2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> ![]()
Author: [email protected]
Create Device Manager Instance
Device Manager在何时创建
Device Manager和Volume Manager、QoS Container Manager等一样,都属于kubelet管理的众多Manager之一。Device Manager在kubelet启动时的NewContainerManager中创建。
pkg/kubelet/cm/container_manager_linux.go:197
func NewContainerManager(mountUtil mount.Interface, cadvisorInterface cadvisor.Interface, nodeConfig NodeConfig, failSwapOn bool, devicePluginEnabled bool, recorder record.EventRecorder) (ContainerManager, error) {
...
glog.Infof("Creating device plugin manager: %t", devicePluginEnabled)
if devicePluginEnabled {
cm.deviceManager, err = devicemanager.NewManagerImpl()
} else {
cm.deviceManager, err = devicemanager.NewManagerStub()
}
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
...
}
ManagerImpl结构体
我们有必要先了解Device Manager的结构体:
// ManagerImpl is the structure in charge of managing Device Plugins.
type ManagerImpl struct {
socketname string
socketdir string
endpoints map[string]endpoint // Key is ResourceName
mutex sync.Mutex
server *grpc.Server
// activePods is a method for listing active pods on the node
// so the amount of pluginResources requested by existing pods
// could be counted when updating allocated devices
activePods ActivePodsFunc
// sourcesReady provides the readiness of kubelet configuration sources such as apiserver update readiness.
// We use it to determine when we can purge inactive pods from checkpointed state.
sourcesReady config.SourcesReady
// callback is used for updating devices' states in one time call.
// e.g. a new device is advertised, two old devices are deleted and a running device fails.
callback monitorCallback
// healthyDevices contains all of the registered healthy resourceNames and their exported device IDs.
healthyDevices map[string]sets.String
// unhealthyDevices contains all of the unhealthy devices and their exported device IDs.
unhealthyDevices map[string]sets.String
// allocatedDevices contains allocated deviceIds, keyed by resourceName.
allocatedDevices map[string]sets.String
// podDevices contains pod to allocated device mapping.
podDevices podDevices
store utilstore.Store
pluginOpts map[string]*pluginapi.DevicePluginOptions
}
下面是核心field的说明:
-
socketname: 就是kubelet对外暴露的socket名,即
kubelet.sock。 -
socketdir: device plugins' socket的存放的目录,
/var/lib/kubelet/device-plugins/。 -
endpoints: map对象,key为Resource Name,value为endpoint接口(包括run,stop,allocate,preStartContainer,getDevices,callback,isStoped,StopGracePeriodExpired),每个endpoint接口对应一个已注册的device plugin,负责与device plugin的gRPC通信及缓存device plugin反馈的device states。
-
server: Register服务暴露的gRPC Server。
-
activePods: 用来获取该节点上所有active pods,即non-Terminated状态的Pods。在kubelet的initializeRuntimeDependentModules时会注册activePods Func为如下函数:
// GetActivePods returns non-terminal pods func (kl *Kubelet) GetActivePods() []*v1.Pod { allPods := kl.podManager.GetPods() activePods := kl.filterOutTerminatedPods(allPods) return activePods } -
callback: 是kubelet收到device plugin的ListAndWatch gRCP stream中有devices state变更时的回调函数,包括有新设备增加、旧设备删除、设备状态变化,所以通过ListAndWatch接口的回调方式,可以实现设备的自动发现和热插拔。
type monitorCallback func(resourceName string, added, updated, deleted []pluginapi.Device) ``` -
healthyDevices: map对象,key为Resource Name,value为对应的健康的device IDs。
-
unhealthyDevices: map对象,key为Resource Name,value为对应的不健康的device IDs。
-
allocatedDevices: map对象,key为Resource Name,value为已经分配出去的device IDs。
-
podDevices: 记录每个pod中每个容器的device分配情况。
