【第二章】PyQt5 data和time模块
date and time
这部分将介绍PyQt5如何使用日期和时间模块。
QDate、QTime、DateTime
PyQt5具有QDate、QDateTime、QTime这几个类用于处理时间和日期问题。
QDate类用于解决日历日期的问题,它包含了指定、比较和修改日期的方法。
QTime类使用时钟时间,它提供了比较时间、确定时间和各种其他时间操纵的方法。
QDateTime是一个将QDate和QTime对象组合成一个对象的类。
Current date and time
PyQt5可以使用currentDate(), currentTime()和currentDateTime()几个方法用于指定当前的日期和时间。
from PyQt5.QtCore import QDate, QTime, QDateTime, Qt
now = QDate.currentDate()
print(now.toString(Qt.ISODate)) # 2019-09-05
print(now.toString(Qt.DefaultLocaleLongDate)) # 2019年9月5日
print(now.toString(Qt.DefaultLocaleShortDate)) # 2019/9/5
datetime = QDateTime.currentDateTime()
print(datetime.toString()) # 周四 9月 5 19:24:50 2019
time = QTime.currentTime()
print(time.toString(Qt.DefaultLocaleLongDate)) # 19:25:29
以上实例使用了多种形式打印了日期、日期时间和时间
now = QDate.currentDate()
这个currentDate()方法返回当前的日期。
print(now.toString(Qt.ISODate))
print(now.toString(Qt.DefaultLocaleLongDate))
获取当前的日期通过以上两种方法分别指定toString不同的Qt.ISODate和Qt.DefaultLocaleLongDate参数输出不同形式的日期。
datetime = QDateTime.currentDateTime()
currentDateTime()返回当前日期和时间。
time = QTime.currentTime()
最后,currentTime()方法返回当前的时间
UTC time
由于地球自转,世界各地分布成多个时区(一共有24个时区),在每一个时区 都有一个不同的当地时间,这种时区的差异有时需要考虑进来。
一个全球时间有助于避免混淆时区和夏令时,因此UTC(Universal Coordinated time 全球统一时间)被当成主要的时间标准。UTC被用于航空、天气预报、飞行计划、空中交通管制许可和地图。与当地时间不同,UTC不会随着季节的变化而有所变化。
from PyQt5.QtCore import QDateTime, Qt
now = QDateTime.currentDateTime()
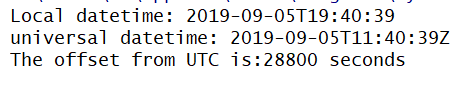
print('Local datetime:', now.toString(Qt.ISODate))
print('universal datetime:', now.toUTC().toString(Qt.ISODate))
print('The offset from UTC is:{} seconds'.format(now.offsetFromUtc()))这个例子获取当前的统一日期时间和本地日期时间。
currentDateTime()方法返回当地当前的日期和时间,我们可以使用toLocalTime()来把世界时转换为当地时间。
同样也可以使用toUTC()方法把当地时间转换为世界时。
offsetFromDateUtc()可以获取当地时间与世界时的差值。
Number of days
通过使用daysInMonth()可以获取某一个月份的天数。
通过使用daysInYear() 可以获取一年的天数。
from PyQt5.QtCore import QDate
d = QDate.currentDate()
print(d.toString())
print('Days in months:{}'.format(d.daysInMonth()))
print('Days in year: {}'.format(d.daysInYear()))这个例子可以获取当前月份及年份的天数,输出如下:
Difference in Days
daysTo()方法用来获取两个日期之间相隔的天数。
from PyQt5.QtCore import QDate
xmas1 = QDate(2019, 1, 1)
xmas2 = QDate(2021, 3, 1)
now = QDate.currentDate()
dayspassed = xmas1.daysTo(now)
print('{} days have passed since last year'.format(dayspassed))
nofdays = now.daysTo(xmas2)
print('There are {} days until graduate'.format(nofdays))本例分别获取了两个日期之间相隔的天数。输出如下。
DateTime arithmetic(时间运算)
以下实例用于处理时间的基本运算,比如增加一天,减少一天。
from PyQt5.QtCore import QDateTime, Qt
now = QDateTime.currentDateTime()
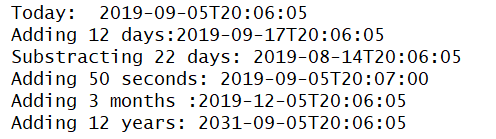
print('Today: ', now.toString(Qt.ISODate))
print('Adding 12 days:{}'.format(now.addDays(12).toString(Qt.ISODate)))
print('Substracting 22 days: {}'.format(now.addDays(-22).toString(Qt.ISODate)))
print('Adding 50 seconds: {}'.format(now.addSecs(55).toString(Qt.ISODate)))
print('Adding 3 months :{}'.format(now.addMonths(3).toString(Qt.ISODate)))
print('Adding 12 years: {}'.format(now.addYears(12).toString(Qt.ISODate)))输出为:
Daylight saving time(夏令时)
通过使用isDayLightTime()检查是否某一日期是否为夏令时。
from PyQt5.QtCore import QDateTime, Qt, QTimeZone
now = QDateTime.currentDateTime()
print('Time Zone:{}'.format(now.timeZoneAbbreviation()))
if now.isDaylightTime():
print("The current date falls into DST time")
else:
print('The current date does not falls into DST time')以上实例判断当前日期是否为夏令时。
输出为:
timeZoneAbbreviation() 返回时区的缩写
isDaylightTime()返回datetime是否为夏令时。
Unix epoch
Unix时代是从00:00:00 UTC on 1 January 1970 (or 1970- 01-01T00:00:00Z ISO 8601)开始的,计算机中的日期和时间根据自该计算机或平台的定义时期以来经过的秒数或时钟周期数确定。
Unix time 是从Unix epoch开始到当前时刻位置的间隔的秒数。
Unix date命令可以在linux下使用。
from PyQt5.QtCore import QDateTime, Qt
now = QDateTime.currentDateTime()
unix_time = now.toSecsSinceEpoch()
print(unix_time)
d = QDateTime.fromSecsSinceEpoch(unix_time)
print(d.toString(Qt.ISODate))这个实例打印输出Unix time并把它转换为QDateTime
now = QDateTime.currentDateTime()
首先,获取当前的日期和时间。
unix_time = now.toSecsSinceEpoch()
然后使用toSecsSinceEpoch方法 返回Unix time
d = QDateTime.fromSecsSinceEpoch(unix_time)
同样,可以使用fromSecsSinceEpoch方法把Unix time 转换为 DateTime