优达学城无人驾驶工程师——P4车道线检测功能
这次讲的是优达学城的无人驾驶工程师的P4项目,利用车前方的摄像头检测车道线,下面开始我们的代码部分。
import numpy as np
import cv2
import glob
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pickle
import matplotlib.image as mpimg
from moviepy.editor import VideoFileClip
from IPython.display import HTML
%matplotlib inline我们先import一些我们需要的包
第二步是计算摄像机标定矩阵和给定一组棋盘图像的畸变系数。
# prepare object points, like (0,0,0), (1,0,0), (2,0,0) ....,(6,5,0)
objp = np.zeros((6*9,3), np.float32)#构建一个72行,3列的零矩阵
objp[:,:2] = np.mgrid[0:9, 0:6].T.reshape(-1,2)#把数组变成网格的顺序
# Arrays to store object points and image points from all the images.
objpoints = [] # 3d points in real world space
imgpoints = [] # 2d points in image plane.
# Make a list of calibration images
images = glob.glob('camera_cal/calibration*.jpg')# Step through the list and search for chessboard corners
for idx, fname in enumerate(images):
img = cv2.imread(fname)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# Find the chessboard corners
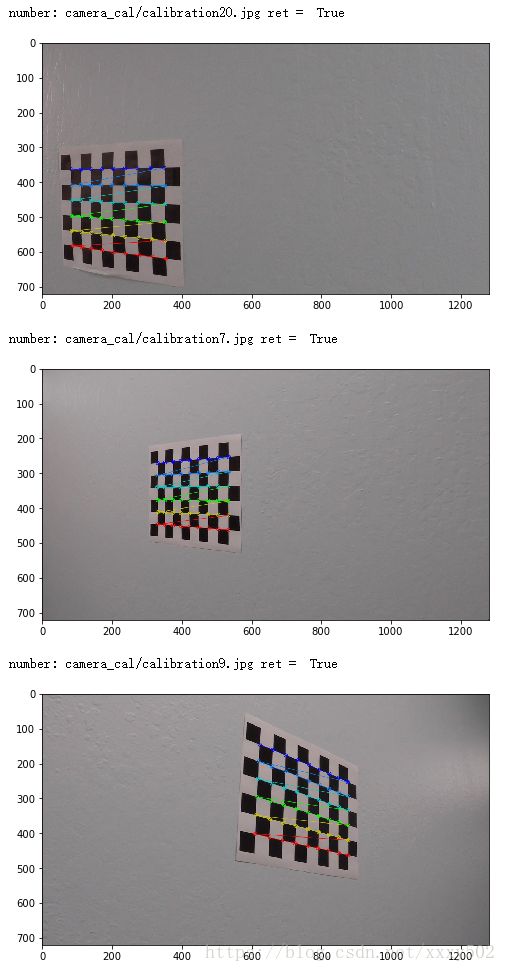
ret, corners = cv2.findChessboardCorners(gray, (9,6), None)
print('number:',fname,'ret = ',ret)
# If found, add object points, image points
if ret == True:
objpoints.append(objp)
imgpoints.append(corners)
# Draw and display the corners
cv2.drawChessboardCorners(img, (9,6), corners, ret)
#write_name = 'corners_found'+str(idx)+'.jpg'
plt.figure(figsize = (8,8))
plt.imshow(img)
plt.show()
#cv2.imwrite(write_name, img)
#cv2.imshow('img', img)
#cv2.waitKey(500)
#cv2.destroyAllWindows()输出效果如下:
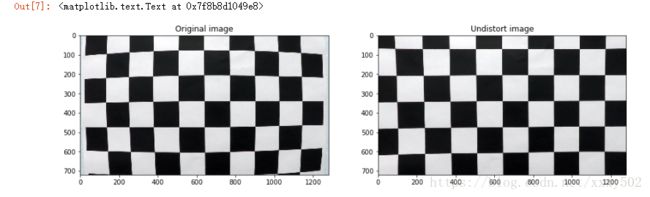
第二步:对原始图像应用失真校正,这里是因为我们的摄像头拍出来的视频会有一定的畸变,所以我们要调整
img = cv2.imread('camera_cal/calibration1.jpg')
print(img.shape)
img_size = (img.shape[1],img.shape[0])
print(img_size)
# Do camera calibration given object points and image points
ret, mtx, dist, rvecs, tvecs = cv2.calibrateCamera(objpoints, imgpoints, img_size,None,None)#标定
#这个函数会返回标定结果、相机的内参数矩阵、畸变系数、旋转矩阵和平移向量。
# Save the camera calibration result for later use (we won't worry about rvecs / tvecs)
dist_pickle = {}
dist_pickle["mtx"] = mtx
dist_pickle["dist"] = dist
pickle.dump( dist_pickle, open( "camera_cal/wide_dist_pickle.p", "wb" ) )def undistort(img):
cal_pickle = pickle.load(open("camera_cal/wide_dist_pickle.p", "rb"))
mtx = cal_pickle['mtx']
dist = cal_pickle['dist']
undist = cv2.undistort(img,mtx,dist,None,mtx)
return undistimage_test = 'camera_cal/calibration1.jpg'
img_test = cv2.imread(image_test)
img_undistort = undistort(img_test)
plt.figure(figsize = (15,15))