// ContainerAllocateResponse为容器内某个device对应的分配信息,包括注入的环境变量、挂载信息、Annotations。 type ContainerAllocateResponse struct { Envs map[string]string Mounts []*Mount Devices []*DeviceSpec Annotations map[string]string } // deviceAllocateInfo type deviceAllocateInfo struct { deviceIds sets.String allocResp *pluginapi.ContainerAllocateResponse } type resourceAllocateInfo map[string]deviceAllocateInfo // Keyed by resourceName. type containerDevices map[string]resourceAllocateInfo // Keyed by containerName. type podDevices map[string]containerDevices // Keyed by podUID. -
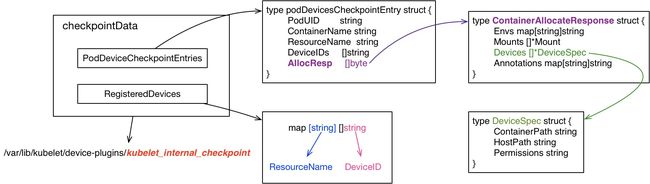
store: 是对checkpointData的文件存储(
/var/lib/kubelet/device-plugins/kubelet_internal_checkpoint),具体存储了每个Pod分配的Devices信息PodDeviceEntries, 以及已经注册的Resource Name及对应的Devices IDs。type checkpointData struct { PodDeviceEntries []podDevicesCheckpointEntry RegisteredDevices map[string][]string // key为Resource Name,value为DeviceIDs } type podDevicesCheckpointEntry struct { PodUID string ContainerName string ResourceName string DeviceIDs []string AllocResp []byte } -
pluginOpts: map对象,key为Resource Name,value为DevicePluginOptions,目前只有一项内容,就是
PreStartRequired bool,表示是否在容器启动前要调用device plugin的PreStartContiner接口。在nvidia-k8s-plugin中,PreStartContainer为空实现。
NewManagerImpl
我们再来看看Device Manager的具体创建实现NewManagerImpl。
pkg/kubelet/cm/devicemanager/manager.go:97
// NewManagerImpl creates a new manager.
func NewManagerImpl() (*ManagerImpl, error) {
// 通过/var/lib/kubelet/device-plugins/kubelet.sock与device plugin交互
return newManagerImpl(pluginapi.KubeletSocket)
}
func newManagerImpl(socketPath string) (*ManagerImpl, error) {
glog.V(2).Infof("Creating Device Plugin manager at %s", socketPath)
if socketPath == "" || !filepath.IsAbs(socketPath) {
return nil, fmt.Errorf(errBadSocket+" %v", socketPath)
}
dir, file := filepath.Split(socketPath)
manager := &ManagerImpl{
endpoints: make(map[string]endpoint),
socketname: file,
socketdir: dir,
healthyDevices: make(map[string]sets.String),
unhealthyDevices: make(map[string]sets.String),
allocatedDevices: make(map[string]sets.String),
pluginOpts: make(map[string]*pluginapi.DevicePluginOptions),
podDevices: make(podDevices),
}
manager.callback = manager.genericDeviceUpdateCallback
// The following structs are populated with real implementations in manager.Start()
// Before that, initializes them to perform no-op operations.
manager.activePods = func() []*v1.Pod { return []*v1.Pod{} }
manager.sourcesReady = &sourcesReadyStub{}
var err error
// 在/var/lib/kubelet/device-plugins/目录下创建file store类型的key-value存储文件kubelet_internal_checkpoint,用来作为kubelet的device plugin的checkpoint。
manager.store, err = utilstore.NewFileStore(dir, utilfs.DefaultFs{})
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to initialize device plugin checkpointing store: %+v", err)
}
return manager, nil
}
- kubelet Device Manager通过
/var/lib/kubelet/device-plugins/kubelet.sock与device plugin交互。 - 注册callback为
genericDeviceUpdateCallback,用来处理对应devices的add,delete,update事件。 - 在
/var/lib/kubelet/device-plugins/目录下创建file store类型的key-value存储文件kubelet_internal_checkpoint,用来作为kubelet的device plugin的checkpoint。- 当监听到devices add/delete/update事件发生时,会更新到
kubelet_internal_checkpoint文件中。 - 当device plugin的stop time超过grace period time(代码写死为5min,不可配置),会从checkpoint中删除对应的devices。在这个时间范围内,Device Manager会继续缓存该endpoint及对应的devices。
- 为Container Allocate Devices后,也会将PodDevices更新到checkpoint中。
- 当监听到devices add/delete/update事件发生时,会更新到
我们来看看callback的实现genericDeviceUpdateCallback的实现,了解Device Manager是如何处理devices的add/delete/update消息的。
pkg/kubelet/cm/devicemanager/manager.go:134
func (m *ManagerImpl) genericDeviceUpdateCallback(resourceName string, added, updated, deleted []pluginapi.Device) {
kept := append(updated, added...)
