sparkSQL13(DStream操作实战、数据源)
文章目录
- DStream操作实战
- 1、 架构图
- 2、 实现流程
- 3、执行查看效果
- sparkStreaming数据源
- 1、文件数据源
- 2、自定义数据源
- 3、RDD队列
DStream操作实战
1 SparkStreaming接受socket数据,实现单词计数WordCount
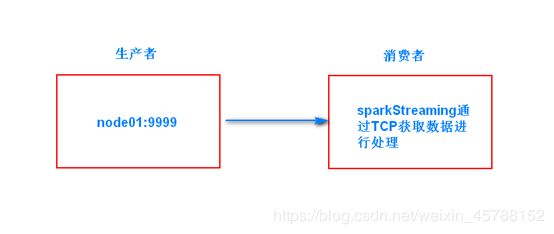
1、 架构图
2、 实现流程
第一步:创建maven工程并导入jar包
<properties>
<scala.version>2.11.8</scala.version>
<spark.version>2.2.0</spark.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.scala-lang</groupId>
<artifactId>scala-library</artifactId>
<version>${scala.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.spark</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-core_2.11</artifactId>
<version>${spark.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.spark</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-sql_2.11</artifactId>
<version>${spark.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.spark/spark-streaming -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.spark</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-streaming_2.11</artifactId>
<version>2.2.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hadoop</groupId>
<artifactId>hadoop-client</artifactId>
<version>2.7.5</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.spark</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-hive_2.11</artifactId>
<version>2.2.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.38</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<sourceDirectory>src/main/scala</sourceDirectory>
<testSourceDirectory>src/test/scala</testSourceDirectory>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.0</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
<encoding>UTF-8</encoding>
<!-- <verbal>true</verbal>-->
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>net.alchim31.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>scala-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.2.0</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>compile</goal>
<goal>testCompile</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<args>
<arg>-dependencyfile</arg>
<arg>${project.build.directory}/.scala_dependencies</arg>
</args>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-shade-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.1.1</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<phase>package</phase>
<goals>
<goal>shade</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<filters>
<filter>
<artifact>*:*</artifact>
<excludes>
<exclude>META-INF/*.SF
META-INF/*.DSA
META-INF/*.RSA
如果依赖包下载不了,下
第二步:node01服务器安装并启动生产者
首先在linux服务器上用YUM安装nc工具,nc命令是netcat命令的简称,它是用来设置路由器。我们可以利用它向某个端口发送数据。
node01服务器执行以下命令安装socket客户端工具,模拟发送数据
yum -y install nc
第三步:通过netcat工具向指定的端口发送数据
node01服务器执行以下命令,向指定的端口9999发送数据
nc -lk 9999
第四步:开发sparkStreaming程序,统计单词出现的次数
package cn.test.spark
import org.apache.spark.streaming.dstream.{DStream, ReceiverInputDStream}
import org.apache.spark.streaming.{Seconds, StreamingContext}
import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
/**
* sparkStreming流式处理接受socket数据,实现单词统计
*/
object SparkStreamingTCP {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//配置sparkConf参数
val sparkConf: SparkConf = new SparkConf().setAppName("SparkStreamingTCP").setMaster("local[2]")
//构建sparkContext对象
val sc: SparkContext = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
//设置日志输出级别
sc.setLogLevel("WARN")
//构建StreamingContext对象,每个批处理的时间间隔
val scc: StreamingContext = new StreamingContext(sc,Seconds(5))
//注册一个监听的IP地址和端口 用来收集数据
val lines: ReceiverInputDStream[String] = scc.socketTextStream("192.168.200.160",9999)
//切分每一行记录
val words: DStream[String] = lines.flatMap(_.split(" "))
//每个单词记为1
val wordAndOne: DStream[(String, Int)] = words.map((_,1))
//分组聚合
val result: DStream[(String, Int)] = wordAndOne.reduceByKey(_+_)
//打印数据
result.print()
scc.start()
