《牛客网 剑指Offer前20题》
《剑指Offer》
- 牛客网 前20道题
- 前言知识
- 面试题1:二维数组中的查找
- 面试题2:二维数组中的查找
- 面试题3:从头到尾打印链表
- 面试题4:重建二叉树 *****
- 面试题5:两个栈实现一个队列
- 面试题6:求旋转数组的最小数字
- 面试题7:编写斐波那契数列
- 面试题8:青蛙跳台阶问题
- 面试题9:变态青蛙跳台阶问题
- 面试题10:2*1小矩形覆盖2*n大矩形问题
- 面试题11:一个整数二进制存储中1的个数
- 面试题12:数值的整数次方
- 面试题13:调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面
- 面试题14:输出链表的倒数第k个节点
- 面试题15:反转链表
- 面试题16:合并两个有序的链表
- 面试题17:判断A树是不是B的子树 *****
- 面试题18:求二叉树的镜像
- 面试题19:顺时针打印矩阵
- 面试题20:自己定义一个可以求出自身最小值的栈
牛客网 前20道题
前言知识
-
优秀的程序员首先要有良好的基本功,基本功在面试编程环境体现在:编程语言、数据结构和算法。
编程语言:以C语言为例,例如把const加在指针不同位置有什么区别。主要考察对编程语言掌握程度。
数据结构:要熟练掌握链表、树、栈、队列和哈希表等数据结构,对链表的插入和删除节点了如指掌,对二叉树的各种遍历方法和递归写法烂熟于心。
算法:基本的查找、排序算法,重点掌握二分查找、归并排序、快速排序。 -
要注重代码的鲁棒性,可靠性,编写的任何函数要格外关注边界条件、特殊输入等看书细枝末节实则至关重要地方。
-
要有清晰的思路,在解决复杂问题时,可以举举例子,试着用图像分析过程等。
-
要注重算法的复杂度,有提高优化效率的能力,例如求斐波那契数列数列,很多人喜欢用递归,但是递归的时间复杂度是以n的指数增加的,如果先求f(1)和f(2),复杂度是O(n)。只要熟知各种数据结构的优缺点,才能选择合适的数据结构解决问题。
剑指Offer中采用C++和C#来编程,我只能用C、java语言实现。
https://www.nowcoder.com/ta/coding-interviews
面试题1:二维数组中的查找
题目:在一个二维数组中(每个一维数组的长度相同),每一行都按照从左到右递增的顺序排序,每一列都按照从上到下递增的顺序排序。请完成一个函数,输入这样的一个二维数组和一个整数,判断数组中是否含有该整数。
思路:由于每行从左到右递增,每列从上到下递增,所以选取数组右上角的数字,如果该数字等于要查找的数字,结束查找过程。如果大于要查找的数字,剔除这个数字所在的列。如果小于要查找的数字,剔除这个数字所在的行。
我犯的错误:
1、二维数组赋值方式未掌握:
int array[][] = new int[][]{{1,2,8,9},{2,4,9,12},{4,7,10,13},{6,8,11,15}};
int array[][] = {{1,2,8,9},{2,4,9,12},{4,7,10,13},{6,8,11,15}};
2、循环边界的判定
3、如何判断一个二维数组不为空,首先二维数组指针不能为空,其次若指针不为空,行长度不能为空,若行长度也不为空,那么列的长度也不能为空。array == null ||array.length == 0||(array.length == 1&&array[0].length == 0)
代码:
public class Solution {
public boolean Find(int target, int [][] array) {
boolean result = false;
if(array == null ||array.length == 0||(array.length == 1&&array[0].length == 0))
return false;
int row = array.length ;
int column = array[0].length;
int i = 0,j = column-1;
while(i<row&&j>=0)
{
if(array[i][j] >target)
{
j --;
}
else if(array[i][j] <target)
{
i ++;
}
else if(array[i][j] == target)
{
result = true;
break;
}
}
return result;
}
}
面试题2:二维数组中的查找
题目:请实现一个函数,将一个字符串中的每个空格替换成“%20”。例如,当字符串为We Are Happy.则经过替换之后的字符串为We%20Are%20Happy。 public String replaceSpace(StringBuffer str)
思路:1、最简单的方式,创建新的字符串,在新的字符串上,遇到空格就替换成“%20”。从前到后。
2、然而,面试官往往如果说在原来的字符串上替换,并且保证原来的字符串有足够的长度,此时就要先计算原有字符串的长度和空格的长度,则可以计算扩充后的字符串长度,那么从后往前遍历,遇到空格就替换成“%20”。
遇到的问题:
1、对StringBuffer类的api不熟,传入的参数是StringBuffer str,傻傻的用str[i]来遍历,StringBuffer的类变量长度是length(),而不是像数组array.length。
