【springCloud系列】springCloud+mybatisPlus+druid+shardingsphere4.1 实现mysql数据库的读写分离 + 多数据源
需要引入的包:
4.1.0
org.apache.shardingsphere
sharding-jdbc-spring-boot-starter
${sharding-sphere.version}
导入包之后,开始配置 yml 文件
spring:
shardingsphere:
dataSource:
names: db-master,db-slave1,db-slave2
# 配置主库
db-master: #org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource
name: master-${spring.application.name}
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driverClassName: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://${seowen.database.master.host}/${seowen.database.master.db}?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&allowMultiQueries=true&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&useSSL=false&autoReconnect=true&failOverReadOnly=false
username: ${seowen.database.master.username}
password: ${seowen.database.master.password}
# 使用druid数据源
filters: stat,wall,config,log4j
#最大连接池数量
maxActive: 10
#最小连接池数量
minIdle: 6
#初始化时建立物理连接的个数。初始化发生在显示调用init方法,或者第一次getConnection时
initialSize: 6
#获取连接时最大等待时间,单位毫秒。配置了maxWait之后,缺省启用公平锁,并发效率会有所下降,如果需要可以通过配置useUnfairLock属性为true使用非公平锁。
maxWait: 60000
# 配置间隔多久才进行一次检测,检测需要关闭的空闲连接,单位是毫秒
timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 300000
# 配置一个连接在池中最小生存的时间,单位是毫秒
minEvictableIdleTimeMillis: 900000
#用来检测连接是否有效的sql
validationQuery: select 'x'
# 申请连接时执行validationQuery检测连接是否有效,做了这个配置会降低性能。
testOnBorrow: false
#归还连接时执行validationQuery检测连接是否有效,做了这个配置会降低性能
testOnReturn: false
#建议配置为true,不影响性能,并且保证安全性。申请连接的时候检测,如果空闲时间大于timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis,执行validationQuery检测连接是否有效。
#testWhileIdle: true
#KeepAlive之后的效果
#初始化连接池时会填充到minIdle数量。
#连接池中的minIdle数量以内的连接,更长的时间超过minEvictableIdleTimeMillis,可以执行keepAlive操作。
#当网络轴向等原因产生的由ExceptionSorter检测出来的死连接被清除后,自动补充连接到minIdle数量。
keepAlive: true
#是否缓存preparedStatement,也就是PSCache。PSCache对支持游标的数据库性能提升巨大,比如说oracle。在mysql下建议关闭。
poolPreparedStatements: false
#要启用PSCache,必须配置大于0,当大于0时,poolPreparedStatements自动触发修改为true。在Druid中,不会存在Oracle下PSCache占用内存过多的问题,可以把这个数值配置大一些,比如说100
maxOpenPreparedStatements: -1
maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize: 10
useGlobalDataSourceStat: true
#timeBetweenLogStatsMillis: 1000
# 通过connectProperties属性来打开mergeSql功能;慢SQL记录
connectProperties: druid.stat.mergeSql=true;druid.stat.slowSqlMillis=500
db-slave1: # 配置第一个从库
name: slave1-${spring.application.name}
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driverClassName: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://${seowen.database.slave1.host}/${seowen.database.slave1.db}?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&allowMultiQueries=true&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&useSSL=false&autoReconnect=true&failOverReadOnly=false
username: ${seowen.database.slave1.username}
password: ${seowen.database.slave1.password}
