLL are compiled with the CREATEDLL_EXPORTS
// symbol defined on the command line. this symbol should not be defined on any project
// that uses this DLL. This way any other project whose source files include this file see
// CREATEDLL_API functions as being imported from a DLL, whereas this DLL sees symbols
// defined with this macro as being exported.
#define EXTERN_C extern "C"
#ifdef CREATEDLL_EXPORTS
#define CREATEDLL_API __declspec(dllexport)
#else
#define CREATEDLL_API __declspec(dllimport)
#endif
// This class is exported from the CreateDll.dll
class CREATEDLL_API CCreateDll {
public:
CCreateDll(void);
// TODO: add your methods here.
};
extern CREATEDLL_API int nCreateDll;
CREATEDLL_API int fnCreateDll(void);
EXTERN_C CREATEDLL_API void printMax(int&,int&);
EXTERN_C CREATEDLL_API void printMin(int& a ,int& b,int& c);//用C语言编译器编译 函数不能重载
//CREATEDLL_API void printMax(int&,int&,int&);
2.CreateDll.cpp
// CreateDll.cpp : Defines the exported functions for the DLL application.
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "CreateDll.h"
#include
using namespace std;
// This is an example of an exported variable
CREATEDLL_API int nCreateDll=0;
// This is an example of an exported function.
CREATEDLL_API int fnCreateDll(void)
{
return 42;
}
EXTERN_C CREATEDLL_API void printMax(int& a ,int& b)
{
std::cout<<"Among ("<b?a:b)<<"\n";
}
EXTERN_C CREATEDLL_API void printMin(int& a ,int& b,int& c)
{
std::cout<<"Among ("< 2)调用者
UseDLL.cpp
#include//包含头文件Windows.h,原因在于程序中用到了LoadLibrary、FreeLibrary、GetProcAddress等Win32 API函数。
#include
//FUNA和FUNB是函数指针类型的声明。
typedef void(*FUNA)(int&,int&);
typedef void(*FUNB)(int&,int&,int&);
int main()
{
const char* dllName = "CreateDLL.dll";
//原始创建时函数名称
//const char* funName1 = "printMax";
//const char* funName2 = "printMax";
//用depend查看器看到CreateDLL.dll导出函数名为?printMax@@YAXAAH00@Z和?printMax@@YAXAAH0@Z
//const char* funName1 = "?printMax@@YAXAAH0@Z";
//const char* funName2 = "?printMax@@YAXAAH00@Z";
//被调用者.def修改后的期望函数名称
// const char* funName1 = "pMaxA2";
// const char* funName2 = "pMaxA3";
//调用external “C”方式创建的dll
const char* funName1 = "printMax";
const char* funName2 = "printMin";
int x(100), y(100), z(100);
HMODULE hDLL = LoadLibrary(dllName);
if(hDLL != NULL)
{
FUNA fp1 = FUNA(GetProcAddress(hDLL,funName1));
if(fp1 != NULL)
{
std::cout<<"Input 2 Numbers:";
std::cin>>x>>y;
fp1(x,y);
}
else
{
std::cout<<"Cannot Find Function "<>x>>y>>z;
fp2(x,y,z);
}
else
{
std::cout<<"Cannot Find Function "< 总结:
1.动态调用发生在程序运行时通过LoadLibrary调用dll。本质上是根据被调者创建时的函数名称(“变异”名称)访问dll 中的函数。
2.被调者创建动态链接库时,为了解决函数名称“变异”问题,常用方法为定义.def 和extern "C"方式。前者本质上就是编译器编译时把函数名称重新命名为我们期望的名称便于调用者调用,后者本质上告诉编译器用C编译器编译,C编译器中编译函数名称唯一,因此函数如果重载的话,就不可用了。前者相对较灵活一些。后者调用者调用时更直观一些。
第2节、静态调用(隐式链接)
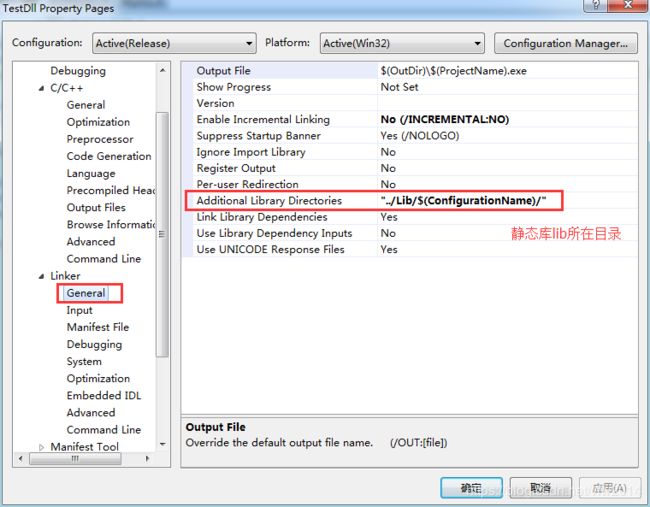
1、依赖lib(lib)
1)配置lib所在路径
仅配置lib所在路径,具体需要依赖哪个lib需要下面指定
2)配置所需依赖文件
指定要依赖的lib,等同于
#pragma comment(lib,"MyDLL.lib")
注:上面两个步骤相当于:(既指定路径,又指定要依赖的项)
#pragma comment(lib,"..\\Lib\\Release\\MyDLL.lib")2、依赖头文件(.h)
1)指定头文件路径
同lib 仅指定要包含的头文件的路径,具体要包含什么头文件,需要在代码中指定
3、将被调用者的dll(MyDLL.dll)放到调用者同一路径下(dll)
4、完整代码
#include//包含头文件Windows.h,原因在于程序中用到了LoadLibrary、FreeLibrary、GetProcAddress等Win32 API函数。
#include
#include "CreateDll.h"//静态链接包含头文件
int main()
{
int x(100), y(100), z(100);
std::cout<<"Input 2 Numbers:";
std::cin>>x>>y;
printMax(x,y);
std::cout<<"Input 3 Numbers:";
std::cin>>x>>y>>z;
printMin(x,y,z);
return 1;
}
5、总结
静态链接,需要工程配置。需要.h 、lib、dll 三个文件;动态链接,无需工程配置,仅需要动态加载被调用者的dll。