m.mutex.Lock()
if _, ok := m.healthyDevices[resourceName]; !ok {
m.healthyDevices[resourceName] = sets.NewString()
}
if _, ok := m.unhealthyDevices[resourceName]; !ok {
m.unhealthyDevices[resourceName] = sets.NewString()
}
for _, dev := range kept {
if dev.Health == pluginapi.Healthy {
m.healthyDevices[resourceName].Insert(dev.ID)
m.unhealthyDevices[resourceName].Delete(dev.ID)
} else {
m.unhealthyDevices[resourceName].Insert(dev.ID)
m.healthyDevices[resourceName].Delete(dev.ID)
}
}
for _, dev := range deleted {
m.healthyDevices[resourceName].Delete(dev.ID)
m.unhealthyDevices[resourceName].Delete(dev.ID)
}
m.mutex.Unlock()
m.writeCheckpoint()
}
- 将callback中收到的devices状态是
Healthy,那么将device ID插入到ManagerImpl中healthDevices中,并从unhealthyDevices中删除。 - 将callback中收到的devices状态是
Unhealthy,那么将device ID插入到ManagerImpl中unhealthDevices中,并从healthyDevices中删除。 - 将device plugin反馈的需要delete的devices从healthDevices和unhealthDevices中一并删除。
- 将ManagerImpl中的数据更新到checkpoint文件中。
Device Manager的启动
前面把Device Manager的创建流程分析了一下,还涉及到checkpoint和callback的分析。接下来,我们继续对Device Manager的Start流程进行分析。
Start Device Manager
Device Manager是在containerManagerImpl的Start时启动的。
pkg/kubelet/cm/container_manager_linux.go:527
func (cm *containerManagerImpl) Start(node *v1.Node,
activePods ActivePodsFunc,
sourcesReady config.SourcesReady,
podStatusProvider status.PodStatusProvider,
runtimeService internalapi.RuntimeService) error {
...
// Starts device manager.
if err := cm.deviceManager.Start(devicemanager.ActivePodsFunc(activePods), sourcesReady); err != nil {
return err
}
return nil
}
- deviceManager.Start的第一个参数是获取该节点的active(non-terminated)Pods的函数。
- SourcesReady是用来跟踪kubelet配置的Pod Sources,这些Sources包括:
- file: 通过static file创建静态Pods。
- http: 通过http接口来获取Pods信息。
- api: 从Kubernetes API Server获取Pods信息,是Kubernetes默认的内部机制。
- *: 表示包含以上全部的Sources类型。
ManagerIml Start
ManagerIml.Start负责启动Device Manager,对外提供gRPC服务。
pkg/kubelet/cm/devicemanager/manager.go:204
// Start starts the Device Plugin Manager amd start initialization of
// podDevices and allocatedDevices information from checkpoint-ed state and
// starts device plugin registration service.
func (m *ManagerImpl) Start(activePods ActivePodsFunc, sourcesReady config.SourcesReady) error {
m.activePods = activePods
m.sourcesReady = sourcesReady
// Loads in allocatedDevices information from disk.
err := m.readCheckpoint()
...
socketPath := filepath.Join(m.socketdir, m.socketname)
os.MkdirAll(m.socketdir, 0755)
// Removes all stale sockets in m.socketdir. Device plugins can monitor
// this and use it as a signal to re-register with the new Kubelet.
