二分搜索树 前中后序(递归和非递归)和层序遍历(动图)
文章目录
- 二分搜索树前序\中序\后序遍历理解
- 二分搜索树前序\中序\后序遍历节点访问顺序图解
- 先序遍历
- 先序遍历动图
- 中序遍历
- 中序遍历动图
- 后序遍历
- 后序遍历动图
- 代码实现
- 递归实现
- 前序遍历/深度优先遍历
- 中序遍历
- 后序遍历
- 非递归实现
- 前序遍历/深度优先遍历
- 中序遍历
- 后序遍历
- 广度优先遍历(层序遍历)
- 广度优先遍历(层序遍历)动图
- 广度优先遍历(层序遍历)代码实现
二分搜索树前序\中序\后序遍历理解
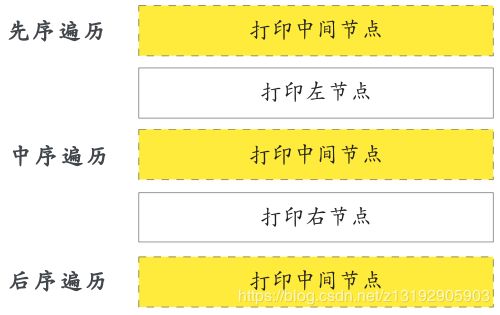
- 先序遍历 -> 先打印中间节点,再依次打印左节点和右节点
- 中序遍历 -> 先打印左节点,再打印中间节点,最后打印右节点
- 后序遍历 -> 先依次打印左节点和右节点,再打印中间节点
二分搜索树前序\中序\后序遍历节点访问顺序图解

上图是一棵示例的二分搜索树,满足左节点<中间节点<右节点
跟随图中的箭头,依次访问
22->13->12->12->12->13->18->18->18->13->22->25->23->23->23->25->26->26->29->29->26->25->22
每个节点都被访问三次
先序遍历
按第一次访问顺序打印,如图,由根节点22出发.依次打印
22->13->12->18->25->23->26->29
先序遍历动图
中序遍历
按第二次访问顺序打印,如图,由根节点出发(此时是第一次访问根节点,不打印),依次打印
12->13->18->22->23->25->26->29
中序遍历动图
后序遍历
按第三次访问顺序打印.如图,由根节点出发(此时是第一次访问根节点,不打印),依次打印
12->18->13->23->29->26->25->22
后序遍历动图
代码实现
-
创建一个类,命名为BinarySearchTree
-
由于在添加\查找操作中都需要对节点进行比较,所以需要实现继承比较类Comparable
-
并且实例代码支持泛型
public class BinarySearchTree<E extends Comparable<E>> {
private class Node {
public E e;
public Node left, right;
public Node(E e) {
this.e = e;
left = null;
right = null;
}
}
private Node root;
}
递归实现
前序遍历/深度优先遍历
// 二分搜索树的前序遍历(暴露给用户调用)
public void preOrder() {
preOrder(root);
}
// 前序遍历以node为根的二分搜索树, 递归算法
private void preOrder(Node node) {
if (node == null)
return;
System.out.println(node.e);
preOrder(node.left);
preOrder(node.right);
}
中序遍历
// 二分搜索树的中序遍历(暴露给用户调用)
public void inOrder() {
inOrder(root);
}
// 中序遍历以node为根的二分搜索树, 递归算法
private void inOrder(Node node) {
if (node == null)
return;
inOrder(node.left);
System.out.println(node.e);
inOrder(node.right);
}
后序遍历
// 二分搜索树的后序遍历(暴露给用户调用)
public void postOrder() {
postOrder(root);
}
// 后序遍历以node为根的二分搜索树, 递归算法
private void postOrder(Node node) {
if (node == null)
return;
postOrder(node.left);
postOrder(node.right);
System.out.println(node.e);
}
非递归实现
本次实现并没有使用教科书上的实现方式,改为模拟系统栈的形式实现
在类中加入内部类
private class Command{
String s; // go, print
Node node;
Command(String s, Node node){
this.s = s;
this.node = node;
}
};
前序遍历/深度优先遍历
// 二分搜索树的非递归前序遍历,其中print表示输出,go表示递归
public void preOrderNR() {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
Stack<Command> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(new Command("go", root));
while (!stack.empty()) {
Command command = stack.pop();
if ("print".equals(command.s)) {
System.out.println(command.node.e);
} else {
if (command.node.right != null) {
stack.push(new Command("go", command.node.right));
}
if (command.node.left != null) {
stack.push(new Command("go", command.node.left));
}
stack.push(new Command("print", command.node));
}
}
}
中序遍历
// 二分搜索树的非递归中序遍历,其中print表示输出,go表示递归
public void inOrderNR() {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
Stack<Command> stack = new Stack<Command>();
stack.push(new Command("go", root));
while (!stack.empty()) {
Command command = stack.pop();
if ("print".equals(command.s)) {
System.out.println(command.node.e);
} else {
if (command.node.right != null)
stack.push(new Command("go", command.node.right));
stack.push(new Command("print", command.node));
if (command.node.left != null)
stack.push(new Command("go", command.node.left));
}
}
}
后序遍历
// 二分搜索树的非递归后序遍历,其中print表示输出,go表示递归
public void postOrderNR() {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
Stack<Command> stack = new Stack<Command>();
stack.push(new Command("go", root));
while (!stack.empty()) {
Command command = stack.pop();
if ("print".equals(command.s)) {
System.out.println(command.node.e);
} else {
assert "go".equals(command.s);
stack.push(new Command("print", command.node));
if (command.node.right != null) {
stack.push(new Command("go", command.node.right));
}
if (command.node.left != null) {
stack.push(new Command("go", command.node.left));
}
}
}
}
广度优先遍历(层序遍历)
层序遍历,顾名思义就是按树的深度,从根节点开始,一层一层向底部遍历,如图⇓,输出结果是
22->13->25->12->18->23->26->29
广度优先遍历(层序遍历)动图
广度优先遍历(层序遍历)代码实现
// 二分搜索树的层序遍历
public void levelOrder() {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(root);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
Node cur = q.remove();
System.out.println(cur.e);
if (cur.left != null) {
q.add(cur.left);
}
if (cur.right != null) {
q.add(cur.right);
}
}
}