2、charAt、deleteCharAt、函数不熟
3、初始化一个char[]字符数组:char[] insertChars = {’%’,‘2’,‘0’};
代码:
public class Solution {
public String replaceSpace(StringBuffer str) {
if(str.length() == 0) return "";
int length = str.length();
int i = length - 1;
char[] insertChars = {'%','2','0'};
while(i>=0)
{
if(str.charAt(i) == ' '){
str.deleteCharAt(i);
str.insert(i, insertChars);
i --;
}
else
{
i--;
}
}
return str.toString();
}
}
面试题3:从头到尾打印链表
题目:输入一个链表,按链表值从尾到头的顺序返回一个ArrayList。
思路:如果我们遍历链表的话,只能从头到尾遍历,但是需要输出的是从尾到头。因此我们可以用栈来实现这种顺序,每经过一个结点时,把这个结点放到栈中,遍历完整个链表后,从栈顶开始输出,此时链表中的数据相当于反转了。
遇到的问题:
1、根本没用过java中的Stack类,使用时要导入java.util.Stack;
2、对特殊的测试用例没有做出很好的处理,当传入的是链表结点时,判断结点是否存在相当于该链表是否存在
3、case通过率为9.09%,用例:{67,0,24,58},对应输出应该为:[58,24,0,67],你的输出为:[24,0,67],原因在于遍历链表时用while(listNode.next !=null){stack.push(listNode.val);}会将最后一个值忘记装入栈中,所以后面要补充。
代码:
/**
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next = null;
*
* ListNode(int val) {
* this.val = val;
* }
* }
*
*/
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode listNode) {
ArrayList<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
if(listNode == null){
return arrayList;
}
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
while(listNode.next != null)
{
stack.push(listNode.val);
listNode = listNode.next;
}
stack.push(listNode.val);
while(!stack.isEmpty())
{
arrayList.add(stack.pop());
}
return arrayList;
}
}
面试题4:重建二叉树 *****
题目:输入某二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果int [] pre,int [] in,请重建出该二叉树。假设输入的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果中都不含重复的数字。例如输入前序遍历序列{1,2,4,7,3,5,6,8}和中序遍历序列{4,7,2,1,5,3,8,6},则重建二叉树并返回。
思路:前序遍历的第一个数字就是根结点值,根据中序遍历的特点在根结点1前面的3个数字都是根结点左子树的值,位于1后面的都是根结点右子树的值。二叉树的构建是由很多个形如 /\ 的3个结点组成的最小二叉树从根结点开始由上往下构成,每次构建这样的最小二叉树getRootNode,关键在于根结点怎么确定?左子树结点、右子树结点如何确定?根结点为每次得到的前序遍历序列的第一个值TreeNode root= new TreeNode(preList[0])。得到根结点后开始构建左子树结点、右子树结点,显然左子树结点、右子树结点可以视为再下一层的子树新的根结点,root.left = getRootNode(左子树结点前序遍历序列,左子树中序遍历序列);root.left = getRootNode(右子树结点前序遍历序列,右子树中序遍历序列);
如何去确定root.left = getRootNode(左子树结点前序遍历序列,左子树中序遍历序列);root.left = getRootNode(右子树结点前序遍历序列,右子树中序遍历序列);中的参数是最难之处。每次都是取前序遍历的第一个值作为最小二叉树的根结点,因此每次遍历只需判断传入的前序二叉树是否有效即可。左子树结点中序遍历序列 = inList.subList(0,index); 右子树结点的中序遍历序列 = inList.subList(index+1,inList.size()); 左子树结点前序遍历序列 = preList.subList(1,左子树结点遍历序列的长度)
右子树结点前序遍历序列 = preList.subList();
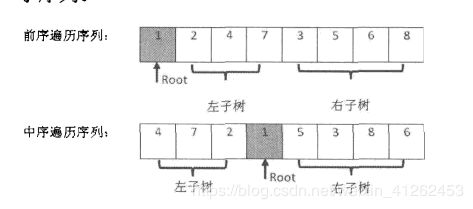

遇到的问题:
1、数组如何用while遍历,原来想用while(array[i] != null)并不行,报错he operator != is undefined for the argument type(s) int, null,应该while(index
/**
* Definition for binary tree
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Solution {
public TreeNode reConstructBinaryTree(int [] pre,int [] in) {
if(pre == null||in == null||pre.length == 0||in.length == 0)
return null;
ArrayList<Integer> preList = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> inList = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i:pre)
preList.add(i);
for(int j:in)
inList.add(j);
return getRootNode(preList,inList);
}
public TreeNode getRootNode(List<Integer> preList,List<Integer> inList)
{
if(preList.size() == 0) return null;
int root = preList.get(0);
TreeNode treeNode = new TreeNode(root);
int index = inList.indexOf(root);
List<Integer> leftinList = inList.subList(0, index);//当前根结点的左子树长度
List<Integer> rightinList = inList.subList(index+1, inList.size());//当前根结点的右子树长度
List<Integer> leftpreList = preList.subList(1, leftinList.size()+1);
List<Integer> rightpreList = preList.subList(preList.size()-rightinList.size(), preList.size());
treeNode.left = getRootNode(leftpreList, leftinList);
treeNode.right = getRootNode(rightpreList, rightinList);
return treeNode;
}
}
面试题5:两个栈实现一个队列
题目:用两个栈来实现一个队列,完成队列的Push和Pop操作。 队列中的元素为int类型。
思路:若给了两个Stack变量,stack1、stack2,想象着有两个弹夹,其中一个stack1一直用于装最新的压人的子弹,另一个弹夹stack2若为空,就将stack1弹出,依次压人stack2,直到stack1为空,这样,stack2的弹出可以保证是最先压人stack1的。
代码:
public void push(int node) {
stack1.push( node);
}
public int pop() {
int temp;
if(stack2.empty())
{
while(!stack1.isEmpty())
{
temp = stack1.pop();
stack2.push(temp);
}
}
return stack2.pop();
}
面试题6:求旋转数组的最小数字
题目:把一个数组最开始的若干个元素搬到数组的末尾,我们称之为数组的旋转。 输入一个非减排序的数组的一个旋转,输出旋转数组的最小元素。 例如数组{3,4,5,1,2}为{1,2,3,4,5}的一个旋转,该数组的最小值为1。 NOTE:给出的所有元素都大于0,若数组大小为0,请返回0。
思路:若是直接遍历数组一遍,返回最小的元素,时间复杂度是O(n),显然达不到面试官的要求。此旋转数组看起来由两个递增的序列组成,最小值在两个序列中间,因此改用二分法,用left、right、mid三个下标,mid = (right+left)/2;若array[mid]>array[left],说明mid位置在第一个递增序列中,若array[mid]
代码:时间复杂度O(n) 运行时间:250ms 占用内存:28424k
public int minNumberInRotateArray(int [] array) {
if(array == null||array.length == 0) return 0;
int min = array[0];
for(int i:array)
{
if(min>i) min = i;
}
return min;
}
时间复杂度O(logn)的二分法:运行时间:238ms 占用内存:28396k
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Solution {
public int minNumberInRotateArray(int [] array) {