if err := m.removeContents(m.socketdir); err != nil {
glog.Errorf("Fail to clean up stale contents under %s: %+v", m.socketdir, err)
}
s, err := net.Listen("unix", socketPath)
if err != nil {
glog.Errorf(errListenSocket+" %+v", err)
return err
}
m.server = grpc.NewServer([]grpc.ServerOption{}...)
pluginapi.RegisterRegistrationServer(m.server, m)
go m.server.Serve(s)
glog.V(2).Infof("Serving device plugin registration server on %q", socketPath)
return nil
}
- 首先读取checkpoint file中数据,恢复ManagerImpl的相关数据,包括:
- podDevices;
- allocatedDevices;
- healthyDevices;
- unhealthyDevices;
- endpoints,注意这里会将endpoint的stop time设置为当前时间,意味着kubelet restart后,需要等待device plugin进行re-register后,才认为这些resource是可用的。
- 然后将
/var/lib/kubelet/device-plugins/下面的所有文件清空,当然checkpiont文件除外,也就是清空所有的socket文件,包括自己的kubelet.sock,以及其他所有之前的device plugin的socket文件。device plugin会监控kubelet.sock文件是否被删除,如果删除,则会触发自己的向kubelet重新注册自己。 - 创建kubelet.sock并启动gRPC Server对外提供gRPC服务,目前只注册了Register服务,用于Device plugin调用进行插件注册。
Register服务
我们就来看看kubelet Device Manager对外提供的唯一gRPC接口Register。
Register
pkg/kubelet/cm/devicemanager/manager.go:289
// Register registers a device plugin.
func (m *ManagerImpl) Register(ctx context.Context, r *pluginapi.RegisterRequest) (*pluginapi.Empty, error) {
glog.Infof("Got registration request from device plugin with resource name %q", r.ResourceName)
metrics.DevicePluginRegistrationCount.WithLabelValues(r.ResourceName).Inc()
var versionCompatible bool
for _, v := range pluginapi.SupportedVersions {
if r.Version == v {
versionCompatible = true
break
}
}
if !versionCompatible {
errorString := fmt.Sprintf(errUnsupportedVersion, r.Version, pluginapi.SupportedVersions)
glog.Infof("Bad registration request from device plugin with resource name %q: %v", r.ResourceName, errorString)
return &pluginapi.Empty{}, fmt.Errorf(errorString)
}
if !v1helper.IsExtendedResourceName(v1.ResourceName(r.ResourceName)) {
errorString := fmt.Sprintf(errInvalidResourceName, r.ResourceName)
glog.Infof("Bad registration request from device plugin: %v", errorString)
return &pluginapi.Empty{}, fmt.Errorf(errorString)
}
// TODO: for now, always accepts newest device plugin. Later may consider to
// add some policies here, e.g., verify whether an old device plugin with the
// same resource name is still alive to determine whether we want to accept
// the new registration.
go m.addEndpoint(r)
return &pluginapi.Empty{}, nil
}
-
注册请求是device plugin向kubelet发送的,注册请求RegisterRequest为:
type RegisterRequest struct { Version string // Kubernetes 1.10对应的device plugin api version为v1beta1 Endpoint string // device plugin对应的socket name ResourceName string Options *DevicePluginOptions } -
这里会检查注册的Resource Name是否符合Extended Resource的规则:
- Resource Name不能属于kubernetes.io,得有自己的domain,比如nvidia.com。
- Resource Name中不能包含
requests.前缀。 - 对应的Resource value只能是整数值。
-
调用addEndpoint进行插件注册。
addEndpoint进行device plugin注册
从上面Register的方法中可见,真正插件注册的逻辑是在addEndpoint中实现的。
pkg/kubelet/cm/devicemanager/manager.go:332
func (m *ManagerImpl) addEndpoint(r *pluginapi.RegisterRequest) {
existingDevs := make(map[string]pluginapi.Device)
m.mutex.Lock()
old, ok := m.endpoints[r.ResourceName]
if ok && old != nil {
// Pass devices of previous endpoint into re-registered one,
// to avoid potential orphaned devices upon re-registration
devices := make(map[string]pluginapi.Device)
for _, device := range old.getDevices() {
devices[device.ID] = device
}
existingDevs = devices
}
m.mutex.Unlock()
socketPath := filepath.Join(m.socketdir, r.Endpoint)
e, err := newEndpointImpl(socketPath, r.ResourceName, existingDevs, m.callback)
if err != nil {
glog.Errorf("Failed to dial device plugin with request %v: %v", r, err)
return
}
m.mutex.Lock()
if r.Options != nil {
m.pluginOpts[r.ResourceName] = r.Options
}
// Check for potential re-registration during the initialization of new endpoint,
// and skip updating if re-registration happens.
