Percolation 渗透算法
Union-Find 并查集算法
解决动态连通性一类问题的一种算法
使用场景:
网络连接判断
变量名等同性
社交网络
实现:
Quick-find
Quick-Union
Weighted quick-union
Weighted quick-union with path compression
蒙特卡洛模拟
也称为计算机随机模拟方法,是一种基于”随机数”的计算方法。特点是,可以在随机采样上计算得到近似结果,随着采样的增多,得到的结果是正确结果的概率逐渐加大
例子,蒙特卡罗方法求π。就是画一个正方形和内切圆,随机撒点,数一下点落在园内和正方形内的数量之比,就是二者面积之比π/4。
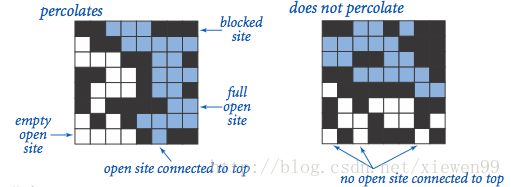
渗透模型
n*n 个点组成的网格,每个点是 Open 或 Closed 状态。假如最底部的点和最顶端的点连通,就说明这个网格系统是渗透的。
比如图中黑色表示 Closed 状态,白色表示 Open,蓝色表示与顶部连通。所以左图是渗透的,右图不是:
应用场景:
判断由绝缘体和金属材料组成的一个物体什么情况可以导电
判断一块多空地形,什么情况可以让水或者油渗透过去
问题
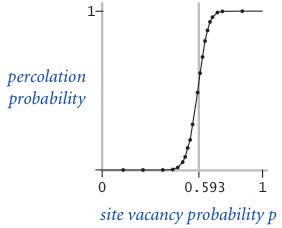
假设每个点是 Open 状态的概率是 p,计算整个系统是渗透的概率。
图片为 20*20、100*100 网格的概率分布:

计算方法概述
利用蒙特卡洛模拟
* 初始化 n*n 全为 Blocked 的网格系统
* 随机 Open 一个点,重复执行,直到整个系统变成渗透的为止
* 上述过程重复 T 次,计算平均值、标准差、96% 置信区间
用 Union-Find 算法判断连通性
增加一个只有顶端虚拟节点的并查集,避免 backwash(其它方法参考:http://www.sigmainfy.com/blog/avoid-backwash-in-percolation.html)

代码
Percolation.java
/******************************************************************************
* Compilation: javac-algs4 Percolation.java
* Execution: java-algs4 Percolation < input.txt
* Dependencies: None
*
* This program reads standard input.
*
* - Reads the grid size n of the percolation system.
* - Creates an n-by-n grid of sites (intially all blocked)
* - Reads in a sequence of sites (row i, column j) to open.
*
* After each site is opened, it checks if the system is percolated.
******************************************************************************/
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdIn;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.WeightedQuickUnionUF;
public class Percolation {
private int gridLength;
private boolean[] grid; // true:open, false:blocked
private WeightedQuickUnionUF wqu; // with virtual top & bottom
private WeightedQuickUnionUF wqu2; // without virtual bottom
private int virtualTop;
// create n-by-n grid, with all sites blocked
public Percolation(int n) {
if (n <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("length must be positive");
}
gridLength = n;
virtualTop = gridLength * gridLength;
grid = new boolean[virtualTop];
// the last two are virtual top & virtual bottom sites
wqu = new WeightedQuickUnionUF(virtualTop + 2);
wqu2 = new WeightedQuickUnionUF(virtualTop + 1);
}
private void validateIndecies(int row, int col) {
if (row <= 0 || row > gridLength)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("row index out of bounds");
if (col <= 0 || col > gridLength)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("col index out of bounds");
}
private int xyTo1D(int row, int col) {
return (row - 1) * gridLength + (col - 1);
}
// open site (row, col) if it is not open already
public void open(int row, int col) {
validateIndecies(row, col);
int self = xyTo1D(row, col);
if (grid[self]) {
return;
}
grid[self] = true;
if (row == 1) {
wqu.union(self, virtualTop);
wqu2.union(self, virtualTop);
}
if (row == gridLength) {
wqu.union(self, virtualTop + 1);
}
int other;
if (row > 1) { // up
other = xyTo1D(row - 1, col);
if (grid[other]) {
wqu.union(self, other);
wqu2.union(self, other);
}
}
if (row < gridLength) { // down
other = xyTo1D(row + 1, col);
if (grid[other]) {
wqu.union(self, other);
wqu2.union(self, other);
}
}
if (col > 1) { // left
other = xyTo1D(row, col - 1);
if (grid[other]) {
wqu.union(self, other);
wqu2.union(self, other);
}
}
if (col < gridLength) { // right
other = xyTo1D(row, col + 1);
if (grid[other]) {
wqu.union(self, other);
wqu2.union(self, other);
}
}
}
// is site (row, col) open?