if(array == null||array.length == 0) return 0;
int left = 0,right = array.length - 1;
int mid = (left+right)/2;
while(right - left>1)
{
if(array[mid]>array[left])
{
left = mid;
mid = (left+right)/2;
}
if(array[mid] == array[left]) left = left +1;
if(array[mid] == array[right]) right = right -1;
if(array[mid]<array[left]&&array[mid]<array[right])
{
right = mid;
mid = (left+right)/2;
}
}
return array[right];
}
}
面试题7:编写斐波那契数列
题目:大家都知道斐波那契数列,现在要求输入一个整数n,请你输出斐波那契数列的第n项(从0开始,第0项为0)。
n<=39
思路:斐波那契数列有递归和循环方式,当然是先求出f1,f2,再循环方式更快。
遇到的问题:
代码:递归方式 运行时间:761ms 占用内存:9428k
public class Solution {
public int Fibonacci(int n) {
if(n == 0) return 0;
if(n == 1||n == 2) return 1;
return Fibonacci(n-1)+Fibonacci(n-2);
}
}
循环方式:运行时间:15ms 占用内存:9328k
public class Solution {
public int Fibonacci(int n) {
if(n == 0) return 0;
if(n == 1||n == 2) return 1;
int f1 = 1,f2 = 1;
int result = 0;
while(n>2)
{
result = f1+f2;
f1 = f2;
f2 = result;
n--;
}
return result;
}
}
面试题8:青蛙跳台阶问题
题目:一只青蛙一次可以跳上1级台阶,也可以跳上2级。求该青蛙跳上一个n级的台阶总共有多少种跳法(先后次序不同算不同的结果)。
思路:对于本题,前提只有 一次 1阶或者2阶的跳法。
a.如果两种跳法,1阶或者2阶,那么假定第一次跳的是一阶,那么剩下的是n-1个台阶,跳法是f(n-1);
b.假定第一次跳的是2阶,那么剩下的是n-2个台阶,跳法是f(n-2)
c.由a\b假设可以得出总跳法为: f(n) = f(n-1) + f(n-2)
d.然后通过实际的情况可以得出:只有一阶的时候 f(1) = 1 ,只有两阶的时候可以有 f(2) = 2
e.可以发现最终得出的是一个斐波那契数列:
遇到的问题:
代码:运行时间:14ms 占用内存:9288k
public class Solution {
public int JumpFloor(int target) {
if(target <= 0) return 0;
if(target == 1) return 1;
if(target == 2) return 2;
int f1 = 1,f2 = 2,result = 0;
while(target >2)
{
result = f1+f2;
f1 = f2;
f2 = result;
target --;
}
return result;
}
}
面试题9:变态青蛙跳台阶问题
题目:一只青蛙一次可以跳上1级台阶,也可以跳上2级……它也可以跳上n级。求该青蛙跳上一个n级的台阶总共有多少种跳法。
思路:关于本题,前提是n个台阶会有一次n阶的跳法。分析如下
若只有1个台阶:f(1) = 1
若只有2个台阶:f(2) = f(2-1) + f(2-2) //f(2-1)表示先跳一阶,f(2-2) 表示2阶先一次跳2阶的次数。
若有3个台阶:f(3) = f(3-1) + f(3-2) + f(3-3) //它可能第一次跳1阶,也可能跳2阶,也有可能跳3阶
若有n个台阶:f(n) = f(n-1) + f(n-2) + f(n-3) + … + f(n-(n-1)) + f(n-n)
此题要求出f(n)的表达式,关键在于,f(n-1) = f(n-1-1)+f(n-1-2)+f(n-1-3)+…+f(n-1-(n-1)) = f(n-2)+f(n-3)+…+f(n-n),所以f(n) = f(n-1)+f(n-1)。
得到最终表达式:n=1 f(n) = 1; n>1,f(n) = 2*f(n-1);
遇到的问题:
代码:运行时间:13ms 占用内存:9408k
public class Solution {
public int JumpFloorII(int target) {
if(target <=0) return 0;
if(target == 1) return 1;
int f1 = 1,result = 0;
while(target >1)
{
result = 2*f1;
f1 = result;
target --;
}
return result;
}
}
面试题10:21小矩形覆盖2n大矩形问题
题目:我们可以用21的小矩形横着或者竖着去覆盖更大的矩形。请问用n个21的小矩形无重叠地覆盖一个2*n的大矩形,总共有多少种方法?
