实验二 Java简单类与对象
实验目的
掌握类的定义,熟悉属性、构造函数、方法的作用,掌握用类作为类型声明变量和方法返回值;
理解类和对象的区别,掌握构造函数的使用,熟悉通过对象名引用实例的方法和属性;
理解static修饰付对类、类成员变量及类方法的影响。
实验内容
写一个名为Rectangle的类表示矩形。其属性包括宽width、高height和颜色color,width和height都是double型的,而color则是String类型的。要求该类具有:
(1) 使用构造函数完成各属性的初始赋值
(2) 使用get…()和set…()的形式完成属性的访问及修改
(3) 提供计算面积的getArea()方法和计算周长的getLength()方法
实验代码:
package homework;
public class Rectangle {
private double width,height;
private String color;
public Rectangle(double width, double height, String color) {
this.setWidth(width);
this.setHeight(height);
this.setColor(color);
}
public Rectangle() {
}
public void setWidth(double width) {
this.width = width;
}
public void setHeight(double height) {
this.height = height;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public double getWidth() {
return width;
}
public double getHeight() {
return height;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public double getArea() {
return this.width*this.height;
}
public double getGetlength() {
return (this.height+this.width)*2;
}
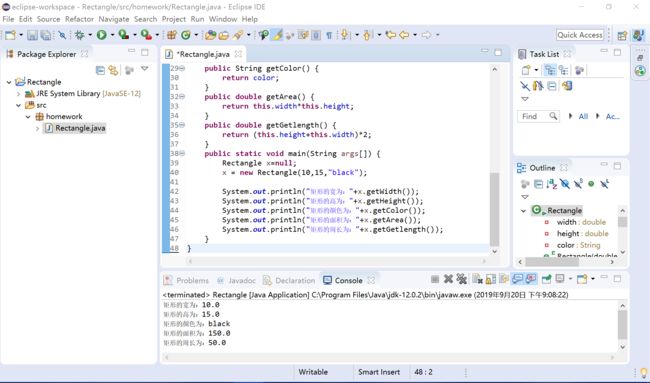
public static void main(String args[]) {
Rectangle x=null;
x = new Rectangle(10,15,"black");
System.out.println("矩形的宽为:"+x.getWidth());
System.out.println("矩形的高为:"+x.getHeight());
System.out.println("矩形的颜色为:"+x.getColor());
System.out.println("矩形的面积为:"+x.getArea());
System.out.println("矩形的周长为:"+x.getGetlength());
}
}实验结果:
银行的账户记录Account有账户的唯一性标识(11个长度的字符和数字的组合),用户的姓名,开户日期,账户密码(六位的数字,可以用0开头),当前的余额。银行规定新开一个账户时,银行方面提供一个标识符、账户初始密码123456,客户提供姓名,开户时客户可以直接存入一笔初始账户金额,不提供时初始余额为0。定义该类,并要求该类提供如下方法:存款、取款、变更密码、可以分别查询账户的标识、姓名、开户日期、当前余额等信息。
实验代码:
package homework;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class bank {
private String id,name,code;
private Date khTime;
private double balance;
public bank(String id, String name, double balance) {
this.id=id;
this.name=name;
this.balance=balance;
this.khTime=new Date();
this.code="123456";
}
public void deposit(double amount) {
this.balance+=balance;
}
public void withdraw(double amount) {
this.balance-=amount;
}
public Date getkhTime() {
return khTime;
}
public void setCreateTime(Date time) {
khTime = time;
}
public void changecode() {
Scanner x=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请重新设置密码:");
String code = x.nextLine();
this.code = code;
x.close();
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public String getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setCode(String code) {
this.code = code;
}
public void setBalance(double balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
public double getBalance() {
return balance;
}
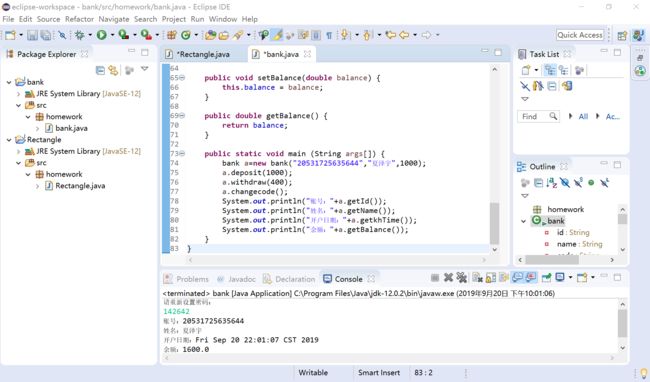
public static void main (String args[]) {
bank a=new bank("20531725635644","夏泽宇",1000);
a.deposit(1000);
a.withdraw(400);
a.changecode();
System.out.println("账号:"+a.getId());
System.out.println("姓名:"+a.getName());
System.out.println("开户日期:"+a.getkhTime());
System.out.println("余额:"+a.getBalance());
}
}实验结果:
总结:
本次实验第二题对我来说确实难度不低,我发现import java.util.Date;与import java.util.Scanner;是必要的,缺少这两句直接多处报错。
查找得知:import java.util.*;导入 java.util包中的类接口。
Java中import的作用是导入要用到的包中的类接口。import就是在java文件开头的地方,先说明会用到那些类别。 接着我们就能在代码中只用类名指定某个类,也就是只称呼名字,不称呼他的姓。这其中包的作用就是给java类进行分拣分类,不同业务逻辑的java类放在同一个包中。比如实体包,工具包。
本周所学内容:
1、public boolean equals(Object anObject)
该方法比较两个字符串,在两个字符串相等的时候返回true,否则返回false。
2、public boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString)
该方法和equals方法相似,不同的地方在于,equalsIgnoreCase方法将忽略字母大小写的区别。例如:验证码不区分大小写
3、replace可以进行替换,也可以进行删除,删除替换为空串即可。
4、“==”比较双方的地址,equals()方法比较双方的内容。所以即使双方内容完全一致,使用“==”来比较仍然会返回false。
:)