plt.subplot(121)
plt.imshow(img_test)
plt.title('Original image')
plt.subplot(122)
plt.imshow(img_undistort)
plt.title('Undistort image')效果图如下:
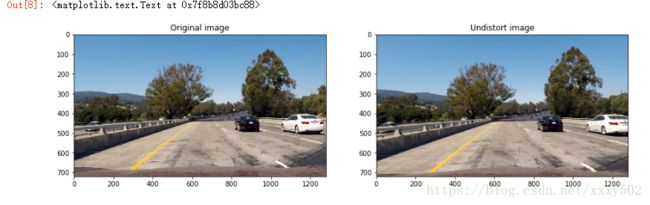
下面是真实情况下测试,可以看出差异。
image_test = 'test_images/test1.jpg'
img_test = plt.imread(image_test)
img_undistort = undistort(img_test)
plt.figure(figsize = (15,15))
plt.subplot(121)
plt.imshow(img_test)
plt.title('Original image')
plt.subplot(122)
plt.imshow(img_undistort)
plt.title('Undistort image')第三步:使用颜色变换、渐变等创建阈值二值图像
#define functions
def grayscale(img):
return cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
def gaussian_blur(img,kernel_size):
return cv2.GaussianBlur(img,(kernel_size,kernel_size),0)
def abs_sobel_thresh(img,orient = 'x',sobel_kernel = 3,thresh = (0,255)):
gray = grayscale(img)
if orient == 'x':
abs_sobel = np.absolute(cv2.Sobel(gray,cv2.CV_64F,1,0,ksize = sobel_kernel))
if orient == 'y':
abs_sobel = np.absolute(cv2.Sobel(gray,cv2.CV_64F,0,1,ksize = sobel_kernel))
scaled_sobel = np.uint8(255 * abs_sobel / np.max(abs_sobel))
binary_output = np.zeros_like(scaled_sobel)
binary_output[(scaled_sobel >= thresh[0]) & (scaled_sobel <= thresh[1])] = 1
return binary_output
def mag_thresh(img, sobel_kernel=3, thresh=(0, 255)):
# Apply the following steps to img
# 1) Convert to grayscale
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
# 2) Take the gradient in x and y separatel
sobel_x = cv2.Sobel(gray,cv2.CV_64F,1,0,ksize = sobel_kernel)
#print(sobel_x)
sobel_y = cv2.Sobel(gray,cv2.CV_64F,0,1,ksize = sobel_kernel)
# 3) Calculate the magnitude
magnitude = np.sqrt(sobel_x ** 2 + sobel_y ** 2)
# 4) Scale to 8-bit (0 - 255) and convert to type = np.uint8
scale_factor = np.max(magnitude) / 255
#print('scale_factor = ',scale_factor)
magnitude = (magnitude / scale_factor).astype(np.uint8)
# 5) Create a binary mask where mag thresholds are met
binary_output = np.zeros_like(magnitude)
# 6) Return this mask as your binary_output image
binary_output[(magnitude >= thresh[0]) & (magnitude <= thresh[1])] = 1
return binary_output
def dir_threshold(img, sobel_kernel=3, thresh=(0, np.pi/2)):
# Grayscale
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
# Calculate the x and y gradients
sobelx = cv2.Sobel(gray, cv2.CV_64F, 1, 0, ksize=sobel_kernel)
sobely = cv2.Sobel(gray, cv2.CV_64F, 0, 1, ksize=sobel_kernel)
# Take the absolute value of the gradient direction,
# apply a threshold, and create a binary image result
absgraddir = np.arctan2(np.absolute(sobely), np.absolute(sobelx))