filters: stat,wall,config,log4j
#最大连接池数量
maxActive: 10
#最小连接池数量
minIdle: 6
#初始化时建立物理连接的个数。初始化发生在显示调用init方法,或者第一次getConnection时
initialSize: 6
#获取连接时最大等待时间,单位毫秒。配置了maxWait之后,缺省启用公平锁,并发效率会有所下降,如果需要可以通过配置useUnfairLock属性为true使用非公平锁。
maxWait: 60000
# 配置间隔多久才进行一次检测,检测需要关闭的空闲连接,单位是毫秒
timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 300000
# 配置一个连接在池中最小生存的时间,单位是毫秒
minEvictableIdleTimeMillis: 900000
#用来检测连接是否有效的sql
validationQuery: select 'x'
# 申请连接时执行validationQuery检测连接是否有效,做了这个配置会降低性能。
testOnBorrow: false
#归还连接时执行validationQuery检测连接是否有效,做了这个配置会降低性能
testOnReturn: false
#建议配置为true,不影响性能,并且保证安全性。申请连接的时候检测,如果空闲时间大于timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis,执行validationQuery检测连接是否有效。
#testWhileIdle: true
#KeepAlive之后的效果
#初始化连接池时会填充到minIdle数量。
#连接池中的minIdle数量以内的连接,更长的时间超过minEvictableIdleTimeMillis,可以执行keepAlive操作。
#当网络轴向等原因产生的由ExceptionSorter检测出来的死连接被清除后,自动补充连接到minIdle数量。
keepAlive: true
#是否缓存preparedStatement,也就是PSCache。PSCache对支持游标的数据库性能提升巨大,比如说oracle。在mysql下建议关闭。
poolPreparedStatements: false
#要启用PSCache,必须配置大于0,当大于0时,poolPreparedStatements自动触发修改为true。在Druid中,不会存在Oracle下PSCache占用内存过多的问题,可以把这个数值配置大一些,比如说100
maxOpenPreparedStatements: -1
maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize: 10
useGlobalDataSourceStat: true
#timeBetweenLogStatsMillis: 1000
# 通过connectProperties属性来打开mergeSql功能;慢SQL记录
connectProperties: druid.stat.mergeSql=true;druid.stat.slowSqlMillis=500
db-slave2: # 配置第二个从库
name: slave2-${spring.application.name}
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driverClassName: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://${seowen.database.slave2.host}/${seowen.database.slave2.db}?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&allowMultiQueries=true&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&useSSL=false&autoReconnect=true&failOverReadOnly=false
username: ${seowen.database.slave2.username}
password: ${seowen.database.slave2.password}
filters: stat,wall,config,log4j
#最大连接池数量
maxActive: 10
#最小连接池数量
minIdle: 6
#初始化时建立物理连接的个数。初始化发生在显示调用init方法,或者第一次getConnection时
initialSize: 6
#获取连接时最大等待时间,单位毫秒。配置了maxWait之后,缺省启用公平锁,并发效率会有所下降,如果需要可以通过配置useUnfairLock属性为true使用非公平锁。
maxWait: 60000
# 配置间隔多久才进行一次检测,检测需要关闭的空闲连接,单位是毫秒
timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 300000
# 配置一个连接在池中最小生存的时间,单位是毫秒
minEvictableIdleTimeMillis: 900000
#用来检测连接是否有效的sql
validationQuery: select 'x'
# 申请连接时执行validationQuery检测连接是否有效,做了这个配置会降低性能。
testOnBorrow: false
#归还连接时执行validationQuery检测连接是否有效,做了这个配置会降低性能
testOnReturn: false
#建议配置为true,不影响性能,并且保证安全性。申请连接的时候检测,如果空闲时间大于timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis,执行validationQuery检测连接是否有效。
#testWhileIdle: true
#KeepAlive之后的效果
#初始化连接池时会填充到minIdle数量。
#连接池中的minIdle数量以内的连接,更长的时间超过minEvictableIdleTimeMillis,可以执行keepAlive操作。