// TODO: simplify the part once we have a better way to handle registered devices
ext := m.endpoints[r.ResourceName]
if ext != old {
glog.Warningf("Some other endpoint %v is added while endpoint %v is initialized", ext, e)
m.mutex.Unlock()
e.stop()
return
}
// Associates the newly created endpoint with the corresponding resource name.
// Stops existing endpoint if there is any.
m.endpoints[r.ResourceName] = e
glog.V(2).Infof("Registered endpoint %v", e)
m.mutex.Unlock()
if old != nil {
old.stop()
}
go func() {
e.run()
e.stop()
m.mutex.Lock()
if old, ok := m.endpoints[r.ResourceName]; ok && old == e {
m.markResourceUnhealthy(r.ResourceName)
}
glog.V(2).Infof("Unregistered endpoint %v", e)
m.mutex.Unlock()
}()
}
-
首先检查注册的这个device plugin是否已经注册过,如果注册过,则获取已经缓存的devices。
-
再检查device plugin的socket是否能dial成功,如果dial失败,则说明device plugin没正常启动。如果dial成功,就根据已经缓存的devices重新初始化Endpoint,EndpointImpl的定义如下:
type endpointImpl struct { client pluginapi.DevicePluginClient clientConn *grpc.ClientConn socketPath string resourceName string stopTime time.Time devices map[string]pluginapi.Device mutex sync.Mutex cb monitorCallback } -
为了防止在EndpointImpl重新初始化的过程中device plugin进行re-register,初始化完成后再次获取缓存中该device plugin的Endpoint,并与初始化之前的Endpoint对象进行比对:
- 如果不是同一个对象,则说明在初始化过程中发生了re-register,那么就invoke Endpoint的stop接口,关闭gRPC连接,并设置Endpoint的stopTime为当前时间,Register流程以失败结束。
- 否则继续后面流程。
-
如果该device plugin之前注册过,那么再重新调用Endpoint的run()启动之前,先调用Endpoint的stop关闭gRPC连接,并设置Endpoint的stopTime为当前时间。
-
然后启动golang协程执行Endpoint的run(),在run方法中:
- 调用device plugin的ListAndWatch gRPC接口,通过长连接持续获取ListAndWatch gRPC stream,
- 从stream流中获取的devices与Endpoint中缓存的devices进行比对,得到需要add/delete/update的devices,
- 然后调用Endpoint的callback(也就是ManagerImpl注册的callback方法genericDeviceUpdateCallback)进行Device Manager的缓存更新并写到checkpoint文件中。
-
直到与device plugin的gRPC连接发生errListAndWatch错误,跳出持续获取stream的死循环,然后调用Endpoint的stop关闭gRPC连接,并设置Endpoint的stopTime为当前时间。
-
invoke stop后,再标记该device plugin对应的所有devices为unhealthy,即设置healthyDevices为空, 所有原来healthy的devices都加到unhealthyDevices中,此时表示注册失败。
调用Device Plugin的Allocate接口
注册UpdatePluginResources为Pod Admit Handler
kubelet在NewMainKubelet中会注册一系列的Pod Admit Handler,当有Pod需要创建的时,都会先调用这些Pod Admit Handler进行处理,其中klet.containerManager.UpdatePluginResources就是kubelet Device Manager为Pod分配devices的。
pkg/kubelet/kubelet.go:893
func NewMainKubelet( ... ) (*Kubelet, error) {
...
klet.admitHandlers.AddPodAdmitHandler(lifecycle.NewPredicateAdmitHandler(klet.getNodeAnyWay, criticalPodAdmissionHandler, klet.containerManager.UpdatePluginResources))
...