#print(absgraddir)
binary_output = np.zeros_like(absgraddir)
binary_output[(absgraddir >= thresh[0]) & (absgraddir <= thresh[1])] = 1
# Return the binary image
return binary_output
def hls_select(img, thresh=(0, 255)):
# 1) Convert to HLS color space
hls = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_RGB2HLS)
# 2) Apply a threshold to the S channel
s_channel = hls[:,:,2]
# 3) Return a binary image of threshold result
binary_output = np.zeros_like(s_channel)
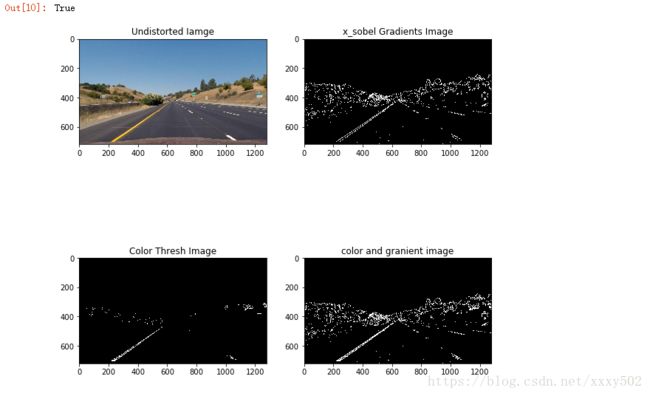
binary_output[(s_channel > thresh[0]) & (s_channel image_test = 'test_images/straight_lines1.jpg'
#img_test = cv2.imread(image_test)
img_test = plt.imread(image_test)
plt.figure(figsize = (10,10))
undist = undistort(img_test)
plt.subplot(221)
plt.imshow(undist)
plt.title('Undistorted Iamge')
cv2.imwrite('./output_images/undist.jpg',undist)
x_sobel = abs_sobel_thresh(undist,thresh = (22,100))
plt.subplot(222)
plt.imshow(x_sobel,cmap = 'gray')
plt.title('x_sobel Gradients Image')
cv2.imwrite('./output_images/x_sobel.jpg',x_sobel)
color_transforms = hls_select(undist,thresh=(150,255))
plt.subplot(223)
plt.imshow(color_transforms,cmap = 'gray')
plt.title('Color Thresh Image')
cv2.imwrite('./output_images/color_transforms.png',color_transforms)
color_x_sobel = np.zeros_like(x_sobel)
color_x_sobel[ (color_transforms == 1) | (x_sobel) == 1 ] = 1
plt.subplot(224)
plt.imshow(color_x_sobel,cmap = 'gray')
plt.title('color and granient image')
cv2.imwrite('./output_images/color_x_sobel.png',color_x_sobel)效果图如下:
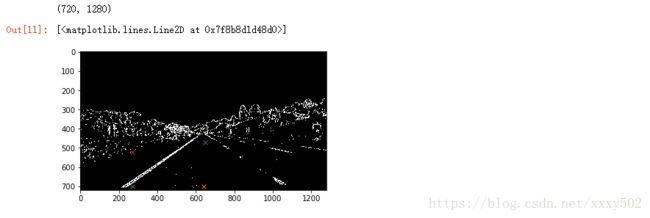
第四步:应用透视变换来修正二值图像。(其实是把图像转换成鸟瞰图)
#找点
plt.imshow(color_x_sobel,cmap = 'gray')
print(color_x_sobel.shape)
# plt.plot(800,510,'x')
# plt.plot(1150,700,'x')
# plt.plot(270,700,'x')
# plt.plot(510,510,'x')
plt.plot(650,470,'x')
plt.plot(640,700,'x')
plt.plot(270,700,'x')
plt.plot(270,520,'x')def warp(img):
img_size = (img.shape[1],img.shape[0])
src = np.float32( [ [800,510],[1150,700],[270,700],[510,510]] )
dst = np.float32( [ [650,470],[640,700],[270,700],[270,540]] )
M = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(src,dst)
#返回透视变换的映射矩阵,就是这里的M
#对于投影变换,我们则需要知道四个点,
#通过cv2.getPerspectiveTransform求得变换矩阵.之后使用cv2.warpPerspective获得矫正后的图片。
Minv = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(dst,src)
warped = cv2.warpPerspective(img,M,img_size,flags = cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
#主要作用:对图像进行透视变换,就是变形
#https://blog.csdn.net/qq_18343569/article/details/47953843
