TensorFlow2-自编码器
TensorFlow2自编码器
简介
深度学习中也有很多无监督学习的算法,其中,自编码器是最为典型的代表。事实上,人工标注的数据毕竟是少数,互联网每天都在产生海量的无标签数据,如何利用这些数据就是无监督学习研究的重点。自编码器被广泛应用于特征提取(数据降维),其降维后的数据,样本之间保留了较多的相关信息。
自编码器
对自编码器这种结构,进行无监督学习的方法就是将输入作为输出,尽可能通过先降维后升维的运算后,保持输入的不变性,从而,降维后的数据包含更多原始的信息。所以,自编码器的端到端过程其实是一个数据重建过程。

关于自编码器的训练,对于不同的数据(二分输入或真值输入)采用不同的损失函数(MSE或CE)。相比于PCA这类矩阵运算方法,自编码器由于非线性特性,丢失信息较少;而且PCA降维后的数据,可解释性变得很低,而AE降维后的数据解释性强且具有聚类效果。
下图左侧为PCA降维后各类数据的二维显示,右侧为自编码器的效果。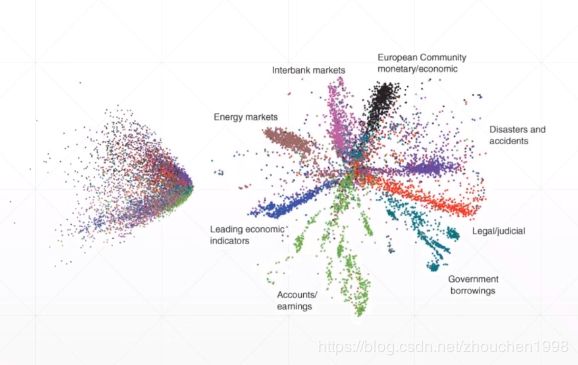
自编码器变种
Denoising AutoEncoders(降噪自编码器),训练时将原始数据加入随机噪声(如高斯噪声),这样,自编码器模型可以较好地从噪声图片中还原真实图片。
Adversarial AutoEncoders(对抗自编码器),训练同时设定一个鉴别器(discriminator),用于坚定中间隐层的输出是否符合标准的指定分布(这是采用GAN(对抗生成网络)的思路)。
Variational AutoEncoders(变分自编码器),用于生成与训练数据类似分布的数据,尽管曾今有过瞩目的表现,但是随着GAN的发展,收到了极大的冲击。
自编码器实战
通过普通的神经元神经网络,利用低维隐层捕获特征,实现如下模型。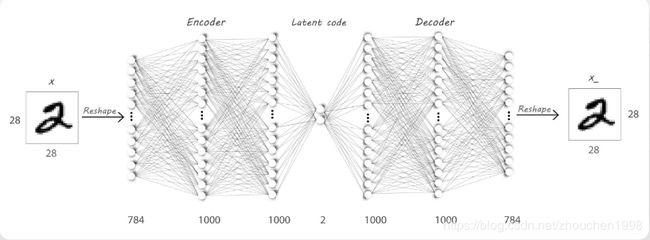
"""
Author: Zhou Chen
Date: 2019/11/17
Desc: About
"""
import os
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
from tensorflow import keras
from tensorflow.keras import Sequential, layers
from PIL import Image
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2'
def save_images(imgs, name):
"""
多图整合保存
:param imgs:
:param name:
:return:
"""
new_im = Image.new('L', (280, 280))
index = 0
for i in range(0, 280, 28):
for j in range(0, 280, 28):
im = imgs[index]
im = Image.fromarray(im, mode='L')
new_im.paste(im, (i, j))
index += 1
new_im.save(name)
h_dim = 20
batchsz = 512
lr = 1e-3
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = keras.datasets.fashion_mnist.load_data()
x_train, x_test = x_train.astype(np.float32) / 255., x_test.astype(np.float32) / 255.
train_db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(x_train)
train_db = train_db.shuffle(batchsz * 5).batch(batchsz)
test_db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(x_test)
test_db = test_db.batch(batchsz)
print(x_train.shape, y_train.shape)
print(x_test.shape, y_test.shape)
class AE(keras.Model):
def __init__(self):
super(AE, self).__init__()
# Encoders
self.encoder = Sequential([
layers.Dense(256, activation=tf.nn.relu),
layers.Dense(128, activation=tf.nn.relu),
layers.Dense(h_dim)
])
# Decoders
self.decoder = Sequential([
layers.Dense(128, activation=tf.nn.relu),
layers.Dense(256, activation=tf.nn.relu),
layers.Dense(784)
])
def call(self, inputs, training=None):
# [b, 784] => [b, 10]
h = self.encoder(inputs)
# [b, 10] => [b, 784]
x_hat = self.decoder(h)
return x_hat
model = AE()
model.build(input_shape=(None, 784))
model.summary()
optimizer = tf.optimizers.Adam(lr=lr)
for epoch in range(100):
for step, x in enumerate(train_db):
# [b, 28, 28] => [b, 784]
x = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 784])
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
x_rec_logits = model(x)
rec_loss = tf.losses.binary_crossentropy(x, x_rec_logits, from_logits=True)
rec_loss = tf.reduce_mean(rec_loss)
grads = tape.gradient(rec_loss, model.trainable_variables)
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, model.trainable_variables))
if step % 100 == 0:
print('epoch', epoch, 'step', step, float(rec_loss))
# evaluation
x = next(iter(test_db))
logits = model(tf.reshape(x, [-1, 784]))
x_hat = tf.sigmoid(logits)
# [b, 784] => [b, 28, 28]
x_hat = tf.reshape(x_hat, [-1, 28, 28])
# [b, 28, 28] => [2b, 28, 28]
x_concat = tf.concat([x, x_hat], axis=0)
x_concat = x_hat
x_concat = x_concat.numpy() * 255.