#当网络轴向等原因产生的由ExceptionSorter检测出来的死连接被清除后,自动补充连接到minIdle数量。
keepAlive: true
#是否缓存preparedStatement,也就是PSCache。PSCache对支持游标的数据库性能提升巨大,比如说oracle。在mysql下建议关闭。
poolPreparedStatements: false
#要启用PSCache,必须配置大于0,当大于0时,poolPreparedStatements自动触发修改为true。在Druid中,不会存在Oracle下PSCache占用内存过多的问题,可以把这个数值配置大一些,比如说100
maxOpenPreparedStatements: -1
maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize: 10
useGlobalDataSourceStat: true
#timeBetweenLogStatsMillis: 1000
# 通过connectProperties属性来打开mergeSql功能;慢SQL记录
connectProperties: druid.stat.mergeSql=true;druid.stat.slowSqlMillis=500
db-slave3: # 另外一个独立的数据源
name: slave3-keda-sys-rabbitmq
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driverClassName: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://${seowen.database.slave3.host}/${seowen.database.slave3.db}?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&allowMultiQueries=true&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&useSSL=false&autoReconnect=true&failOverReadOnly=false
username: ${seowen.database.slave3.username}
password: ${seowen.database.slave3.password}
filters: stat,wall,config,log4j
#最大连接池数量
maxActive: 10
#最小连接池数量
minIdle: 6
#初始化时建立物理连接的个数。初始化发生在显示调用init方法,或者第一次getConnection时
initialSize: 6
#获取连接时最大等待时间,单位毫秒。配置了maxWait之后,缺省启用公平锁,并发效率会有所下降,如果需要可以通过配置useUnfairLock属性为true使用非公平锁。
maxWait: 60000
# 配置间隔多久才进行一次检测,检测需要关闭的空闲连接,单位是毫秒
timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 300000
# 配置一个连接在池中最小生存的时间,单位是毫秒
minEvictableIdleTimeMillis: 900000
#用来检测连接是否有效的sql
validationQuery: select 'x'
# 申请连接时执行validationQuery检测连接是否有效,做了这个配置会降低性能。
testOnBorrow: false
#归还连接时执行validationQuery检测连接是否有效,做了这个配置会降低性能
testOnReturn: false
#建议配置为true,不影响性能,并且保证安全性。申请连接的时候检测,如果空闲时间大于timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis,执行validationQuery检测连接是否有效。
#testWhileIdle: true
#KeepAlive之后的效果
#初始化连接池时会填充到minIdle数量。
#连接池中的minIdle数量以内的连接,更长的时间超过minEvictableIdleTimeMillis,可以执行keepAlive操作。
#当网络轴向等原因产生的由ExceptionSorter检测出来的死连接被清除后,自动补充连接到minIdle数量。
keepAlive: true
#是否缓存preparedStatement,也就是PSCache。PSCache对支持游标的数据库性能提升巨大,比如说oracle。在mysql下建议关闭。
poolPreparedStatements: false
#要启用PSCache,必须配置大于0,当大于0时,poolPreparedStatements自动触发修改为true。在Druid中,不会存在Oracle下PSCache占用内存过多的问题,可以把这个数值配置大一些,比如说100
maxOpenPreparedStatements: -1
maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize: 10
useGlobalDataSourceStat: true
#timeBetweenLogStatsMillis: 1000
# 通过connectProperties属性来打开mergeSql功能;慢SQL记录
connectProperties: druid.stat.mergeSql=true;druid.stat.slowSqlMillis=500
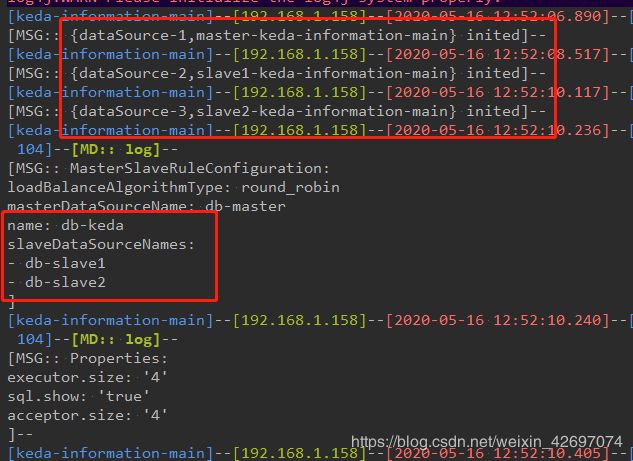
masterslave: # 配置读写分离
load-balance-algorithm-type: round_robin # 配置从库选择策略,提供轮询与随机,这里选择用轮询//random 随机 //round_robin 轮询
name: db-keda
master-data-source-name: db-master
slave-data-source-names: db-slave1,db-slave2
props:
sql.show: true # 开启SQL显示,默认值: false,注意:仅配置读写分离时不会打印日志!!!