unpersp = cv2.warpPerspective(warped, Minv, img_size, flags=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
return warped, unpersp, Minvwarped_img,unpersp, Minv = warp(color_x_sobel)
plt.imshow(warped_img,cmap = 'gray')
plt.show()
plt.imshow(unpersp,cmap = 'gray')
plt.show()效果如下:
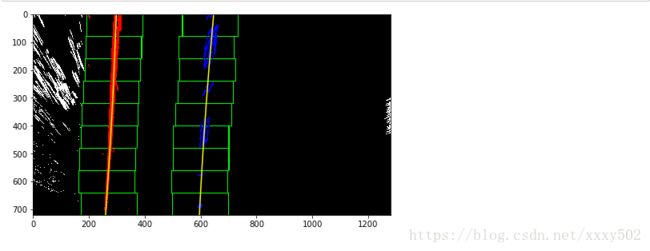
第五步: 检测车道像素,并适合找到车道边界。def find_lines(img,print = True):
#假设您已经创建了一个被扭曲的二进制图像,称为“binary_warped”
#取图像下半部分的直方图
histogram= np.sum(img[img.shape[0] //2:,:],axis = 0)
#创建一个输出图像来绘制和可视化结果
out_img = np.dstack((img,img,img))*255
# plt.imshow(out_img)
# plt.show()
#找出直方图的左半边和右半边的峰值
#这些将是左行和右行的起点
midpoint = np.int(histogram.shape[0] // 4)
leftx_base = np.argmax(histogram[:midpoint])
#np.argmax 是返回最大值所在的位置
rightx_base = np.argmax(histogram[midpoint:]) + midpoint
#这里是要返回右边HOG值最大所在的位置,所以要加上midpoint
#选择滑动窗口的数量
nwindows = 9
#设置窗口的高度
window_height = np.int(img.shape[0] // nwindows)
#确定所有的x和y位置非零像素在图像,这里就是吧img图像中非0元素(就是不是黑的地方就找出来,一行是x,一行是y)
nonzero = img.nonzero()
#返回numpy数组中非零的元素
#对于二维数组b2,nonzero(b2)所得到的是一个长度为2的元组。http://www.cnblogs.com/1zhk/articles/4782812.html
nonzeroy = np.array(nonzero[0])
nonzerox = np.array(nonzero[1])
#为每个窗口当前位置更新
leftx_current = leftx_base
rightx_current = rightx_base
#设置窗口的宽度+ / -
margin = 100
#设置最小数量的像素发现重定位窗口
minpix = 50
#创建空的列表接收左和右车道像素指数
left_lane_inds = []
right_lane_inds = []
#遍历窗口
for window in range(nwindows):
#识别窗口边界在x和y(左、右)
win_y_low = img.shape[0] - (window + 1) * window_height #就是把图像切成9分,一分一分的算HOG
#print('win_y_low',win_y_low)
win_y_high = img.shape[0] - window * window_height
win_xleft_low = leftx_current - margin
#print('win_xleft_low',win_xleft_low)
win_xleft_high = leftx_current + margin
#print('win_xleft_high = ',win_xleft_high)
win_xright_low = rightx_current - margin
#print('win_xright_low = ',win_xright_low)
win_xright_high = rightx_current + margin
#print('win_xright_high = ',win_xright_high)
#把网格画在可视化图像上
cv2.rectangle(out_img,(win_xleft_low,win_y_low),(win_xleft_high,win_y_high),(0,255,0),2)#通过确定对角线 画矩形
cv2.rectangle(out_img,(win_xright_low,win_y_low),(win_xright_high,win_y_high),(0,255,0),2)
# plt.imshow(out_img)
# plt.show()
# print('left !!!! ',win_xleft_low,win_y_low,win_xleft_high,win_y_high)
# print('right !!!!! ',win_xright_low,win_y_low,win_xright_high,win_y_high)
#识别非零像素窗口内的x和y
good_left_inds = ( (nonzeroy >= win_y_low) & (nonzeroy < win_y_high)
& (nonzerox >= win_xleft_low) & (nonzerox < win_xleft_high)).nonzero()[0]
