根据用户输入的口令,计算出存储在数据库中的MD5口令:
【廖雪峰Python习题集】常用内建模块
datetime:
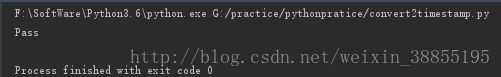
假设你获取了用户输入的日期和时间如2015-1-21 9:01:30,以及一个时区信息如UTC+5:00,均是str,请编写一个函数将其转换为timestamp:
import re
from datetime import datetime,timezone,timedelta
def to_timestamp(dt_str,tz_str):
#str转换为datetime
cday = datetime.strptime(dt_str, '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
t = tz_str.split('C')
t2 = t[1].split(':')
hour = int(t2[0])
mine = int(t2[1])
#创建时区UTC时间
tz_utc = timezone(timedelta(hours=hour,minutes=mine))
#强制设置UTC时间
dt = cday.replace(tzinfo=tz_utc)
#返回timestamp时间
return dt.timestamp()
if __name__ == "__main__":
t1 = to_timestamp('2015-6-1 08:10:30','UTC+7:00')
assert t1 == 1433121030.0 ,t1
t2 = to_timestamp('2015-5-31 16:10:30', 'UTC-09:00')
assert t2 == 1433121030.0 , t2
print('Pass')base64:
请写一个能处理去掉=的base64解码函数:
import base64
def safe_base64_decode(s):
if not s.__contains__(b'=='):
s = s + b'=='
return base64.b64decode(s)
if __name__ =="__main__":
assert b'abcd' == safe_base64_decode(b'YWJjZA==') ,safe_base64_decode('YWJjZA==')
assert b'abcd' == safe_base64_decode(b'YWJjZA') , safe_base64_decode('YWJjZA')
print('Pass')显示结果如下图所示:
struct:
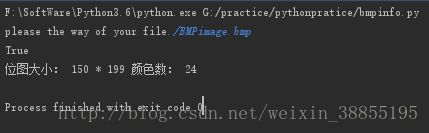
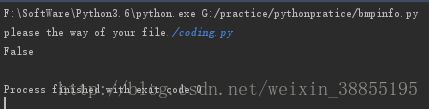
请编写一个bmpinfo.py,可以检查任意文件是否是位图文件,如果是,打印出图片大小和颜色数:
import struct
def bmpinfo(str):
f = open(str, 'rb')
s = f.read(30)
h = struct.unpack('显示结果如下图所示:
#是位图文件时:
#不是位图文件时:
hashlib:
练习1:
def calc_md5(password):
pass
存储MD5的好处是即使运维人员能访问数据库,也无法获知用户的明文口令。
设计一个验证用户登录的函数,根据用户输入的口令是否正确,返回True或False:
db = {
'michael': 'e10adc3949ba59abbe56e057f20f883e',
'bob': '878ef96e86145580c38c87f0410ad153',
'alice': '99b1c2188db85afee403b1536010c2c9'
}
def login(user, password):
pass
采用MD5存储口令是否就一定安全呢?也不一定。假设你是一个黑客,已经拿到了存储MD5口令的数据库,如何通过MD5反推用户的明文口令呢?暴力破解费事费力,真正的黑客不会这么干。
考虑这么个情况,很多用户喜欢用123456,888888,password这些简单的口令,于是,黑客可以事先计算出这些常用口令的MD5值,得到一个反推表:
'e10adc3949ba59abbe56e057f20f883e': '123456'
'21218cca77804d2ba1922c33e0151105': '888888'
'5f4dcc3b5aa765d61d8327deb882cf99': 'password'
这样,无需破解,只需要对比数据库的MD5,黑客就获得了使用常用口令的用户账号。
对于用户来讲,当然不要使用过于简单的口令。但是,我们能否在程序设计上对简单口令加强保护呢?
由于常用口令的MD5值很容易被计算出来,所以,要确保存储的用户口令不是那些已经被计算出来的常用口令的MD5,这一方法通过对原始口令加一个复杂字符串来实现,俗称“加盐”:
def calc_md5(password):
return get_md5(password + 'the-Salt')
经过Salt处理的MD5口令,只要Salt不被黑客知道,即使用户输入简单口令,也很难通过MD5反推明文口令。
但是如果有两个用户都使用了相同的简单口令比如123456,在数据库中,将存储两条相同的MD5值,这说明这两个用户的口令是一样的。有没有办法让使用相同口令的用户存储不同的MD5呢?