x_concat = x_concat.astype(np.uint8)
save_images(x_concat, 'images/rec_epoch_%d.png' % epoch)
"""
Author: Zhou Chen
Date: 2019/11/17
Desc: About
"""
import os
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
from tensorflow import keras
from tensorflow.keras import Sequential, layers
from PIL import Image
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2'
def save_images(imgs, name):
new_im = Image.new('L', (280, 280))
index = 0
for i in range(0, 280, 28):
for j in range(0, 280, 28):
im = imgs[index]
im = Image.fromarray(im, mode='L')
new_im.paste(im, (i, j))
index += 1
new_im.save(name)
h_dim = 20
batchsz = 512
lr = 1e-3
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = keras.datasets.fashion_mnist.load_data()
x_train, x_test = x_train.astype(np.float32) / 255., x_test.astype(np.float32) / 255.
# we do not need label
train_db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(x_train)
train_db = train_db.shuffle(batchsz * 5).batch(batchsz)
test_db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(x_test)
test_db = test_db.batch(batchsz)
print(x_train.shape, y_train.shape)
print(x_test.shape, y_test.shape)
z_dim = 10
class VAE(keras.Model):
def __init__(self):
super(VAE, self).__init__()
# Encoder
self.fc1 = layers.Dense(128)
self.fc2 = layers.Dense(z_dim) # 均值
self.fc3 = layers.Dense(z_dim) # 方差
# Decoder
self.fc4 = layers.Dense(128)
self.fc5 = layers.Dense(784)
def encoder(self, x):
h = tf.nn.relu(self.fc1(x))
mu = self.fc2(h)
log_var = self.fc3(h) # 取log方差
return mu, log_var
def decoder(self, z):
out = tf.nn.relu(self.fc4(z))
out = self.fc5(out)
return out
def reparameterize(self, mu, log_var):
epsilon = tf.random.normal(log_var.shape)
std = tf.exp(log_var) ** 0.5
z = mu + std * epsilon
return z
def call(self, inputs, training=None):
# [b, 784] => mu:[b, z_dim], log_var[b, z_dim]
mu, log_var = self.encoder(inputs)
# reparameterization技巧
z = self.reparameterize(mu, log_var)
x_hat = self.decoder(z)
return x_hat, mu, log_var
model = VAE()
model.build(input_shape=(3, 784))
optimizer = tf.optimizers.Adam(lr)
for epoch in range(1000):
for step, x in enumerate(train_db):
x = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 784])
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
x_rec_logits, mu, log_var = model(x)
rec_loss = tf.nn.sigmoid_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=x, logits=x_rec_logits)
rec_loss = tf.reduce_sum(rec_loss) / x.shape[0]
kl_div = -0.5 * (log_var + 1 - mu ** 2 - tf.exp(log_var))
kl_div = tf.reduce_sum(kl_div) / x.shape[0]
loss = rec_loss + 1. * kl_div
grads = tape.gradient(loss, model.trainable_variables)
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(grads, model.trainable_variables))
if step % 100 == 0:
print(epoch, step, 'kl div:', float(kl_div), 'rec loss:', float(rec_loss))
# evaluation
z = tf.random.normal((batchsz, z_dim))
logits = model.decoder(z)
x_hat = tf.sigmoid(logits)
x_hat = tf.reshape(x_hat, [-1, 28, 28]).numpy() * 255.
x_hat = x_hat.astype(np.uint8)
save_images(x_hat, 'images/sampled_epoch%d.png' % epoch)
x = next(iter(test_db))
x = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 784])
x_hat_logits, _, _ = model(x)
x_hat = tf.sigmoid(x_hat_logits)
x_hat = tf.reshape(x_hat, [-1, 28, 28]).numpy() * 255.
x_hat = x_hat.astype(np.uint8)
save_images(x_hat, 'images/rec_epoch%d.png' % epoch)
补充说明
- 本文介绍了Auto-Encoder在TensorFlow2中的实现,更详细的可以查看官方文档。
- 具体的代码同步至我的Github仓库欢迎star;博客同步至我的个人博客网站,欢迎查看其他文章。
- 如有疏漏,欢迎指正。