good_right_inds = ( (nonzeroy >= win_y_low) & (nonzeroy < win_y_high)
& (nonzerox >= win_xright_low) & (nonzerox < win_xright_high)).nonzero()[0]
#添加这些指标列表
left_lane_inds.append(good_left_inds)
right_lane_inds.append(good_right_inds)
#如果上面大于minpix,重新定位下一个窗口的平均位置
if len(good_left_inds) > minpix:
leftx_current = np.int(np.mean(nonzerox[good_left_inds]))
if len(good_right_inds) > minpix:
rightx_current = np.int(np.mean(nonzerox[good_right_inds]))
#连接索引的数组
left_lane_inds = np.concatenate(left_lane_inds)
#把list改成numpy格式而已
right_lane_inds = np.concatenate(right_lane_inds)
#提取左和右线像素位置
leftx = nonzerox[left_lane_inds]
lefty = nonzeroy[left_lane_inds]
rightx = nonzerox[right_lane_inds]
righty = nonzeroy[right_lane_inds]
#最小二乘多项式拟合。(不懂)
left_fit = np.polyfit(lefty, leftx, 2)
right_fit = np.polyfit(righty, rightx, 2)
#画图
ploty = np.linspace(0,img.shape[0] -1,img.shape[0]) #用此来创建等差数列
left_fitx = left_fit[0] * ploty ** 2 + left_fit[1] * ploty +left_fit[2]
right_fitx = right_fit[0] * ploty ** 2 +right_fit[1] * ploty + right_fit[2]
#这步的意思是把曲线拟合出来,
out_img[nonzeroy[left_lane_inds], nonzerox[left_lane_inds]] = [255, 0, 0]
out_img[nonzeroy[right_lane_inds], nonzerox[right_lane_inds]] = [0, 0, 255]
if print == True:
plt.figure(figsize=(8,8))
plt.imshow(out_img)
plt.plot(left_fitx, ploty, color='yellow')
plt.plot(right_fitx, ploty, color='yellow')
plt.show()
return out_img,left_fit,right_fitfind_line_imgae,left_fit,right_fit = find_lines(warped_img)效果如下:
第六步:确定车道和车辆位置对中心的曲率
def curvature(left_fit,right_fit,binary_warped,print_data = True):
ploty = np.linspace(0,binary_warped.shape[0] -1 , binary_warped.shape[0])
y_eval = np.max(ploty)
#y_eval就是曲率,这里是选择最大的曲率
ym_per_pix = 30/720#在y维度上 米/像素
xm_per_pix = 3.7/700#在x维度上 米/像素
#确定左右车道
leftx = left_fit[0]*ploty**2 + left_fit[1]*ploty + left_fit[2]
rightx = right_fit[0]*ploty**2 + right_fit[1]*ploty + right_fit[2]
#定义新的系数在米
left_fit_cr = np.polyfit(ploty*ym_per_pix, leftx*xm_per_pix, 2)
right_fit_cr = np.polyfit(ploty*ym_per_pix, rightx*xm_per_pix, 2)
#最小二乘法拟合
#计算新的曲率半径
left_curverad = ((1 + (2*left_fit_cr[0]*y_eval*ym_per_pix + left_fit_cr[1])**2)**1.5) / np.absolute(2*left_fit_cr[0])
right_curverad = ((1 + (2*right_fit_cr[0]*y_eval*ym_per_pix + right_fit_cr[1])**2)**1.5) / np.absolute(2*right_fit_cr[0])
#计算中心点,线的中点是左右线底部的中间
left_lane_bottom = (left_fit[0]*y_eval)**2 + left_fit[0]*y_eval + left_fit[2]
right_lane_bottom = (right_fit[0]*y_eval)**2 + right_fit[0]*y_eval + right_fit[2]
lane_center = (left_lane_bottom + right_lane_bottom)/2.