如果假定用户无法修改登录名,就可以通过把登录名作为Salt的一部分来计算MD5,从而实现相同口令的用户也存储不同的MD5。
import hashlib
def get_md5(str):
md5 = hashlib.md5()
md5.update(str.encode('utf-8'))
return md5.hexdigest()
def calc_md5(password):
return get_md5(password)
db = {
'michael':'e10adc3949ba59abbe56e057f20f883e',
'bob':'878ef96e86145580c38c87f0410ad153',
'alice':'99b1c2188db85afee403b1536010c2c9'
}
def login(user,password):
if db[user] == password:
return True
else:
return False
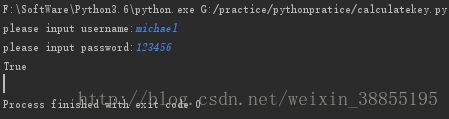
if __name__ == "__main__":
username = input('please input username:')
password = input('please input password:')
pwd = calc_md5(password)
print(login(username,pwd))
显示结果如下图所示:
练习2:
根据用户输入的登录名和口令模拟用户注册,计算更安全的MD5:
db = {}
def register(username,password):
dn[username] = get_md5(password + username + 'the-Salt')
然后,根据修改后的MD5算法实现用户登录的验证:
def login(username,password):
pass
import hashlib
def get_md5(str):
md5 = hashlib.md5()
md5.update(str.encode('utf-8'))
return md5.hexdigest()
db = {}
def register(username,password):
db[username] = get_md5(password + username + 'the-Salt')
def login(username,password):
pwd = get_md5(password + username + 'the-Salt')
if db[username] == pwd:
return True
else:
return False
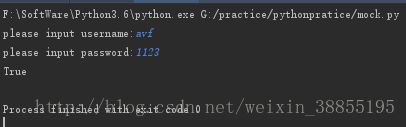
if __name__ == "__main__":
username = input('please input username:')
password = input('please input password:')
register(username,password)
print(login(username,password))显示结果如下图所示:
XML:
请利用SAX编写程序解析Yahoo的XML格式的天气预报,获取当天和第二天的天气:
http://weather.yahooapis.com/forecastrss?u=c&w=2151330
参数w是城市代码,要查询某个城市代码,可以在weather.yahoo.com搜索城市,浏览器地址栏的URL就包含城市代码
from xml.parsers.expat import ParserCreate
weather_dict = {}
which_day = 0
class WeatherSaxHandler(object):
def start_element(self,name,attrs):
global weather_dict,which_day
if name=='yweather:location':
weather_dict['city']=attrs['city']
weather_dict['country'] = attrs['country']
if name == 'yweather:forecast':
which_day+=1
if which_day == 1 :
weather = {
'text':attrs['text'],
'low':int(attrs['low']),
'high':int(attrs['high'])
}
weather_dict['today'] = weather
elif which_day == 2:
weather={
'text': attrs['text'],
'low':int(attrs['low']),
'high':int(attrs['high'])
}
weather_dict['tomorrow'] = weather
def char_data(self,name):
pass
def end_element(self,text):
pass
def parse_weather(xml):
wea = WeatherSaxHandler()
parser = ParserCreate()
parser.StartElementHandler = wea.start_element
parser.EndElementHandler = wea.end_element
parser.CharacterDataHandler = wea.char_data
parser.Parse(xml)
return weather_dict
data = r'''
Yahoo! Weather - Beijing, CN
Wed, 27 May 2015 11:00 am CST
-
39.91
116.39
Wed, 27 May 2015 11:00 am CST
'''
if __name__ == "__main__":
weather = parse_weather(data)
assert weather['city'] == 'Beijing', weather['city']
assert weather['country'] == 'China', weather['country']
assert weather['today']['text'] == 'Partly Cloudy', weather['today']['text']
assert weather['today']['low'] == 20, weather['today']['low']
assert weather['today']['high'] == 33, weather['today']['high']
assert weather['tomorrow']['text'] == 'Sunny', weather['tomorrow']['text']
assert weather['tomorrow']['low'] == 21, weather['tomorrow']['low']
assert weather['tomorrow']['high'] == 34, weather['tomorrow']['high']
print('Weather:', str(weather))
显示结果如下图所示:
HTMLParser:
找一个网页,例如:https://www.python.org/events/python-events,用浏览器查看源码并复制,然后尝试解析一下HTML,输出Python官网发布的会议时间,名称和地点
from html.parser import HTMLParser
from html.entities import name2codepoint
from urllib import request,parse
class MyHTMLParser(HTMLParser):
in_title = False
in_loca = False
in_time = False
times = []
def handle_starttag(self, tag, attrs):
if ('class','event-title') in attrs:
self.in_title =True