}
pkg/kubelet/cm/container_manager_linux.go:618
func (cm *containerManagerImpl) UpdatePluginResources(node *schedulercache.NodeInfo, attrs *lifecycle.PodAdmitAttributes) error {
return cm.deviceManager.Allocate(node, attrs)
}
Allocate
kubelet在创建Pod前,会invoke Device Manager的Allocate方法,为Pod中的每个Container请求分配对应的devices,kubelet会将请求转发到对应的Endpoint的Allocate方法, 然后请求会到对应的device plugin进行处理。
pkg/kubelet/cm/devicemanager/manager.go:259
func (m *ManagerImpl) Allocate(node *schedulercache.NodeInfo, attrs *lifecycle.PodAdmitAttributes) error {
pod := attrs.Pod
devicesToReuse := make(map[string]sets.String)
// TODO: Reuse devices between init containers and regular containers.
for _, container := range pod.Spec.InitContainers {
if err := m.allocateContainerResources(pod, &container, devicesToReuse); err != nil {
return err
}
m.podDevices.addContainerAllocatedResources(string(pod.UID), container.Name, devicesToReuse)
}
for _, container := range pod.Spec.Containers {
if err := m.allocateContainerResources(pod, &container, devicesToReuse); err != nil {
return err
}
m.podDevices.removeContainerAllocatedResources(string(pod.UID), container.Name, devicesToReuse)
}
m.mutex.Lock()
defer m.mutex.Unlock()
// quick return if no pluginResources requested
if _, podRequireDevicePluginResource := m.podDevices[string(pod.UID)]; !podRequireDevicePluginResource {
return nil
}
m.sanitizeNodeAllocatable(node)
return nil
}
- 调用allocateContainerResources为Pod中的init container分配devices,并更新ManagerImpl中PodDevices缓存;
- 调用allocateContainerResources为Pod中的regular container分配devices,并更新ManagerImpl中PodDevices缓存;
- 调用sanitizeNodeAllocatable更新scheduler cache中Node对应Resource Name的Allocatable Resource;
allocateContainerResources
pkg/kubelet/cm/devicemanager/manager.go:608
func (m *ManagerImpl) allocateContainerResources(pod *v1.Pod, container *v1.Container, devicesToReuse map[string]sets.String) error {
podUID := string(pod.UID)
contName := container.Name
allocatedDevicesUpdated := false
// Extended resources are not allowed to be overcommitted.
// Since device plugin advertises extended resources,
// therefore Requests must be equal to Limits and iterating
// over the Limits should be sufficient.
for k, v := range container.Resources.Limits {
resource := string(k)
needed := int(v.Value())
glog.V(3).Infof("needs %d %s", needed, resource)
if !m.isDevicePluginResource(resource) {
continue
}
// Updates allocatedDevices to garbage collect any stranded resources
// before doing the device plugin allocation.
if !allocatedDevicesUpdated {
m.updateAllocatedDevices(m.activePods())
allocatedDevicesUpdated = true
}
allocDevices, err := m.devicesToAllocate(podUID, contName, resource, needed, devicesToReuse[resource])
if err != nil {
return err
}
if allocDevices == nil || len(allocDevices) <= 0 {
continue
}
startRPCTime := time.Now()
m.mutex.Lock()
e, ok := m.endpoints[resource]
m.mutex.Unlock()
if !ok {
m.mutex.Lock()
m.allocatedDevices = m.podDevices.devices()
m.mutex.Unlock()
return fmt.Errorf("Unknown Device Plugin %s", resource)
}
devs := allocDevices.UnsortedList()
glog.V(3).Infof("Making allocation request for devices %v for device plugin %s", devs, resource)
resp, err := e.allocate(devs)
metrics.DevicePluginAllocationLatency.WithLabelValues(resource).Observe(metrics.SinceInMicroseconds(startRPCTime))
if err != nil {
m.mutex.Lock()
m.allocatedDevices = m.podDevices.devices()
m.mutex.Unlock()
return err
}
// Update internal cached podDevices state.