center_image = 640
center = (lane_center - center_image)*xm_per_pix#转换成米
if print_data == True:
#现在的曲率半径已经转化为米了
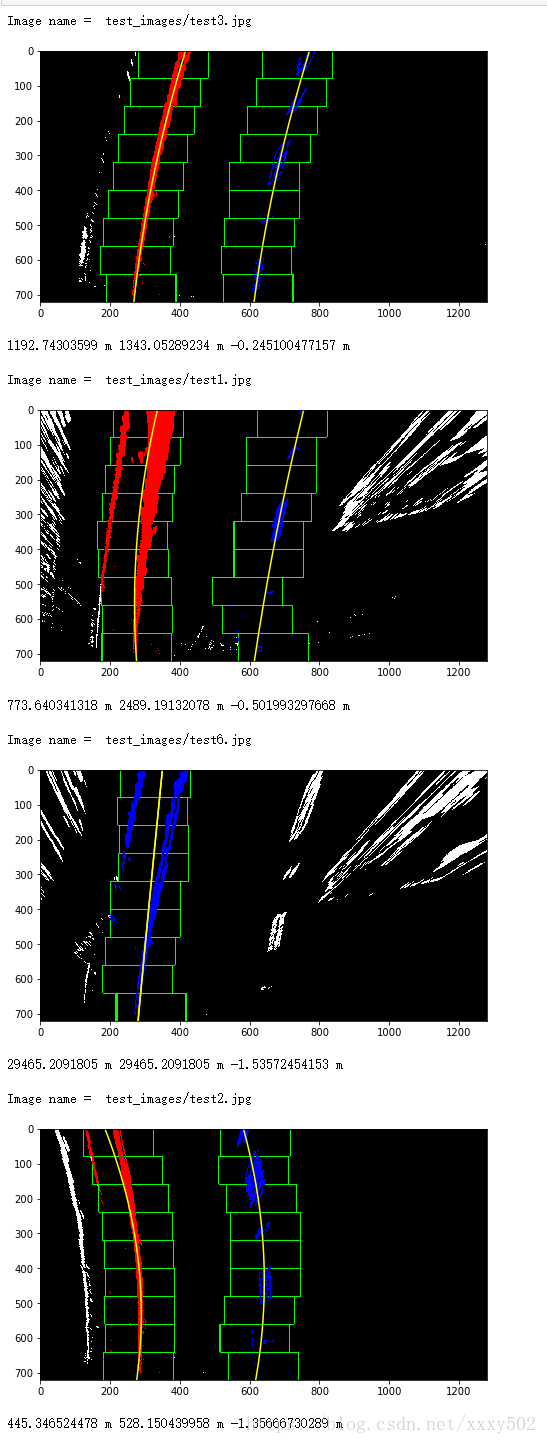
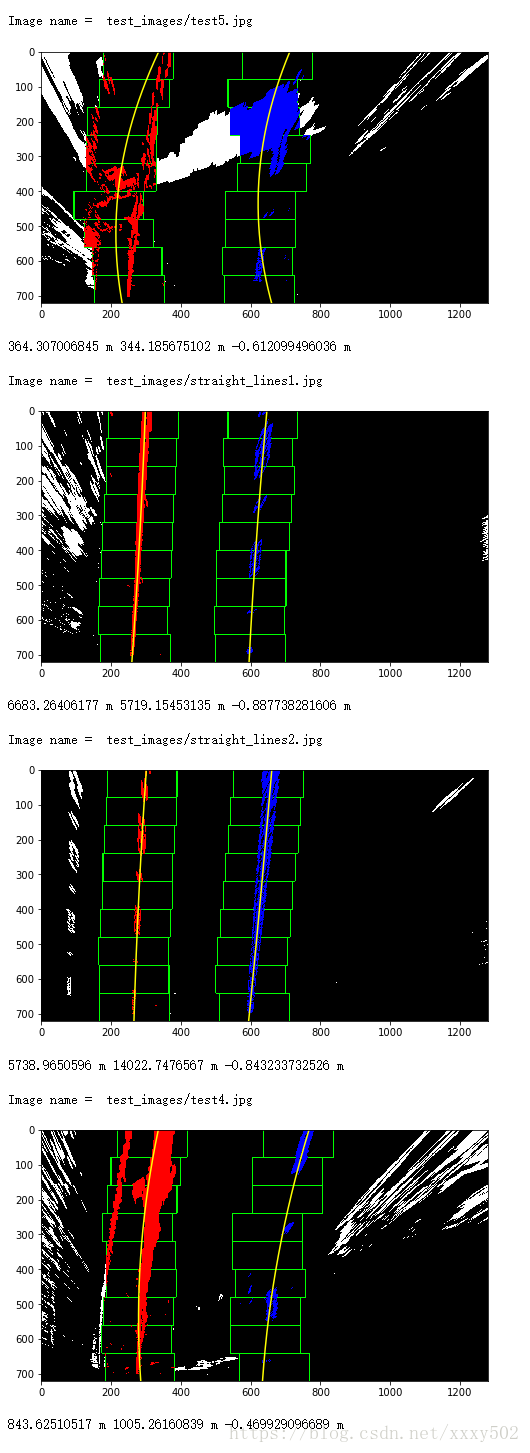
print(left_curverad, 'm', right_curverad, 'm', center, 'm')
return left_curverad, right_curverad, centerimport glob
import os
new_path = os.path.join("test_images/","*.jpg")
for infile in glob.glob(new_path):
#读图
img = plt.imread(infile)
#畸变
undist = undistort(img)
#sobel算子
x_sobel = abs_sobel_thresh(undist,thresh = (22,100))
#hls颜色阈值
color_transforms = hls_select(undist,thresh=(90,255))
#sobel加hls
color_x_sobel = np.zeros_like(x_sobel)
color_x_sobel[ (color_transforms == 1) | (x_sobel) == 1 ] = 1
#弯曲图像(warped)
print()
print('Image name = ',infile)
warped_img,unpersp, Minv = warp(color_x_sobel)
#画线
find_line_imgae,left_fit,right_fit = find_lines(warped_img)
#算曲率
curvature(left_fit,right_fit,find_line_imgae)第七步:将检测到的巷道边界扭曲回原始图像
def show_info(img,left_cur,right_cur,center):
#在图片中显示出曲率
cur = (left_cur + right_cur) / 2
font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX
# 使用默认字体
cv2.putText(img,'Curvature = %d(m)' % cur,(50,50),font,1,(255,255,255),2)
#照片/添加的文字/左上角坐标/字体/字体大小/颜色/字体粗细
#添加文字
if center < 0:
fangxiang = 'left'
else:
fangxiang = 'right'
cv2.putText(img,'the angle is %.2fm of %s'%(np.abs(center),fangxiang),(50,100),font,1,(255,255,255),2)def draw_lines(undist,warped,left_fit,right_fit,left_cur,right_cur,center,show_img = True):
#创建一个全黑的底层图去划线
warp_zero = np.zeros_like(warped).astype(np.uint8)
color_warp = np.dstack((warp_zero,warp_zero,warp_zero))
ploty = np.linspace(0,warped.shape[0]-1,warped.shape[0])
#添加新的多项式在X轴Y轴
left_fitx = left_fit[0] * ploty**2 + left_fit[1]*ploty + left_fit[2]
right_fitx = right_fit[0] * ploty**2 + right_fit[1]*ploty + right_fit[2]
#把X和Y变成可用的形式
pts_left = np.array([np.transpose(np.vstack([left_fitx, ploty]))])