思路:类似这种思考题,最关键的是依次分析出n = 1,n = 2,n = 3…前几种情况,若可以也要分析出f(n)和f(n - 1) f(n-2)之间关系,通过画矩阵,当n=1 时,只有1种方法;当n=2 时,有2种方法。当n=3时,有3种方法。当n=4时,有5种方法。所以明显又是一个斐波那契数列。
遇到的问题:
代码:运行时间:15ms占用内存:9324k
public class Solution {
public int RectCover(int target) {
if(target<1) return 0;
if(target == 1) return 1;
if(target == 2) return 2;
int f1 = 1,f2 = 2,result = 0;
while(target>2)
{
result = f1+f2;
f1 = f2;
f2 = result;
target --;
}
return result;
}
}
面试题11:一个整数二进制存储中1的个数
题目:输入一个整数,输出该数二进制表示中1的个数。其中负数用补码表示。
思路:思路1、想象一下一个数在计算机中是以二进制存储的,那么这个数每次与1进行位运算,然后再右移,那么可以得到所有的1。但是,二进制的负数的以补码的形式存储,及时向右移位,最高位仍然会以1补上,所以会导致死循环。解决办法,java中有>>> 无符号右移。思路2、比较惊艳的做法:把一个整数减去1,再与原整数做与运算,做完与运算还不为0,count++。
遇到的问题:
代码:运行时间:15ms 占用内存:9324k
public class Solution {
public int NumberOf1(int n) {
int count = 0;
while(n != 0)
{
if((n & 1 ) == 1) count ++;
n = n >>> 1;
}
return count;
}
}
更加巧妙的方法:运行时间:17ms 占用内存:9360k
public class Solution {
public int NumberOf1(int n) {
int count = 0;
while(n != 0)
{
n = (n-1) & n;
count++;
}
return count;
}
}
面试题12:数值的整数次方
题目:给定一个double类型的浮点数base和int类型的整数exponent。求base的exponent次方。
思路:
遇到的问题:1、考虑的不够全面,自以为题目简单,没有考虑exponent为0或者为负数。
2、编写过程中,逻辑不够严谨,简单的逻辑总共提交了3次
代码:运行时间:48ms占用内存:10336k
public class Solution {
public double Power(double base, int exponent) {
if(exponent == 0) return 1;
if(exponent <0)
{
exponent = (-1)*exponent;
return 1.0/getPower(base,exponent);
}
else
{
return getPower(base,exponent);
}
}
public double getPower(double base,int exponent)
{
double result = base;
if(exponent == 1) return base;
while(exponent > 1)
{
result = result*base;
exponent --;
}
return result;
}
}
更加高端的代码:递归 运行时间:61ms 占用内存:10400k
public class Solution {
public double Power(double base, int exponent) {
if(exponent == 0) return 1;
if(exponent <0)
{
exponent = (-1)*exponent;
return 1.0/getPower(base,exponent);
}
else
{
return getPower(base,exponent);
}
}
public double getPower(double base,int exponent)
{
if(exponent == 0) return 1;
if(exponent == 1) return base;
double result = getPower(base,exponent >>1);
result *=result;
if((exponent &0x01) == 1)
result *= base;
return result;
}
}
面试题13:调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面
题目:输入一个整数数组,实现一个函数来调整该数组中数字的顺序,使得所有的奇数位于数组的前半部分,所有的偶数位于数组的后半部分,并保证奇数和奇数,偶数和偶数之间的相对位置不变。此处是最难的
思路:我的思路:空间换时间,最简单的一种,拷贝一个数组,遍历两次。
遇到的问题:1、使用了两个指针left、right来从左到右,从右到左移动,left碰到偶数停止搜索,right–碰到奇数停止搜索,然后两者交换,直到right-left>1不成立,退出循环。用例:[1,2,3,4,5,6,7]对应输出应该为:[1,3,5,7,2,4,6]你的输出为:[1,7,3,5,4,6,2],没有考虑相对位置不变。
代码:运行时间:运行时间:24ms 占用内存:9224k
public class Solution {
public void reOrderArray(int [] array) {
if(array == null ||array.length == 0)
return ;
if(array.length == 1) return ;
int[] temp = array.clone();
int i = 0,j = 0;
for( i = 0;i<temp.length;i++)
{
if(temp[i]%2 == 1) {
array[j] = temp[i];
j++;
}
}
for(i = 0;i<temp.length;i++)
{
if(temp[i]%2 == 0){
array[j] = temp[i];
j++;
}
}
}
}
面试题14:输出链表的倒数第k个节点
题目:输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点。
思路:1我的思路:用一个栈,先遍历链表,将每个结点入栈,并记录栈的长度,反向循环k次。需要导入Stack类的包java.util.Stack;2、若不用栈,可以用两个指针first,second,让first先走k-1步,然后second和first一起走,直到first走到结点末,second即为倒数第k个。