executor.size: 4 #工作线程数量最大,默认值: 无限制
acceptor.size: 4 # accept连接的线程数量,默认为cpu核数2倍
seowen:
database:
master:
host: 192.168.1.1:3307
db: seowen_information
username: root
password: 123456
slave1:
host: 192.168.1.2:3307
db: seowen_information
username: root
password: 123456
slave2:
host: 192.168.1.3:3307
db: seowen_information
username: root
password: 123456
slave3:
host: 192.168.1.4:3308
db: seowen_rabbitmq
username: root
password: 123456参数说明:
names: db-master,db-slave1,db-slave2 声明sharding 的主从数据源key, 一主二从。 可以注意到,我实际上是有配置第4个数据源--slave3, 但是并没有声明在此。
原因,因为 slave3是一个独立的数据源,跟 其他三个数据源的业务上无任何关系,仅仅是用来 记录 rabbitmq的收发记录的。
此外,每个数据源的连接池都用了 druld
然后启动项目,报如下错误:
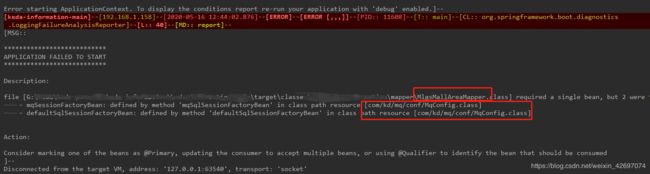
Error starting ApplicationContext. To display the conditions report re-run your application with 'debug' enabled.]--
[keda-information-main]--[192.168.1.158]--[2020-05-16 10:14:12.052]--[ERROR]--[ERROR [,,,]]--[PID:: 23044]--[T:: main]--[CL:: org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.LoggingFailureAnalysisReporter]--[L:: 40]--[MD:: report]--
[MSG::
***************************
APPLICATION FAILED TO START
***************************
Description:
Failed to configure a DataSource: 'url' attribute is not specified and no embedded datasource could be configured.
Reason: Failed to determine a suitable driver class
Action:
Consider the following:
If you want an embedded database (H2, HSQL or Derby), please put it on the classpath.
If you have database settings to be loaded from a particular profile you may need to activate it (no profiles are currently active).
]--
Disconnected from the target VM, address: '127.0.0.1:53512', transport: 'socket'
Process finished with exit code 1
在出现这个错误的地方,往上翻看, 会看如下内容:
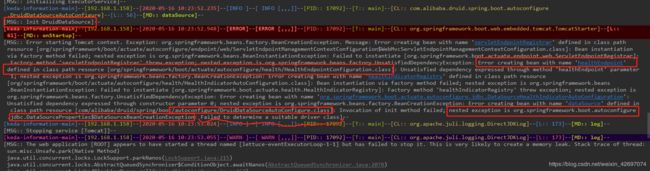
因为我使用的是 druid,从圈出来的地方,可以看到在系统启动的时候,druid 的 DruidDataSourceAutoConfigure会启动自动装配,并调用 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceProperties的数据源属性配置, 但是我上面的配置,并没有配置 spring原生的 spring.dataSource 属性, 所以 自然就无法找到 url 的相关配置,那druid就会创建失败。
解决方式:禁用 Druid的数据源自动配置 DruidDataSourceAutoConfigure.class,
同时官方建议,禁止 JtaAutoConfiguration.class
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = {DruidDataSourceAutoConfigure.class,JtaAutoConfiguration.class})
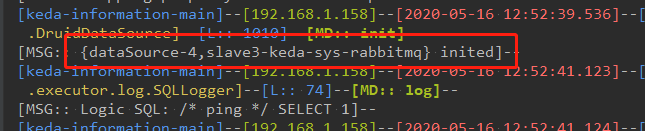
重新启动,出现如下,代表成功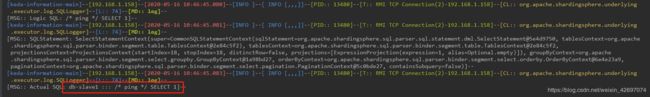
同时,打开druid的 监控平台: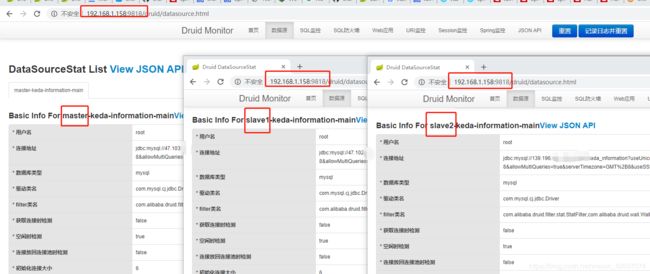 "
"
可以看到,只有三个数据源(master、slave1、slave2),并没有 slave3. 查看源码如下:
package org.apache.shardingsphere.shardingjdbc.spring.boot;
import com.google.common.base.Preconditions;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.core.yaml.swapper.MasterSlaveRuleConfigurationYamlSwapper;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.core.yaml.swapper.ShardingRuleConfigurationYamlSwapper;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.core.yaml.swapper.impl.ShadowRuleConfigurationYamlSwapper;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.encrypt.yaml.swapper.EncryptRuleConfigurationYamlSwapper;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.shardingjdbc.api.EncryptDataSourceFactory;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.shardingjdbc.api.MasterSlaveDataSourceFactory;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.shardingjdbc.api.ShadowDataSourceFactory;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.shardingjdbc.api.ShardingDataSourceFactory;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.shardingjdbc.spring.boot.common.SpringBootPropertiesConfigurationProperties;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.shardingjdbc.spring.boot.encrypt.EncryptRuleCondition;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.shardingjdbc.spring.boot.encrypt.SpringBootEncryptRuleConfigurationProperties;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.shardingjdbc.spring.boot.