#np.transpose 转置
pts_right = np.array([np.flipud(np.transpose(np.vstack([right_fitx, ploty])))])
#向上/向下翻转阵列。
pts = np.hstack((pts_left, pts_right))
#填充图像
cv2.fillPoly(color_warp, np.int_([pts]), (255,0, 0))
#透视变换
newwarp = cv2.warpPerspective(color_warp, Minv, (color_warp.shape[1], color_warp.shape[0]))
#叠加图层
result = cv2.addWeighted(undist, 1, newwarp, 0.5, 0)
show_info(result, left_cur, right_cur, center)
if show_img == True:
plt.figure(figsize = (10,10))
plt.imshow(result)
plt.show()
return resultimport glob
import os
new_path = os.path.join("test_images/","*.jpg")
for infile in glob.glob(new_path):
print('the image is ',infile)
#读图
img = plt.imread(infile)
#畸变
undist = undistort(img)
#sobel算子
x_sobel = abs_sobel_thresh(undist,thresh = (22,100))
#mag_thresh
mag_binary = mag_thresh(undist,thresh =(30,90))
#dir_threshold
dir_binary = dir_threshold(undist, sobel_kernel=15, thresh=(0.7, 1.3))
#hls颜色阈值
color_transforms = hls_select(undist,thresh=(150,255))
#sobel加hls
color_x_sobel = np.zeros_like(x_sobel)
color_x_sobel[ (x_sobel == 1) | (color_transforms == 1) ] = 1
#弯曲图像
warped_img, unpersp, Minv = warp(color_x_sobel)
#画线
find_line_imgae,left_fit,right_fit = find_lines(warped_img,print = False)
#算曲率
left_curverad, right_curverad, center = curvature(left_fit,right_fit,find_line_imgae,print_data = False)
#画图
result = draw_lines(undist,warped_img,left_fit,right_fit,left_curverad,right_curverad,center)第八步:输出车道边界的可视化显示和车道曲率和车辆位置的数值估计
def check(left_fit, right_fit):
#Performs a sanity check on the lanes
#1. Check if left and right fit returned a value
if len(left_fit) ==0 or len(right_fit) == 0:
status = False
else:
#Check distance b/w lines
ploty = np.linspace(0, 20, num=10 )
left_fitx = left_fit[0]*ploty**2 + left_fit[1]*ploty + left_fit[2]
right_fitx = right_fit[0]*ploty**2 + right_fit[1]*ploty + right_fit[2]
delta_lines = np.mean(right_fitx - left_fitx)