scc.awaitTermination()
}
}
由于使用的是本地模式"local[2]"所以可以直接在本地运行该程序
注意:要指定并行度,如在本地运行设置setMaster(“local[2]”),相当于启动两个线程,一个给receiver,一个给computer。如果是在集群中运行,必须要求集群中可用core数大于1。
3、执行查看效果
(1)先执行nc -lk 9999
(2)然后在执行以上代码
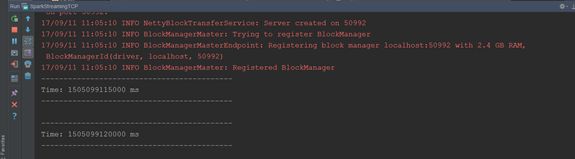
(3)不断的在(1)中输入不同的单词,观察IDEA控制台输出
![]()
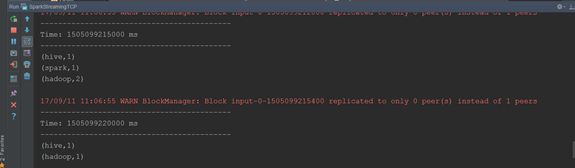
现象:sparkStreaming每隔5s计算一次当前5s内的数据,然后将每个批次的数据输出。
sparkStreaming数据源
Spark Streaming原生支持一些不同的数据源。一些“核心”数据源已经被打包到Spark Streaming 的 Maven 工件中,而其他的一些则可以通过 spark-streaming-kafka 等附加工件获取。每个接收器都以 Spark 执行器程序中一个长期运行的任务的形式运行,因此会占据分配给应用的 CPU 核心。此外,我们还需要有可用的 CPU 核心来处理数据。这意味着如果要运行多个接收器,就必须至少有和接收器数目相同的核心数,还要加上用来完成计算所需要的核心数。例如,如果我们想要在流计算应用中运行 10 个接收器,那么至少需要为应用分配 11 个 CPU 核心。所以如果在本地模式运行,不要使用local或者local[1]
1、文件数据源
Socket数据流前面的例子已经看到过。
文件数据流:能够读取所有HDFS API兼容的文件系统文件,通过fileStream方法进行读取
streamingContext.fileStream[KeyClass, ValueClass, InputFormatClass](dataDirectory)
Spark Streaming 将会监控 dataDirectory 目录并不断处理移动进来的文件,记住目前不支持嵌套目录。
- 文件需要有相同的数据格式
- 文件进入 dataDirectory的方式需要通过移动或者重命名来实现。
- 一旦文件移动进目录,则不能再修改,即便修改了也不会读取新数据。
如果文件比较简单,则可以使用 streamingContext.textFileStream(dataDirectory)方法来读取文件。文件流不需要接收器,不需要单独分配CPU核。
Hdfs读取实例:
提前需要在HDFS上建好目录。
import org.apache.spark.streaming.dstream.DStream
import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
import org.apache.spark.streaming.{Seconds, StreamingContext}
object StreamingFile {
def updateFunc(newValues:Seq[Int],runnintCount:Option[Int]):Option[Int] = {
val finalResult = runnintCount.getOrElse(0) + newValues.sum
Option(finalResult)
}
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//设置sparkConf配置
val sparkConf: SparkConf = new SparkConf().setAppName("streamingFile").setMaster("local[2]")
//通过sparkConf得到sparkContext
val sparkContext = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
//设置日志输出级别
sparkContext.setLogLevel("WARN")
//通过sparkContext得到streamingContext
val streamingContext = new StreamingContext(sparkContext,Seconds(5))
//设置sparkStreaming保存目录
streamingContext.checkpoint("./hdfs-data")
//读取hdfs某一个目录下的所有的文件
val fileStream: DStream[String] = streamingContext.textFileStream("hdfs://node01:8020/stream-data")
//文件内容按照空格进行切分
val words: DStream[String] = fileStream.flatMap(x => x.split(" "))
//每个单词记作为1
val wordAndOne: DStream[(String, Int)] = words.map(x => (x,1))
//更新每个单词的状态,传入一个我们自定义的updateFunction
val key: DStream[(String, Int)] = wordAndOne.updateStateByKey(updateFunc)
key.print()
streamingContext.start()
streamingContext.awaitTermination()
}
}
2、自定义数据源
如果已经存在的数据源满足不了我们的要求,我们还可以自定义sparkStreaming的数据源进行数据的采集处理
通过继承Receiver,并实现onStart、onStop方法来自定义数据源采集。
需求:自定义数据源,接收socket收据,并统计每个单词出现的次数
自定义数据源示例代码如下
class CustomReceiver(host: String, port: Int)
extends Receiver[String](StorageLevel.MEMORY_AND_DISK_2) with Logging {
def onStart() {
// Start the thread that receives data over a connection
new Thread("Socket Receiver") {
override def run() { receive() }
}.start()
}
def onStop() {
// There is nothing much to do as the thread calling receive()
// is designed to stop by itself if isStopped() returns false
}
/** Create a socket connection and receive data until receiver is stopped */
private def receive() {
var socket: Socket = null
var userInput: String = null
try {
// Connect to host:port
socket = new Socket(host, port)
// Until stopped or connection broken continue reading
val reader = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8))
userInput = reader.readLine()
while(!isStopped && userInput != null) {
store(userInput)
userInput = reader.readLine()
}
reader.close()
socket.close()
// Restart in an attempt to connect again when server is active again
restart("Trying to connect again")
} catch {
case e: java.net.ConnectException =>
// restart if could not connect to server
restart("Error connecting to " + host + ":" + port, e)
case t: Throwable =>