masterslave.MasterSlaveRuleCondition;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.shardingjdbc.spring.boot.masterslave.SpringBootMasterSlaveRuleConfigurationProperties;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.shardingjdbc.spring.boot.shadow.ShadowRuleCondition;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.shardingjdbc.spring.boot.shadow.SpringBootShadowRuleConfigurationProperties;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.shardingjdbc.spring.boot.sharding.ShardingRuleCondition;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.shardingjdbc.spring.boot.sharding.SpringBootShardingRuleConfigurationProperties;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.spring.boot.datasource.DataSourcePropertiesSetterHolder;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.spring.boot.util.DataSourceUtil;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.spring.boot.util.PropertyUtil;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.transaction.spring.ShardingTransactionTypeScanner;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.underlying.common.config.inline.InlineExpressionParser;
import org.apache.shardingsphere.underlying.common.exception.ShardingSphereException;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigureBefore;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnProperty;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.EnvironmentAware;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Conditional;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.core.env.StandardEnvironment;
import org.springframework.jndi.JndiObjectFactoryBean;
import javax.naming.NamingException;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* Spring boot starter configuration.
*/
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("org.apache.shardingsphere.spring.boot.converter")
@EnableConfigurationProperties({
SpringBootShardingRuleConfigurationProperties.class,
SpringBootMasterSlaveRuleConfigurationProperties.class, SpringBootEncryptRuleConfigurationProperties.class,
SpringBootPropertiesConfigurationProperties.class, SpringBootShadowRuleConfigurationProperties.class})
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.shardingsphere", name = "enabled", havingValue = "true", matchIfMissing = true)
@AutoConfigureBefore(DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class)
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class SpringBootConfiguration implements EnvironmentAware {
private final SpringBootShardingRuleConfigurationProperties shardingRule;
private final SpringBootMasterSlaveRuleConfigurationProperties masterSlaveRule;
private final SpringBootEncryptRuleConfigurationProperties encryptRule;
private final SpringBootShadowRuleConfigurationProperties shadowRule;
private final SpringBootPropertiesConfigurationProperties props;
private final Map dataSourceMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
private final String jndiName = "jndi-name";
/**
* Get sharding data source bean.
*
* @return data source bean
* @throws SQLException SQL exception
*/
@Bean
@Conditional(ShardingRuleCondition.class)
public DataSource shardingDataSource() throws SQLException {
return ShardingDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(dataSourceMap, new ShardingRuleConfigurationYamlSwapper().swap(shardingRule), props.getProps());
}
/**
* Get master-slave data source bean.
*
* @return data source bean
* @throws SQLException SQL exception
*/
@Bean
@Conditional(MasterSlaveRuleCondition.class)
public DataSource masterSlaveDataSource() throws SQLException {
return MasterSlaveDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(dataSourceMap, new MasterSlaveRuleConfigurationYamlSwapper().swap(masterSlaveRule), props.getProps());
}
/**
* Get encrypt data source bean.
*
* @return data source bean
* @throws SQLException SQL exception
*/
@Bean
@Conditional(EncryptRuleCondition.class)
public DataSource encryptDataSource() throws SQLException {
return EncryptDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(dataSourceMap.values().iterator().next(), new EncryptRuleConfigurationYamlSwapper().swap(encryptRule), props.getProps());
}
/**
* Get shadow data source bean.
*
* @return data source bean
* @throws SQLException SQL exception
*/
@Bean
@Conditional(ShadowRuleCondition.class)
public DataSource shadowDataSource() throws SQLException {
return ShadowDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(dataSourceMap, new ShadowRuleConfigurationYamlSwapper().swap(shadowRule), props.getProps());
}
/**
* Create sharding transaction type scanner.
*
* @return sharding transaction type scanner
*/
@Bean
public ShardingTransactionTypeScanner shardingTransactionTypeScanner() {
return new ShardingTransactionTypeScanner();
}
@Override
public final void setEnvironment(final Environment environment) {
String prefix = "spring.shardingsphere.datasource.";
for (String each : getDataSourceNames(environment, prefix)) {
try {
dataSourceMap.put(each, getDataSource(environment, prefix, each));
} catch (final ReflectiveOperationException ex) {
throw new ShardingSphereException("Can't find datasource type!", ex);
} catch (final NamingException namingEx) {
throw new ShardingSphereException("Can't find JNDI datasource!", namingEx);
}
}
}
private List getDataSourceNames(final Environment environment, final String prefix) {
StandardEnvironment standardEnv = (StandardEnvironment) environment;
standardEnv.setIgnoreUnresolvableNestedPlaceholders(true);
return null == standardEnv.getProperty(prefix + "name")
? new InlineExpressionParser(standardEnv.getProperty(prefix + "names")).splitAndEvaluate() : Collections.singletonList(standardEnv.getProperty(prefix + "name"));
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private DataSource getDataSource(final Environment environment, final String prefix, final String dataSourceName) throws ReflectiveOperationException, NamingException {
Map dataSourceProps = PropertyUtil.handle(environment, prefix + dataSourceName.trim(), Map.class);
Preconditions.checkState(!dataSourceProps.isEmpty(), "Wrong datasource properties!");
if (dataSourceProps.containsKey(jndiName)) {
return getJndiDataSource(dataSourceProps.get(jndiName).toString());
}
DataSource result = DataSourceUtil.getDataSource(dataSourceProps.get("type").toString(), dataSourceProps);
DataSourcePropertiesSetterHolder.getDataSourcePropertiesSetterByType(dataSourceProps.get("type").toString()).ifPresent(
dataSourcePropertiesSetter -> dataSourcePropertiesSetter.propertiesSet(environment, prefix, dataSourceName, result));
return result;
}
private DataSource getJndiDataSource(final String jndiName) throws NamingException {
JndiObjectFactoryBean bean = new JndiObjectFactoryBean();
bean.setResourceRef(true);
bean.setJndiName(jndiName);
bean.setProxyInterface(DataSource.class);
bean.afterPropertiesSet();
return (DataSource) bean.getObject();
}
} 其中的主要方法如下: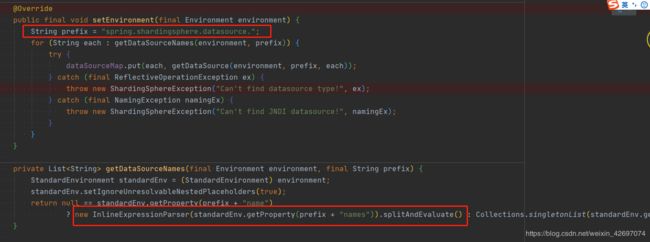
从以上源码可以发现,该方法是先获取names 属性,分割成 List
由此,可以明白。 shardingsphere 是通过 声明的 names 的属性 ,来创建相应的数据源。 而我的 slave3 没有声明,所以就不会被创建。 也就不会被 sharding所管辖。 可以以此,实现多数据源的目的。
重要:
既然,sharding没有创建 slave3数据源, 那我可以自己创建,并设置相关配置。代码如下:
@Configuration
//@PropertySource(value = "classpath:datasource.properties",
// ignoreResourceNotFound = true,encoding = "UTF-8")
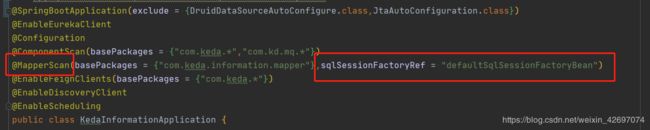
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.kd.mq.mapper", sqlSessionFactoryRef = "mqSessionFactoryBean")
public class MqConfig {
private final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MqConfig.class);
/**
* 获取 mq 数据源配置信息,并创建 DruidDataSource
* @return
*/
@Bean(name = "mqDataSource")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.shardingsphere.datasource.db-slave3")
public DataSource druidDataSource(){
return DruidDataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
/**
* 创建 mq的 MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean, 并将上面创建的数据源,注入进去
* @param mqDataSource
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
@Bean("mqSessionFactoryBean")
public MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean mqSqlSessionFactoryBean(
@Qualifier("mqDataSource")DataSource mqDataSource)throws Exception {
MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean mybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean = new MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean();
mybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean.setDataSource(mqDataSource);
mybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean.setTypeHandlersPackage("com.kd.mq.handle");
return mybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean;
}
/**
* 获取配置文件的 mybatis-plus 配置,并设置为 Primary。不然会报错
* @return
*/
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mybatis-plus")
@Bean("defaultMybatisPlus")
@Primary
public MybatisPlusProperties defaultMybatisPlus(){
return new MybatisPlusProperties();
}
/**
* 创建 主从数据源 的MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean,并注入 sharding创建的数据源,
* 和 mybatis-plus 配置 以及 自定义的Interceptor拦截器数组,这样才能使 mybatis-plus的相关配置起效
*
* @param dataSource
* @param mybatisPlusProperties
* @param interceptor
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
@Bean("defaultSqlSessionFactoryBean")
public MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean defaultSqlSessionFactoryBean(@Qualifier("masterSlaveDataSource") DataSource dataSource
, @Qualifier("defaultMybatisPlus") MybatisPlusProperties mybatisPlusProperties
, Interceptor[] interceptor)throws Exception {
// 这里用 MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean 代替了 SqlSessionFactoryBean,否则 MyBatisPlus 不会生效
MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean mybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean = new MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean();
mybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean.setDataSource(dataSource);
mybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean.setConfiguration(mybatisPlusProperties.getConfiguration());
mybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean.setConfigurationProperties(mybatisPlusProperties.getConfigurationProperties());
mybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean.setGlobalConfig(mybatisPlusProperties.getGlobalConfig());
mybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean.setTypeAliasesPackage(mybatisPlusProperties.getTypeAliasesPackage());
mybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean.setTypeAliasesSuperType(mybatisPlusProperties.getTypeAliasesSuperType());
mybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean.setTypeEnumsPackage(mybatisPlusProperties.getTypeEnumsPackage());
mybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean.setTypeHandlersPackage(mybatisPlusProperties.getTypeHandlersPackage());
//获取 mybatis 配置的 mapper文件
mybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean.setMapperLocations(this.getResources(mybatisPlusProperties.getMapperLocations()));
mybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean.setPlugins(interceptor);
return mybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean;
}
/**
* 配置事务管理器,注入 主从数据源。 不然事务无法起作用
* @param dataSource
* @return
*/
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager(@Qualifier("masterSlaveDataSource") DataSource dataSource){
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
}
/**
* 加载 mybatis 配置的 mapper 文件
* @param strings
* @return
* @throws IOException
*/
private Resource[] getResources(String [] strings) throws IOException {
if (ArrayUtils.isNotEmpty(strings)) {
ResourcePatternResolver resolver = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();
List list = new ArrayList<>(strings.length);
for (String str :strings){
list.addAll(Arrays.asList(resolver.getResources(str)));
}
return list.toArray(new Resource[list.size()]);
}
return null;
}
}