java学习之集合容器
集合
集合:用来收集一组数据的数据结构
数组的缺点:长度固定,操作数据繁琐,效率低。
集合关系图:

List
List:数据有序可重复
LinkedList
底层是双向链表,两端数据操作数据快
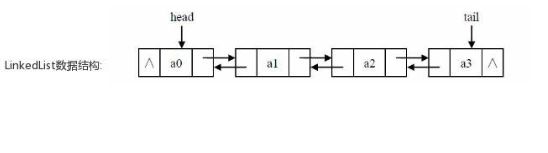
常见方法:
add(数据)
get(i)
size()
remove(i)
remove(数据)
iterator()
用来辅助创建迭代器对象
新建的迭代器,用来遍历当前集合
addFirst() 添加数据在头部
addLast() 添加数据在尾部
getFirst()
getLast()
removeFirst()
removeLast()
方法案例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
* <> 泛型
* 限制集合中,存放的数据类型
* 泛型不支持基本类型,要是包装类型
*/
LinkedList<String> list =
new LinkedList<>();
list.add("aaa");
list.add("ddd");
list.add("ooo");
list.add("bbb");
list.add("qqq");
list.add("aaa");
list.add("aaa");
System.out.println(list.size());
System.out.println(list);
//下标1位置插入 "###"
list.add(1, "###");
System.out.println(list);
//删除下标1位置
list.remove(1);
System.out.println(list);
//取值
System.out.println(list.get(0));
System.out.println(list.get(list.size()-1));
//遍历
for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++) {
System.out.println(list.get(i));
}
}
ArrayList
底层是可增长数组,查询速度快
底层数组默认初始长度为10,放满后会自动增加1.5倍的容量
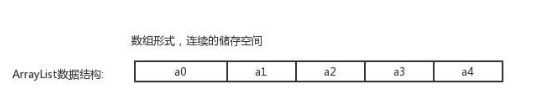
创建对象:
new ArrayList(); //内部数组初始容量 10
new ArrayList(100); //内部数组初始容量是指定的值
ArrayList和LinkedList区别:
方法:与LinkedList相同,但是没有操作两端操作数据的方法
如果仅在两端操作数据,选择linkedList
数据量小时,频繁增删数据使用LinkedList
Set
HashSet
特点:
元素唯一不可重复
底层是哈希表结构(也就是HashMap)
元素的存与取的顺序不能保证一致
保证元素的唯一:
重写hashcode方法和equals方法
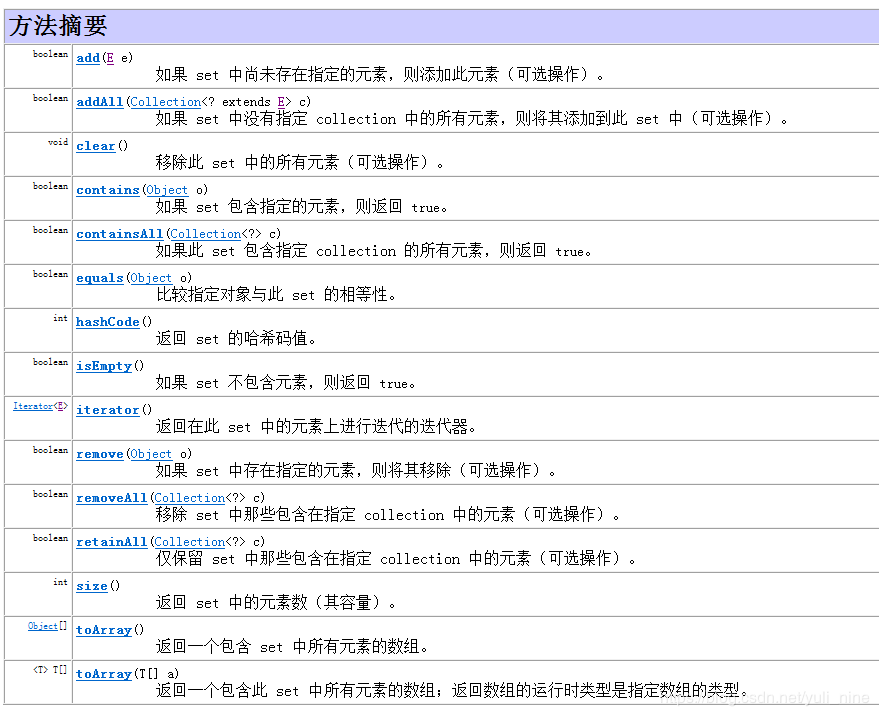
HashSet和LinkedHashSet常用方法:
LinkedHashSet
元素唯一不能重复
底层结构是 哈希表结构 + 链表结构
元素的存与取的顺序一致
Map
HashMap
作用:快速定位、查找数据
键:
不可重复,无序
方法:
put(k, v)
get(k)
size()
remove(k)
hashcode()
Object的方法,Object中默认实现是使用内存地址作为哈希值
如果对象作为键,放入hashmap应该重写hashcode方法,使用属性数据,来计算哈希值
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<Integer, String> map =
new HashMap<>();
map.put(9527, "张三");
map.put(9528, "李四");
map.put(9529, "王五");
map.put(9530, "刘六");
map.put(9531, "小强");
System.out.println(map.size());
System.out.println(map);
System.out.println(map.get(9527));
System.out.println(map.get(9999));
System.out.println(map.remove(9530));
System.out.println(map);
}
哈希算法:
key.Hashcode()计算出一个哈希值,在用哈希算法算出一个下标index,然后将key,value封装成一个Entry对象放到index位置,有空余位置就直接放入,如果index位置有值,则通过equals方法进行比较是否相等,如果相同就进行覆盖value值,不相等就链到后边空余位置。当链表长度达到8就会自动进化成红黑树,减少到6个则会充新变成哈希链表。
哈希算法实现:
public class Point {
private int x;
private int y;
public Point() {
super();
}
public Point(int x, int y) {
super();
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public int getX() {
return x;
}
public void setX(int x) {
this.x = x;
}
public int getY() {
return y;
}
public void setY(int y) {
this.y = y;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "("+x+", "+y+")";
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
/*
* 用属性数据,来计算哈希值
*
* *) 属性相同,要计算出相同的哈希值
* *) 属性不同,要尽量计算出不同哈希值
*
* 有一种算法,是数学家发明的
* 是一种有效的,惯用算法
*/
int p = 31;
int r = 1;
r = r*p + x;
r = r*p + y;
return r;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if(obj == null) return false;
if(obj == this) return true;
if(! (obj instanceof Point)) return false;
Point p = (Point) obj;
return x == p.x && y == p.y;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Point a = new Point(1, 2);
Point b = new Point(1, 2);
//1.哈希值必须相同,才能保证计算出相同下标
System.out.println(a.hashCode());
System.out.println(b.hashCode());
//2.即使哈希值相同,equal()也必须相等
//才能覆盖,否则链表连在一起
System.out.println(a.equals(b));
HashMap<Point, String> map =
new HashMap<>();
map.put(a, "2亿");
map.put(b, "1.9亿");
System.out.println(map);
}
}
其他
集合倒序实现方法:
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Entry<Integer,User>>() {
public int compare(Entry<Integer, User> o1, Entry<Integer, User> o2) {
//按照要求根据 User 的 age 的倒序进行排
return o2.getValue().getAge()-o1.getValue().getAge();
} });