犯的错误:1、没有考虑输入的k值可能小于链表的长度
代码:运行时间:19ms 占用内存:9300k
/*
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next = null;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}*/
import java.util.Stack;
public class Solution {
public ListNode FindKthToTail(ListNode head,int k) {
if(head == null||k <= 0) return null;
ListNode tempNode = head;
ListNode result = new ListNode(0);
Stack stack = new Stack();
int length = 0;
while(tempNode.next != null)
{
stack.push(tempNode);
tempNode = tempNode.next;
length++;
}
stack.push(tempNode);
length++;
if(k>length) return null;
while(k>0)
{
result = (ListNode)stack.pop();
k --;
}
return result;
}
}
使用双指针方式:运行时间:20ms 占用内存:9420k
public class Solution {
public ListNode FindKthToTail(ListNode head,int k) {
if(head == null||k <= 0) return null;
ListNode first = head;
ListNode second = head;
int i = 0,length = 1;
while(first.next != null)
{
first = first.next;
length++;
}
first = head;
if(k>length) return null;
while(i <= k-2)
{
first = first.next;
i++;
}
while(first.next != null)
{
first = first.next;
second = second.next;
}
return second;
}
}
面试题15:反转链表
题目:输入一个链表,反转链表后,输出新链表的表头。
思路:我的思路:栈,先将链表的值入栈,再不断新建链表结点,连接新链表
犯的错误:
代码:运行时间:19ms 占用内存:9484k
import java.util.Stack;
public class Solution {
public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null) return null;
Stack stack = new Stack();
ListNode temp = head,newNode = head;
while(temp.next != null)
{
stack.push(temp.val);
temp = temp.next;
}
stack.push(temp.val);
ListNode newHead = new ListNode((int)stack.pop());
temp = newHead;
while(!stack.isEmpty())
{
newNode = new ListNode((int)stack.pop());
temp.next = newNode;
temp = newNode;
}
return newHead;
}
}
面试题16:合并两个有序的链表
题目:输入两个单调递增的链表,输出两个链表合成后的链表,当然我们需要合成后的链表满足单调不减规则。
思路:用两个链表进行遍历,并两两比较,新建一个链表头。若其中有一个链表的遍历的结点 == null,退出循环,剩下的那个链表直接补在新建的链表上
遇到的错误:我之前一直习惯、并以为判断链表遍历结束的循环语句只能 while(list1.next != null&& list2.next !=null),用 while(list1 != null&& list2 !=null)也可,即使链表list2遍历的时候下一个结点不存在,仍然可以list2 = list2.next
代码:运行时间:22ms 占用内存:9688k
public class Solution {
public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1,ListNode list2) {
//先传入参数判断
if(list1 == null &&list2 == null) return null;
if(list1 == null &&list2 != null) return list2;
if(list2 == null &&list1 != null) return list1;
ListNode newHead = new ListNode(0);
if(list2.val >= list1.val) {
newHead = new ListNode(list1.val);
list1 = list1.next;
}
else
{
newHead = new ListNode(list2.val);
list2 = list2.next;
}
ListNode tempNode = newHead;
ListNode newNode = newHead;
while(list1 != null&& list2 !=null)
{
if(list1.val >= list2.val)
{
newNode = new ListNode(list2.val);
list2 = list2.next;
tempNode.next = newNode;
tempNode = newNode;
}
else
{
newNode = new ListNode(list1.val);
list1 = list1.next;
tempNode.next = newNode;
tempNode = newNode;
}
}
if(list1 == null)
{
tempNode.next = list2;
}
if(list2 == null)
{
tempNode.next = list1;
}
return newHead;
}
}
面试题17:判断A树是不是B的子树 *****
题目:输入两棵二叉树A,B,判断B是不是A的子结构。(ps:我们约定空树不是任意一个树的子结构)
思路:分两步,看B子树的根结点是否存在A子树中,若存在,看B子树根结点的子树是否与A子树中的相同。当遇到A子树中有多个B子树的根结点时,怎么办?