m.mutex.Lock()
m.podDevices.insert(podUID, contName, resource, allocDevices, resp.ContainerResponses[0])
m.mutex.Unlock()
}
// Checkpoints device to container allocation information.
return m.writeCheckpoint()
}
- device plugin提供的Resource属于Kubernetes Extended Resources,所以其Resource QoS只能是Guaranted。
- 每次在为Pod分配devices之前,都去检查一下此时的active pods,并与podDevices缓存中的pods进行比对,将已经terminated的Pods的devices从podDevices中删除,即进行了devices的GC操作。
- 从healthyDevices中随机分配对应数量的devices给该Pod,并注意更新allocatedDevices,否则会导致一个device被分配给多个Pod。
- 拿到devices后,就调用Endpoint的Allocate方法(进而调用对应device plugin的Allocate gRPC Service),device plugin返回ContainerAllocateResponse(包括注入的环境变量、挂载信息、Annotations)。
- 更新podDevices缓存信息,并将ManagerImpl中缓存数据更新到checkpoint文件中。
思考:当init container结束后,对应分配的devices会被释放吗? 目前还不会释放devices,在Allocate前只会回收Terminated Pods的devices,并没有回收init container的devices。要优化这个也是比较简单的,只要修改上面代码中updateAllocatedDevices方法内的逻辑就行了,增加init container的devices回收逻辑。
所以当前版本最好不会要在init container中使用devices,虽然这种场景几乎不存在。
维护NodeStatus中Device Plugin管理的Resource Capacity
当kubelet更新node status时会调用GetCapacity更新device plugins对应的Resource信息。
pkg/kubelet/kubelet_node_status.go:599
func (kl *Kubelet) setNodeStatusMachineInfo(node *v1.Node) {
...
devicePluginCapacity, devicePluginAllocatable, removedDevicePlugins = kl.containerManager.GetDevicePluginResourceCapacity()
...
}
pkg/kubelet/cm/container_manager_linux.go:881
func (cm *containerManagerImpl) GetDevicePluginResourceCapacity() (v1.ResourceList, v1.ResourceList, []string) {
return cm.deviceManager.GetCapacity()
}
下面是GetCapacity的具体代码实现,逻辑很简单:
- 检测healthyDevices对应的device plugin是否已经从缓存中删除或者已经停止超过5min,如果满足以上条件之一,则从endpoints和healthyDevices缓存中删除这些devices。
- 检测unhealthyDevices对应的device plugin是否已经从缓存中删除或者已经停止超过5min,如果满足以上条件之一,则从endpoints和unhealthyDevices缓存中删除这些devices。
- 如果缓存发生变化,则更新到checkpoint文件中。
pkg/kubelet/cm/devicemanager/manager.go:414
func (m *ManagerImpl) GetCapacity() (v1.ResourceList, v1.ResourceList, []string) {
needsUpdateCheckpoint := false
var capacity = v1.ResourceList{}
var allocatable = v1.ResourceList{}
deletedResources := sets.NewString()
m.mutex.Lock()
for resourceName, devices := range m.healthyDevices {
e, ok := m.endpoints[resourceName]
if (ok && e.stopGracePeriodExpired()) || !ok {
if !ok {
glog.Errorf("unexpected: healthyDevices and endpoints are out of sync")
}
delete(m.endpoints, resourceName)
delete(m.healthyDevices, resourceName)
deletedResources.Insert(resourceName)
needsUpdateCheckpoint = true
} else {
capacity[v1.ResourceName(resourceName)] = *resource.NewQuantity(int64(devices.Len()), resource.DecimalSI)
allocatable[v1.ResourceName(resourceName)] = *resource.NewQuantity(int64(devices.Len()), resource.DecimalSI)
}
}
for resourceName, devices := range m.unhealthyDevices {
e, ok := m.endpoints[resourceName]
if (ok && e.stopGracePeriodExpired()) || !ok {
if !ok {
glog.Errorf("unexpected: unhealthyDevices and endpoints are out of sync")
}
delete(m.endpoints, resourceName)
delete(m.unhealthyDevices, resourceName)
deletedResources.Insert(resourceName)
needsUpdateCheckpoint = true