// restart if there is any other error
restart("Error receiving data", t)
}
}
}
可以通过streamingContext.receiverStream()
来使用自定义的数据采集源
val customReceiverStream = ssc.receiverStream(new CustomReceiver(host, port))
val words = lines.flatMap(_.split(" "))
完整代码执行如下
import java.io.{BufferedReader, InputStreamReader}
import java.net.Socket
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets
import org.apache.spark.SparkConf
import org.apache.spark.storage.StorageLevel
import org.apache.spark.streaming.{Seconds, StreamingContext}
import org.apache.spark.streaming.receiver.Receiver
class CustomReceiver (host: String, port: Int) extends Receiver[String](StorageLevel.MEMORY_AND_DISK_2) {
override def onStart(): Unit = {
// Start the thread that receives data over a connection
new Thread("Socket Receiver") {
override def run() { receive() }
}.start()
}
override def onStop(): Unit = {
// There is nothing much to do as the thread calling receive()
// is designed to stop by itself if isStopped() returns false
}
/** Create a socket connection and receive data until receiver is stopped */
private def receive() {
var socket: Socket = null
var userInput: String = null
try {
// Connect to host:port
socket = new Socket(host, port)
// Until stopped or connection broken continue reading
val reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8))
userInput = reader.readLine()
while(!isStopped && userInput != null) {
// 传送出来
store(userInput)
userInput = reader.readLine()
}
reader.close()
socket.close()
// Restart in an attempt to connect again when server is active again
restart("Trying to connect again")
} catch {
case e: java.net.ConnectException =>
// restart if could not connect to server
restart("Error connecting to " + host + ":" + port, e)
case t: Throwable =>
// restart if there is any other error
restart("Error receiving data", t)
}
}
}
object CustomReceiver {
def main(args: Array[String]) {
val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[2]").setAppName("NetworkWordCount")
val ssc = new StreamingContext(conf, Seconds(1))
// Create a DStream that will connect to hostname:port, like localhost:9999
val lines = ssc.receiverStream(new CustomReceiver("master01", 9999))
// Split each line into words
val words = lines.flatMap(_.split(" "))
//import org.apache.spark.streaming.StreamingContext._ // not necessary since Spark 1.3
// Count each word in each batch
val pairs = words.map(word => (word, 1))
val wordCounts = pairs.reduceByKey(_ + _)
// Print the first ten elements of each RDD generated in this DStream to the console
wordCounts.print()
ssc.start() // Start the computation
ssc.awaitTermination() // Wait for the computation to terminate
//ssc.stop()
}
}
3、RDD队列
测试过程中,可以通过使用streamingContext.queueStream(queueOfRDDs)来创建DStream,每一个推送到这个队列中的RDD,都会作为一个DStream处理。
import org.apache.spark.SparkConf
import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD
import org.apache.spark.streaming.{Seconds, StreamingContext}
import scala.collection.mutable
object QueueRdd {
def main(args: Array[String]) {
val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[2]").setAppName("QueueRdd")
val ssc = new StreamingContext(conf, Seconds(1))
// Create the queue through which RDDs can be pushed to
// a QueueInputDStream
//创建RDD队列
val rddQueue = new mutable.SynchronizedQueue[RDD[Int]]()
// Create the QueueInputDStream and use it do some processing
// 创建QueueInputDStream
val inputStream = ssc.queueStream(rddQueue)
//处理队列中的RDD数据
val mappedStream = inputStream.map(x => (x % 10, 1))
val reducedStream = mappedStream.reduceByKey(_ + _)
//打印结果
reducedStream.print()
//启动计算
ssc.start()
// Create and push some RDDs into
for (i <- 1 to 30) {
rddQueue += ssc.sparkContext.makeRDD(1 to 300, 10)
Thread.sleep(2000)
//通过程序停止StreamingContext的运行
//ssc.stop()
}
}
}