python内置函数汇总
内置函数(BIF, built-in functions)是python内置对象类型之一,不需要额外导入任何模块即可直接使用,这些内置对象都封装在内置模块_builtins_之中,用C语言实现并且进行了大量优化,具有非常快的运行速度,推荐优先使用。
使用内置函数dir()函数可以查看所有内置函数和内置对象。
使用help()函数可以查看某个函数的用法。
内置函数共有68个,在这里,我挑一些经常使用需要大家熟练掌握的函数进行介绍,至于其他函数的用法可以参考这里的教程。点击这里,查看教程
- abs():返回数值的绝对值
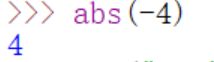
- all():用于判断所给定的可迭代参数中是否所有元素都为true,是的话返回True,否则返回False

- any():用于判断所给定的可迭代参数中是否所有元素都为false,是的话返回False,有一个true则返回True

- bin():返回整数所对应的2进制字符串

- bool():根据传入的参数的逻辑值创建一个布尔值

- chr():返回整数所对应的Unicode字符

- complex():根据传入参数创建一个新的复数
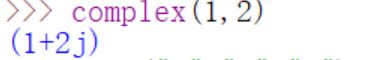
- dict():根据传入的参数创建一个新的字典
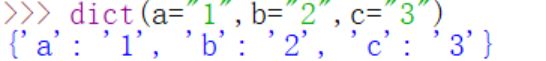
- dir():返回一个列表,包含对象的所有属性

- divmod() :返回两个数值的商和余数

- eval():执行所给定的字符串表达式,并且返回表达式的值

- float():根据传入的参数创建一个浮点数

- help():返回对象的帮助信息
- hex():返回整数所对应的16进制字符串

- id():返回对象的内存地址

- input():读取用户输入值

- int():根据传入的参数创建一个整数
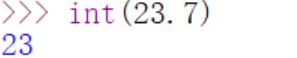
- len():返回传入对象的长度
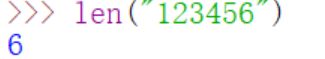
- list():根据传入的参数创建一个新的列表
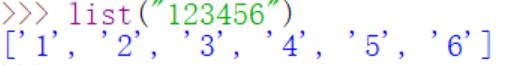
- max():返回可迭代对象中的元素中的最大值或者所有参数的最大值
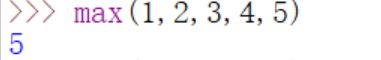
- min():返回可迭代对象中的元素中的最小值或者所有参数的最小值
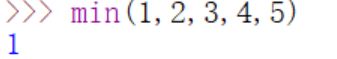
- oct():返回整数所对应的8进制字符串
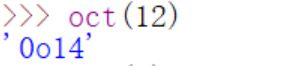
- ord():返回Unicode字符对应的整数

- pow():返回两个数值的幂运算值

- print():打印输出

- round():对传入的参数进行四舍五入运算,可以指定保留小数的位数

- set():根据传入的参数创建一个新的集合

- str():根据传入的参数创建一个字符串

- sum():对传入的参数进行求和运算
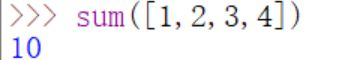
- tuple():根据传入的参数创建一个新的元组

- type():返回传入对象的类型。
可以观察到内置函数和自定义函数的类型是不同的。
In [1]: print(type(dir))
In [2]: def dosth():
...: print("dosth被调用")
...: print(type(dosth))

可以使用==来判断某个对象的类型是否是制定的类型。
对于基本的数据类型,可以使用其对应的类名。如果不是基本的数据类型,则需
要使用标准库types中定义的变量。
In [1]: print(type("123")==str)
True
In [2]: import types
In [3]: print(type(print)==types.BuiltinFunctionType)
True
In [4]: print(type(dosth)==types.FunctionType)
True
- issubclass():用于判断类对象与类对象之间的关系。第一个参数是类对象,第二个参数是类对象或者由类对象组成的元组。返回值是True或者False
In [1]: class A(object):
...: pass
...: class B(A):
...: pass
...: class C(object):
...: pass
...: class D(object):
...: pass
...: print(issubclass(B,A))
True
In [2]: print(issubclass(B,(C,D)))
False
In [3]: print(issubclass(B,(A,C)))
True
In [1]: print(issubclass(bool,int))
True
In [2]: print(issubclass(bool,(int,str)))
True
- isinstance():用于判断实例对象和类对象之间的关系。第一个参数是实例对象,第二个参数是类对象或者有类对象组成的元组。返回值为True或者False
In [1]: class A(object):
...: pass
...: class B(object):
...: pass
...: print(isinstance(A(),A))
True
In [2]: print(isinstance(A(),(A,B)))
True
- hasattr(object,name)用于判断指定对象object是否有参数name指定的属性或者方法。返回值为True或者False
In [1]: class A(object):
...: age = 18
...: def func(self):
...: print("func被调用")
...: a = A()
In [2]: print(hasattr(a,"age"))
True
In [3]: print(hasattr(a,"name"))
False
In [4]: print(hasattr(a,"func"))
True
- getattr(object,name[,default])用于获得指定的对象object中名为name的属性或者方法。
如果不指定参数default,那么当object中不存在名为name的属性或者方法时,抛出AttributeError。
如果指定参数default,那么当object中不存在名为name的属性或者方法时,就会返回default。
getattr(object,name)等价于:object.name。
In [5]: print(getattr(a,"age"))
18
In [6]: f = getattr(a,"func")
In [7]: f()
func被调用
- setattr(object,name,value)用于在指定的object对象中添加或修改名为参数name的属性或者方法,添加或修改后的值为value。
setattr(object,name,value)等价于:object.name = value。
In [8]: setattr(a,"name","mingming")
In [9]: print(getattr(a,"name"))
mingming
- delattr(object,name)用于删除指定的对象object中名为参数name的属性或者方法。
delattr(object,name)等价于:del object.name
In [10]: delattr(a,"name")
In [11]: print(hasattr(a,"name"))
False
- repr()将对象转化为供解释器读取的形式。返回值是给程序开发者看的,是为调试服务。
In [1]: str("hello,\nworld")
Out[1]: 'hello,\nworld'
In [2]: repr("hello,\nworld")
Out[2]: "'hello,\\nworld'"
In [3]: a = "hello"
In [4]: str(a)
Out[4]: 'hello'
In [5]: repr(a)
Out[5]: "'hello'"
In [6]: eval(repr(a)) == a
Out[6]: True
In [7]: eval(str(a)) == a
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
NameError Traceback (most recent call last)
in
----> 1 eval(str(a)) == a
in
NameError: name 'hello' is not defined
- callable()用于判断指定对象是否可以调用,除了函数对象可调用,对于实现了特殊方法__call__()的类对象,其实例对象也是可以调用的。
In [1]: callable(print)
Out[1]: True
In [2]: def do_sth():
...: pass
...:
In [3]: callable(do_sth)
Out[3]: True
In [4]: class MyClass(object):
...: def __call__(cls,*args,**kwargs):
...: print(args,kwargs)
...: mc = MyClass()
In [5]: callable(mc)
Out[5]: True