} else {
capacityCount := capacity[v1.ResourceName(resourceName)]
unhealthyCount := *resource.NewQuantity(int64(devices.Len()), resource.DecimalSI)
capacityCount.Add(unhealthyCount)
capacity[v1.ResourceName(resourceName)] = capacityCount
}
}
m.mutex.Unlock()
if needsUpdateCheckpoint {
m.writeCheckpoint()
}
return capacity, allocatable, deletedResources.UnsortedList()
}
GetCapacity更新NodeStatus如下数据:
- registered device plugin resource Capacity
- registered device plugin resource Allocatable
- previously registered resources that are no longer active
调用Device Plugin的PreStartContainer接口
在kubelet的GetResource中,会调用DeviceManager的GetDeviceRunContainerOptions,并将这些options添加到kubecontainer.RunContainerOptions中。RunContainerOptions包括Envs、Mounts、Devices、PortMappings、Annotations等信息。
pkg/kubelet/cm/container_manager_linux.go:601
// TODO: move the GetResources logic to PodContainerManager.
func (cm *containerManagerImpl) GetResources(pod *v1.Pod, container *v1.Container) (*kubecontainer.RunContainerOptions, error) {
opts := &kubecontainer.RunContainerOptions{}
// Allocate should already be called during predicateAdmitHandler.Admit(),
// just try to fetch device runtime information from cached state here
devOpts, err := cm.deviceManager.GetDeviceRunContainerOptions(pod, container)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
} else if devOpts == nil {
return opts, nil
}
opts.Devices = append(opts.Devices, devOpts.Devices...)
opts.Mounts = append(opts.Mounts, devOpts.Mounts...)
opts.Envs = append(opts.Envs, devOpts.Envs...)
opts.Annotations = append(opts.Annotations, devOpts.Annotations...)
return opts, nil
}
- Device Manager的GetDeviceRunContainerOptions会根据pluginOpts的PreStartRequired是否为true,决定是否调用device plugin的PreStartContainer gRPC Service。
注意:如果某个device plugin的PreStartRequired为true,那么需要注册kubelet Device Manager调用device plugin的PreStartContainer接口的超时时间是30s,即30s内必须完成PreStartContainer的逻辑并返回。
pkg/kubelet/cm/devicemanager/manager.go:688
// GetDeviceRunContainerOptions checks whether we have cached containerDevices
// for the passed-in and returns its DeviceRunContainerOptions
// for the found one. An empty struct is returned in case no cached state is found.
func (m *ManagerImpl) GetDeviceRunContainerOptions(pod *v1.Pod, container *v1.Container) (*DeviceRunContainerOptions, error) {
podUID := string(pod.UID)
contName := container.Name
for k := range container.Resources.Limits {
resource := string(k)
if !m.isDevicePluginResource(resource) {
continue
}
err := m.callPreStartContainerIfNeeded(podUID, contName, resource)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
}
m.mutex.Lock()
defer m.mutex.Unlock()
return m.podDevices.deviceRunContainerOptions(string(pod.UID), container.Name), nil
}
- 然后deviceRunContainerOptions负责封装Container的Envs、Mount points、Device files、Annotations。
总结
本文对Kubelet Device Manager的核心代码进行了走读分析,对其整个工作流有了较深的理解。另外,分别对kubelet的Register服务、kubelet调用device plugin的Allocate接口等做了分析,尤其要注意kubelet device plugins的checkpoint机制(/var/lib/kubelet/device-plugins/kubelet_internal_checkpoint)的重要性。