public boolean isOpen(int row, int col) {
validateIndecies(row, col);
return grid[xyTo1D(row, col)];
}
// is site (row, col) full?
public boolean isFull(int row, int col) {
validateIndecies(row, col);
return wqu2.connected(virtualTop, xyTo1D(row, col));
}
// does the system percolate?
public boolean percolates() {
return wqu.connected(virtualTop, virtualTop + 1);
}
// test client (optional)
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
Percolation percolation = new Percolation(0);
Percolation percolation = new Percolation(1);
percolation.open(0, 1);
percolation.open(1, 0);
*/
/*
Percolation percolation = new Percolation(2);
percolation.open(1, 1);
percolation.open(1, 2);
for (int i = 1; i <= 2; i++) {
for(int j = 1; j <= 2; j++) {
StdOut.println("" + percolation.isFull(i, j) + " " + percolation.isOpen(i, j));
}
}
StdOut.println("percolation is " + percolation.percolates());
*/
int n = StdIn.readInt();
Percolation percolation = new Percolation(n);
while (!StdIn.isEmpty()) {
int row = StdIn.readInt();
int col = StdIn.readInt();
percolation.open(row, col);
}
StdOut.println("percolation is " + percolation.percolates());
}
}PercolationStats.java
/******************************************************************************
* Compilation: javac-algs4 PercolationStats.java
* Execution: java-algs4 PercolationStats length trails
* Dependencies: Percolation.java
*
* This program takes the length of grid and trails.
*
******************************************************************************/
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdRandom;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdStats;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.StdOut;
public class PercolationStats {
private int gridLength;
private double[] trailsResult;
private double resultMean;
private double resultStddev;
private double resultconfidenceLo;
private double resultconfidenceHi;
// perform trials independent experiments on an n-by-n grid
public PercolationStats(int n, int trials) {
if (n <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("length must be positive");
}
if (trials <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("trials must be positive");
}
gridLength = n;
if (gridLength == 1) {
resultMean = 1;
resultStddev = Double.NaN;
resultconfidenceLo = Double.NaN;
resultconfidenceHi = Double.NaN;
}
else {
trailsResult = new double[trials];
for (int i = 0; i < trials; i++) {
trailsResult[i] = oneTrial(gridLength);
}
resultMean = StdStats.mean(trailsResult);
resultStddev = StdStats.stddev(trailsResult);
double diff = (1.96 * resultStddev) / Math.sqrt(trials);
resultconfidenceLo = resultMean - diff;
resultconfidenceHi = resultMean + diff;
}
}
private double oneTrial(int length) {
int openedCount = 0;
Percolation percolation = new Percolation(length);
while (!percolation.percolates()) {
int row = StdRandom.uniform(length) + 1;
int col = StdRandom.uniform(length) + 1;
if (!percolation.isOpen(row, col)) {
percolation.open(row, col);
openedCount++;
}
}
return (double) openedCount / (length * length);
}
// sample mean of percolation threshold
public double mean() {
return resultMean;
}
// sample standard deviation of percolation threshold
public double stddev() {
return resultStddev;
}
// low endpoint of 95% confidence interval
public double confidenceLo() {
return resultconfidenceLo;
}
// high endpoint of 95% confidence interval
public double confidenceHi() {
return resultconfidenceHi;
}
// test client
public static void main(String[] args) {
int length = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
int trials = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
PercolationStats percolations = new PercolationStats(length, trials);
StdOut.println("mean = " + percolations.mean());
StdOut.println("stddev = " + percolations.stddev());
StdOut.println("95% confidence interval = "
+ percolations.confidenceLo() + ", "
+ percolations.confidenceHi());
}
}-eof-