if delta_lines >= 150 and delta_lines <=430: #apprrox delta in pixels
status = True
else:
status = False
# # Calculate slope of left and right lanes at midpoint of y (i.e. 360)
# L_0 = 2*left_fit[0]*360+left_fit[1]
# R_0 = 2*right_fit[0]*360+right_fit[1]
# delta_slope_mid = np.abs(L_0-R_0)
# # Calculate slope of left and right lanes at top of y (i.e. 720)
# L_1 = 2*left_fit[0]*720+left_fit[1]
# R_1 = 2*right_fit[0]*720+right_fit[1]
# delta_slope_top = np.abs(L_1-R_1)
# #Check if lines are parallel at the middle
# if delta_slope_mid<=0.1:
# status = True
# else:
# status = False
return statusdef process_video(img):
global last_left
global last_right
global left_fit
global right_fit
#畸变
undist = undistort(img)
#sobel算子
x_sobel = abs_sobel_thresh(undist,thresh = (22,100))
#hls颜色阈值
color_transforms = hls_select(undist,thresh=(150,255))
#sobel加hls
color_x_sobel = np.zeros_like(x_sobel)
color_x_sobel[ (x_sobel == 1) | (color_transforms == 1) ] = 1
#弯曲图像
warped_img, unpersp, Minv = warp(color_x_sobel)
#画线
find_line_imgae,left_fit,right_fit = find_lines(warped_img,print = False)
#check
status = check(left_fit,right_fit)
if status == True:
last_left , last_right = left_fit,right_fit
else:
left_fit,right_fit = last_left,last_right
#算曲率
left_curverad, right_curverad, center = curvature(left_fit,right_fit,find_line_imgae,print_data = False)
#画图
result = draw_lines(undist,warped_img,left_fit,right_fit,left_curverad,right_curverad,center,show_img=False)
return result#Create video file pipeline
output = 'test_video.mp4'
clip1 = VideoFileClip("project_video.mp4")
#clip1 = VideoFileClip("project_video.mp4").subclip(20,28)
out_clip = clip1.fl_image(process_video) #NOTE: this function expects color images!!
%time out_clip.write_videofile(output, audio=False)HTML("""
""".format(output))上述所有的图片和视频都可在https://github.com/udacity/CarND-Advanced-Lane-Lines下载。