elif ('class','event-location') in attrs:
self.in_loca = True
elif tag =='time':
self.in_time = True
self.times=[]
def handle_endtag(self, tag):
if tag == 'h3':self.in_title = False
if tag =='span':self.in_loca = False
if tag =='time':
self.in_time = False
print('Time:'+'-'.join(self.times))
def handle_startendtag(self, tag, attrs):
pass
def handle_data(self, data):
if self.in_title:
print('Title: '+data.strip())
if self.in_loca:
print('Location: '+data.strip())
if self.in_time:
self.times.append(data)
def handle_comment(self, data):
pass
def handle_entityref(self, name):
pass
def handle_charref(self, name):
pass
if __name__ == "__main__":
with request.urlopen('https://www.python.org/events/python-events') as f:
data=f.read()
req = data.decode('utf-8')
parser = MyHTMLParser()
parser.feed(req)F:\SoftWare\Python3.6\python.exe F:/SoftWare/Python3.6/Lib/urllib/explainHtml.py
Title: Django Girls Koforidua
Time:11 Nov. – 12 Nov. - 2017
Location: Koforidua, Ghana
Title: PuPPy, Seattle's Python user group's monthly meeting
Time:11 Nov.- 2017
Location: Seattle Humane, 13212 SE Eastgate Way, Bellevue, WA 98005, USA
Title: PyHPC 2017: 7th Workshop on Python for High-Performance and Scientific Computing
Time:12 Nov. – 13 Nov. - 2017
Location: Denver, CO, USA
Title: PyRoma Meetup
Time:14 Nov.- 2017
Location: Rome, Italy
Title: PyCon Jamaica 2017
Time:16 Nov. – 19 Nov. - 2017
Location: Kingston, Jamaica
Title: PyConAr 2017
Time:17 Nov. – 20 Nov. - 2017
Location: Haya De La Torre S/N, Córdoba, Cordoba, Argentina
Title: Django Girls Santa Barbara
Time:18 Nov. – 19 Nov. - 2017
Location: UCSB, Santa Barbara, California
Title: PyTexas 2017
Time:18 Nov. – 19 Nov. - 2017
Location: 119 Nueces St, Austin, TX 78701, USA
Title: PyCon Canada 2017
Time:18 Nov. – 22 Nov. - 2017
Location: Montreal, Quebec, Canada
Title: SciPy India 2017
Time:29 Nov. – 01 Dec. - 2017
Location: LCH, IIT Bombay, Powai, Mumbai, India
Title: Kiwi PyCon 2017
Time:02 Dec. – 04 Dec. - 2017
Location: Auckland, New Zealand
Title: Django Girls Pereira, Colombia
Time:02 Dec. – 03 Dec. - 2017
Location: Pereira, Colombia
Title: Django Girls Ibagué
Time:02 Dec. – 03 Dec. - 2017
Location: Ibagué, Colombia
Title: North Bay Python 2017
Time:02 Dec. – 04 Dec. - 2017
Location: Petaluma, California, USA
Title: PyCon Indonesia 2017
Time:09 Dec. – 10 Dec. - 2017
Location: Surabaya, Indonesia
Title: Indy Startup Row Pitch Event
Time:09 Jan. – 10 Jan. - 2018
Location: Indianapolis, IN, US
Title: Python Meeting Düsseldorf (PyDDF)
Time:17 Jan.- 2018
Location: Bürgerhaus, Bachstr. 145, 40217 Düsseldorf
Title: PyCascades 2018
Time:22 Jan. – 24 Jan. - 2018
Location: Vancouver, BC V6A, Canada
Title: PyCon Cameroon 2018
Time:24 Jan. – 29 Jan. - 2018
Location: Limbe, Cameroon
Title: Pythology One-Day Conference: Security Best Practices
Time:02 Feb. – 03 Feb. - 2018
Location: Fishers, IN, USA
Title: FOSDEM 2018
Time:03 Feb. – 05 Feb. - 2018
Location: ULB Campus du Solbosch, Av. F. D. Roosevelt 50, 1050 Bruxelles, Belgium
Title: PyCon Pune 2018
Time:08 Feb. – 12 Feb. - 2018
Location: Pune, India
Title: PyCon Colombia 2018
Time:09 Feb. – 12 Feb. - 2018
Location: Medellin, Colombia
Title: PyCon SK 2018
Time:09 March – 12 March - 2018
Location: Bratislava, Slovakia
Title: PyCon IT 9
Time:19 April – 23 April - 2018
Location: Hotel Mediterraneo - Lungarno del Tempio, 44, 50121 Firenze FI, Italy
Title: GeoPython 2018
Time:07 May – 10 May - 2018
Location: Basel, Switzerland
Title: PyCon US 2018
Time:09 May – 18 May - 2018
Location: Cleveland, Ohio, USA
Title: PyCon US 2019
Time:01 May – 10 May - 2019
Location: Cleveland, Ohio, USA
Process finished with exit code 0
urllib:
利用urllib读取XML,将XML一节的数据由硬编码改为由urllib获取: