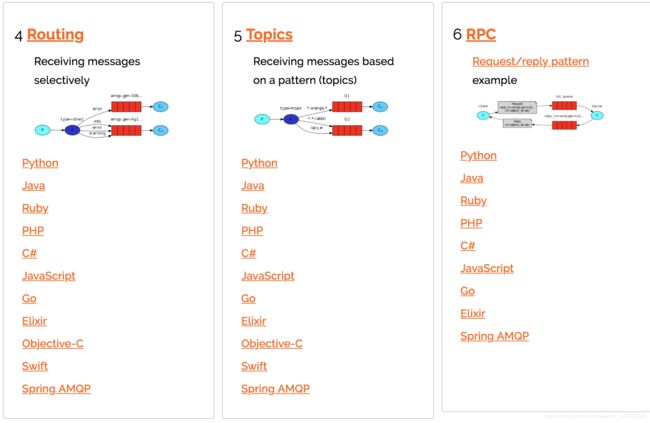
RabbitMQ的6种消息类型实现
消息队列是什么,知乎网友“祁达方”的解释:什么是消息队列
1. RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ是流行的开源消息队列系统,用erlang语言开发。RabbitMQ是AMQP(高级消息队列协议)的标准实现。支持多种客户端。
2. RabbitMQ消息测试
2.1 6种消息类型
2.2 添加RabbitMQ的依赖
创建Spring Boot项目,并依赖spring-boot-starter-amqp
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.3 Simple,简单模式
import com.example.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
public class Producer {
private final static String QUEUE_NAME = "test_queue";
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
// 获取到连接以及mq通道
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
// 从连接中创建通道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 声明(创建)队列
channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);
// 消息内容
String message = "Hello World!";
channel.basicPublish("", QUEUE_NAME, null, message.getBytes());
System.out.println(" Producer:'" + message + "'");
//关闭通道和连接
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
}
- 第2步,消费者消费
import com.example.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Consumer {
private final static String QUEUE_NAME = "test_queue";
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
// 获取到连接以及mq通道
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);
// 监听队列
channel.basicConsume(QUEUE_NAME, true, new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
// 获取消息
String message = new String(body);
System.out.println(" Consumer:'" + message + "'");
}
});
}
}
2.4 Work,工作模式
import com.example.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Consumer1 {
private final static String QUEUE_NAME = "test_queue_work";
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
// 获取到连接以及mq通道
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);
// 同一时刻服务器只会发一条消息给消费者,如果不设置这句代码,就没有能者多劳的特性而是公平接收
channel.basicQos(1);
// 监听队列,手动返回完成
channel.basicConsume(QUEUE_NAME, false, new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
String message = new String(body);
System.out.println(" Consumer1:'" + message + "'");
//休眠
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 返回确认状态
channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag(), false);
}
});
}
}
- 第2步,消费者2消费监听
import com.example.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Consumer2 {
private final static String QUEUE_NAME = "test_queue_work";
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
// 获取到连接以及mq通道
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);
// 同一时刻服务器只会发一条消息给消费者,如果不设置这句代码,就没有能者多劳的特性而是公平接收
channel.basicQos(1);
// 监听队列,手动返回完成
channel.basicConsume(QUEUE_NAME, false, new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
String message = new String(body);
System.out.println(" Consumer2:'" + message + "'");
//休眠
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 返回确认状态
channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag(), false);
}
});
}
}
2.5 消息的确认模式
当我们发送消息后,服务端如何知道消息已经被消费,在RabbitMQ里有两种模式:
- 自动模式。不管消费者获取到消息后是否是成功处理消息,服务端都认为是成功的
- 手动模式。消费者获取到消息后,服务器会将消息标记为不可用,等待消费者反馈,如果不反馈,则一直标记为不可用
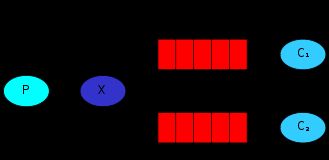
2.6 Pub/Sub,订阅模式
一条消息可以被多个消费者同时获取
生产者将消息发送到交换机
消费者将自己对应的队列注册到交换机
当发送消息后 所有注册的队列的消费者都可以收到消息
- 第1步,执行生产者逻辑,并注册了一个fanout交换机
import com.example.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
public class Producer {
private final static String EXCHANGE_NAME = "test_exchange_fanout";
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
// 获取到连接以及mq通道
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 声明exchange
channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME, "fanout");
// 消息内容
String message = "商品已经被更新,id=1001";
channel.basicPublish(EXCHANGE_NAME, "", null, message.getBytes());
System.out.println(" 后台系统:'" + message + "'");
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
}
- 第2步,消费者1把接收消息的队列绑定到交换机
import com.example.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Consumer1 {
private final static String QUEUE_NAME = "test_queue_pubsub_1";
private final static String EXCHANGE_NAME = "test_exchange_fanout";
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
// 获取到连接以及mq通道
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);
// 绑定队列到交换机
channel.queueBind(QUEUE_NAME, EXCHANGE_NAME, "");
// 同一时刻服务器只会发一条消息给消费者
channel.basicQos(1);
// 监听队列,手动返回完成
channel.basicConsume(QUEUE_NAME, false, new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
// 获取消息
String message = new String(body);
System.out.println(" 前台系统:'" + message + "'");
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag(), false);
}
});
}
}
- 第3步,消费者2把接收消息的队列绑定到交换机
import com.example.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Consumer2 {
private final static String QUEUE_NAME = "test_queue_pubsub_2";
private final static String EXCHANGE_NAME = "test_exchange_fanout";
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
// 获取到连接以及mq通道
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);
// 绑定队列到交换机
channel.queueBind(QUEUE_NAME, EXCHANGE_NAME, "");
// 同一时刻服务器只会发一条消息给消费者
channel.basicQos(1);
// 监听队列,手动返回完成
channel.basicConsume(QUEUE_NAME, false, new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
// 获取消息
String message = new String(body);
System.out.println(" 搜索系统:'" + message + "'");
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag(), false);
}
});
}
}
- 第4步,生产者发送消息测试
当消费者1和消费者2绑定完成后,此时生产者再发送一条消息,消费者1和消费者2都会收到。
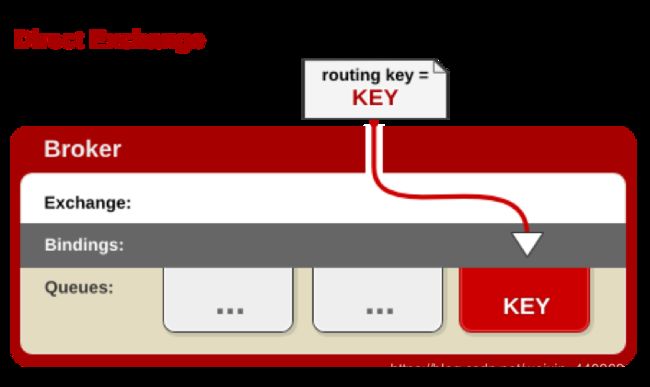
2.7 Routing,路由模式
生产者将消息发送到了 type 为 direct 模式的交换机
消费者的队列再将自己绑定到路由的时候会给自己绑定一个 key
只有消费者发送对应 key 格式的消息时候 队列才会收到消息
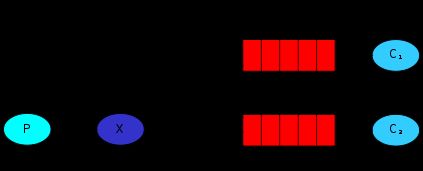
- 第1步,执行生产者逻辑,并注册了一个direct交换机
import com.example.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
public class Producer {
private final static String EXCHANGE_NAME = "test_exchange_direct";
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
// 获取到连接以及mq通道
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 声明exchange
channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME, "direct");
// 消息内容
String message = "商品删除,id=1002";
channel.basicPublish(EXCHANGE_NAME, "delete", null, message.getBytes());
System.out.println(" 后台系统: '" + message + "'");
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
}
- 第2步,消费者1把接收消息的队列绑定到交换机
import com.example.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Consumer1 {
private final static String QUEUE_NAME = "test_queue_direct_1";
private final static String EXCHANGE_NAME = "test_exchange_direct";
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
// 获取到连接以及mq通道
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);
// 绑定队列到交换机
channel.queueBind(QUEUE_NAME, EXCHANGE_NAME, "update");
channel.queueBind(QUEUE_NAME, EXCHANGE_NAME, "delete");
// 同一时刻服务器只会发一条消息给消费者
channel.basicQos(1);
// 监听队列,手动返回完成
channel.basicConsume(QUEUE_NAME, false, new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
// 获取消息
String message = new String(body);
System.out.println(" 前台系统: '" + message + "'");
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag(), false);
}
});
}
}
- 第3步,消费者2把接收消息的队列绑定到交换机
import com.example.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Consumer2 {
private final static String QUEUE_NAME = "test_queue_direct_2";
private final static String EXCHANGE_NAME = "test_exchange_direct";
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
// 获取到连接以及mq通道
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);
// 绑定队列到交换机
channel.queueBind(QUEUE_NAME, EXCHANGE_NAME, "insert");
channel.queueBind(QUEUE_NAME, EXCHANGE_NAME, "update");
channel.queueBind(QUEUE_NAME, EXCHANGE_NAME, "delete");
// 同一时刻服务器只会发一条消息给消费者
channel.basicQos(1);
// 定义队列的消费者
// 监听队列,手动返回完成
channel.basicConsume(QUEUE_NAME, false, new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
// 获取消息
String message = new String(body);
System.out.println(" 搜索系统: '" + message + "'");
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag(), false);
}
});
}
}
- 第4步,生产者发送消息测试
当消费者1和消费者2绑定完成后,此时生产者分别发送insert、update、delete消息,消费者1会收到update、delete消息,消费者2会收到insert、update、delete消息。
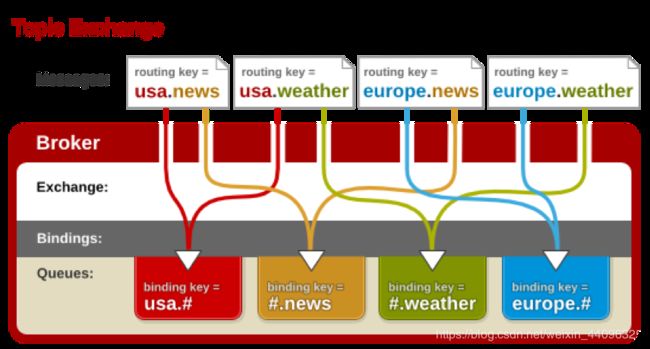
2.8 Topics,通配符模式
Topic Exchange:将路由键和某模式进行匹配。此时队列需要绑定要一个模式上。符号“#”匹配一个或多个词,符号“”匹配不多不少一个词。因此“audit.#”能够匹配到“audit.irs.corporate”,但是“audit.” 只会匹配到“audit.irs”

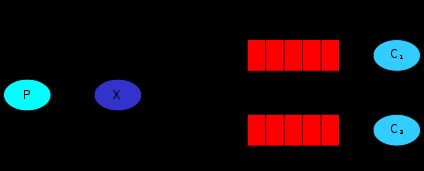
- 第1步,执行生产者逻辑,并注册了一个topic交换机
import com.example.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
public class Producer {
private final static String EXCHANGE_NAME = "test_exchange_topic";
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
// 获取到连接以及mq通道
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 声明exchange
channel.exchangeDeclare(EXCHANGE_NAME, "topic");
// 消息内容
String message = "商品删除,id=1002";
channel.basicPublish(EXCHANGE_NAME, "item.delete", null, message.getBytes());
System.out.println(" 后台系统: '" + message + "'");
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
}
- 第2步,消费者1把接收消息的队列绑定到交换机
import com.example.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Consumer1 {
private final static String QUEUE_NAME = "test_queue_topic_1";
private final static String EXCHANGE_NAME = "test_exchange_topic";
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
// 获取到连接以及mq通道
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);
// 绑定队列到交换机
channel.queueBind(QUEUE_NAME, EXCHANGE_NAME, "item.update");
channel.queueBind(QUEUE_NAME, EXCHANGE_NAME, "item.delete");
// 同一时刻服务器只会发一条消息给消费者
channel.basicQos(1);
// 监听队列,手动返回完成
channel.basicConsume(QUEUE_NAME, false, new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
// 获取消息
String message = new String(body);
System.out.println(" 前台系统: '" + message + "'");
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag(), false);
}
});
}
}
- 第3步,消费者2把接收消息的队列绑定到交换机
import com.example.rabbitmq.util.ConnectionUtil;
import com.rabbitmq.client.*;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Consumer2 {
private final static String QUEUE_NAME = "test_queue_topic_2";
private final static String EXCHANGE_NAME = "test_exchange_topic";
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
// 获取到连接以及mq通道
Connection connection = ConnectionUtil.getConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
// 声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);
// 绑定队列到交换机
channel.queueBind(QUEUE_NAME, EXCHANGE_NAME, "item.#");
// 同一时刻服务器只会发一条消息给消费者
channel.basicQos(1);
// 定义队列的消费者
// 监听队列,手动返回完成
channel.basicConsume(QUEUE_NAME, false, new DefaultConsumer(channel) {
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
// 获取消息
String message = new String(body);
System.out.println(" 搜索系统: '" + message + "'");
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag(), false);
}
});
}
}
- 第4步,生产者发送消息测试
当消费者1和消费者2绑定完成后,此时生产者分别发送item.insert、item.update、item.delete消息,消费者1会收到item.update、itemdelete消息,消费者2会收到item.#所有消息。