遇到的问题:此题难的很,一脸懵逼,目前只能大致理解,自己编不出来
代码:
public class Solution {
public static boolean HasSubtree(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
boolean result = false;
//当Tree1和Tree2都不为零的时候,才进行比较。否则直接返回false
if (root2 != null && root1 != null) {
//如果找到了对应Tree2的根节点的点
if(root1.val == root2.val){
//以这个根节点为为起点判断是否包含Tree2
result = doesTree1HaveTree2(root1,root2);
}
//如果找不到,那么就再去root的左儿子当作起点,去判断时候包含Tree2
if (!result) {
result = HasSubtree(root1.left,root2);
}
//如果还找不到,那么就再去root的右儿子当作起点,去判断时候包含Tree2
if (!result) {
result = HasSubtree(root1.right,root2);
}
}
//返回结果
return result;
}
public static boolean doesTree1HaveTree2(TreeNode node1, TreeNode node2) {
//如果Tree2已经遍历完了都能对应的上,返回true
if (node2 == null) {
return true;
}
//如果Tree2还没有遍历完,Tree1却遍历完了。返回false
if (node1 == null) {
return false;
}
//如果其中有一个点没有对应上,返回false
if (node1.val != node2.val) {
return false;
}
//如果根节点对应的上,那么就分别去子节点里面匹配
return doesTree1HaveTree2(node1.left,node2.left) && doesTree1HaveTree2(node1.right,node2.right);
}
}
面试题18:求二叉树的镜像
题目:操作给定的二叉树,将其变换为源二叉树的镜像。

思路:遍历所有的二叉树结点,每个结点调用递归函数传入该结点的左子树结点和右子树结点,若结点为空,则返回。
遇到的错误:
代码:运行时间:22ms
占用内存:9404k
/**
public class TreeNode {
int val = 0;
TreeNode left = null;
TreeNode right = null;
public TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
*/
public class Solution {
public void Mirror(TreeNode root) {
if(root ==null) return;
TreeNode temp = null;
temp = root.right;
root.right = root.left;
root.left = temp;
Mirror(root.left);
Mirror(root.right);
}
}
面试题19:顺时针打印矩阵
题目:输入一个矩阵,按照从外向里以顺时针的顺序依次打印出每一个数字,例如,如果输入如下4 X 4矩阵: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 则依次打印出数字1,2,3,4,8,12,16,15,14,13,9,5,6,7,11,10.
思路:
遇到的错误:
代码:运行时间:22ms 占用内存:9688k
面试题20:自己定义一个可以求出自身最小值的栈
题目:定义栈的数据结构,请在该类型中实现一个能够得到栈中所含最小元素的min函数(时间复杂度应为O(1))。
思路:1、我的思路:重写链表结点,用链表实现栈的结构,栈顶即链表的表头
2、官方思路:用两个栈,一个数据栈,一个最小值栈。最小值栈
遇到的错误:
我的代码:在eclipse中我测试了感觉没有问题,牛客网提示
public class Solution {
private LinkSq linkSq = new LinkSq();
class LinkNode{
int val;
LinkNode next;
LinkNode(int val)
{
this.val = val;
}
}
class LinkSq{
LinkNode head = new LinkNode(0);
int count = 0;
}
public void push(int node) {
LinkNode temp = new LinkNode(node);
temp.next = linkSq.head.next;
linkSq.head = temp;
linkSq.count ++;
}
public int pop() {
int result = linkSq.head.val;
if(linkSq.count <= 0) return 0;
linkSq.head = linkSq.head.next;
linkSq.count --;
return result;
}
public int top() {
return linkSq.head.val;
}
public int min() {
if(linkSq.count<=0) return 0;
LinkNode temp = linkSq.head;
int count = linkSq.count;
int min = temp.val;
while(count > 0)
{
if(min>temp.val)
{
min = temp.val;
temp = temp.next;
count --;
}
else
{
temp = temp.next;
count --;
}
}
return min;
}
}
暂时不知道什么地方有问题,看不懂它的测试案例到底怎么测试提示:

官方的参考答案:需要注意栈的peek()是只取栈顶的值,但不移除, peek()或者pop()函数得到的值都是Obeject类型,要和int比较的话要进行强转先。运行时间:21ms 占用内存:9204k
import java.util.Stack;
public class Solution {
private Stack data = new Stack();
private Stack min = new Stack();
public void push(int node) {
data.push(node);
if(min.isEmpty()) min.push(node);
if(!min.isEmpty()) //若min栈不为空
{
if((int)min.peek()>node)
min.push(node);
}
}
public void pop() {
if(data.isEmpty()) return;
int temp = (int)data.pop();
if(temp == (int)min.peek())
min.pop();
}
public int top() {
return (int)data.peek();
}
public int min() {
return (int)min.peek();
}
}