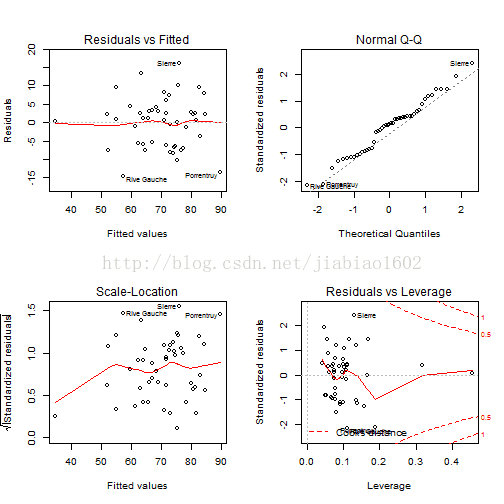R语言:多元线性回归和模型检验
利用swiss数据集进行多元线性回归研究
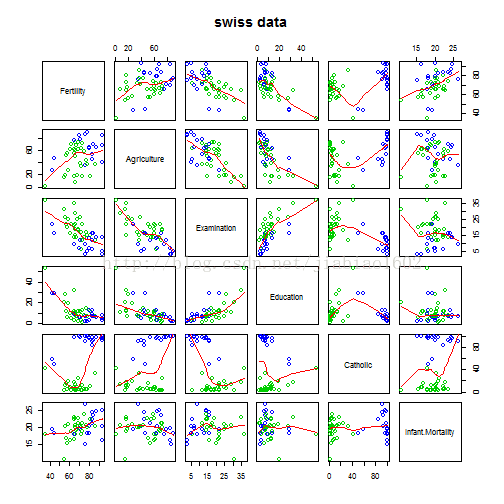
# 先查看各变量间的散点图
pairs(swiss, panel = panel.smooth, main = "swiss data",
col = 3 + (swiss$Catholic > 50))
# 利用全部变量建立多元线性回归
a=lm(Fertility ~ . , data = swiss)
summary(a)
##
## Call:
## lm(formula = Fertility ~ ., data = swiss)
##
## Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -15.274 -5.262 0.503 4.120 15.321
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
## (Intercept) 66.9152 10.7060 6.25 1.9e-07 ***
## Agriculture -0.1721 0.0703 -2.45 0.0187 *
## Examination -0.2580 0.2539 -1.02 0.3155
## Education -0.8709 0.1830 -4.76 2.4e-05 ***
## Catholic 0.1041 0.0353 2.95 0.0052 **
## Infant.Mortality 1.0770 0.3817 2.82 0.0073 **
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## Residual standard error: 7.17 on 41 degrees of freedom
## Multiple R-squared: 0.707, Adjusted R-squared: 0.671
## F-statistic: 19.8 on 5 and 41 DF, p-value: 5.59e-10
# 从结果看,Education变量的p值一颗星就都没有,说明对模型极不显著。
# R中提供了add1 drop1函数来针对线性模型进行变量的增减处理
drop1(a)
## Single term deletions
##
## Model:
## Fertility ~ Agriculture + Examination + Education + Catholic +
## Infant.Mortality
## Df Sum of Sq RSS AIC
## 2105 191
## Agriculture 1 308 2413 195
## Examination 1 53 2158 190
## Education 1 1163 3268 209
## Catholic 1 448 2553 198
## Infant.Mortality 1 409 2514 197
# 从结果看,去掉Education这个变量后,AIC最小,所以下一步可以剔除该变量进行建模。
b=update(a,.~.-Education)
summary(b)
##
## Call:
## lm(formula = Fertility ~ Agriculture + Examination + Catholic +
## Infant.Mortality, data = swiss)
##
## Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -23.919 -3.553 -0.649 6.596 14.177
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
## (Intercept) 59.6027 13.0425 4.57 4.2e-05 ***
## Agriculture -0.0476 0.0803 -0.59 0.55669
## Examination -0.9680 0.2528 -3.83 0.00042 ***
## Catholic 0.0261 0.0384 0.68 0.50055
## Infant.Mortality 1.3960 0.4626 3.02 0.00431 **
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## Residual standard error: 8.82 on 42 degrees of freedom
## Multiple R-squared: 0.545, Adjusted R-squared: 0.501
## F-statistic: 12.6 on 4 and 42 DF, p-value: 8.27e-07
#从接下来的结果看,有两个变量不显著,R平方也仅有0.53,模型效果极不理想。需要进一步进行研究。
# 幸好R有step函数,可以对模型进行变量自动筛选,根据AIC最小原则进行
b=step(a,direction="backward")
## Start: AIC=190.7
## Fertility ~ Agriculture + Examination + Education + Catholic +
## Infant.Mortality
##
## Df Sum of Sq RSS AIC
## - Examination 1 53 2158 190
## 2105 191
## - Agriculture 1 308 2413 195
## - Infant.Mortality 1 409 2514 197
## - Catholic 1 448 2553 198
## - Education 1 1163 3268 209
##
## Step: AIC=189.9
## Fertility ~ Agriculture + Education + Catholic + Infant.Mortality
##
## Df Sum of Sq RSS AIC
## 2158 190
## - Agriculture 1 264 2422 193
## - Infant.Mortality 1 410 2568 196
## - Catholic 1 957 3115 205
## - Education 1 2250 4408 221
summary(b)
##
## Call:
## lm(formula = Fertility ~ Agriculture + Education + Catholic +
## Infant.Mortality, data = swiss)
##
## Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -14.676 -6.052 0.751 3.166 16.142
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
## (Intercept) 62.1013 9.6049 6.47 8.5e-08 ***
## Agriculture -0.1546 0.0682 -2.27 0.0286 *
## Education -0.9803 0.1481 -6.62 5.1e-08 ***
## Catholic 0.1247 0.0289 4.31 9.5e-05 ***
## Infant.Mortality 1.0784 0.3819 2.82 0.0072 **
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## Residual standard error: 7.17 on 42 degrees of freedom
## Multiple R-squared: 0.699, Adjusted R-squared: 0.671
## F-statistic: 24.4 on 4 and 42 DF, p-value: 1.72e-10
接下来,对建模的变量和模型进行回归诊断的研究
首先,对自变量进行正态性检验
shapiro.test(swiss$Agriculture)
##
## Shapiro-Wilk normality test
##
## data: swiss$Agriculture
## W = 0.9664, p-value = 0.193
shapiro.test(swiss$Examination)
##
## Shapiro-Wilk normality test
##
## data: swiss$Examination
## W = 0.9696, p-value = 0.2563
shapiro.test(swiss$Education)
##
## Shapiro-Wilk normality test
##
## data: swiss$Education
## W = 0.7482, p-value = 1.312e-07
shapiro.test(swiss$Catholic)
##
## Shapiro-Wilk normality test
##
## data: swiss$Catholic
## W = 0.7463, p-value = 1.205e-07
shapiro.test(swiss$Infant.Mortality)
##
## Shapiro-Wilk normality test
##
## data: swiss$Infant.Mortality
## W = 0.9776, p-value = 0.4978
对各变量的正态性检验结果来看,变量Education和Catholic的p值小于0.05,故这两个变量数据不符合正态性分布。
现在,对模型的残差也进行正态性检验(回归模型的残差也要符合正态分布)
b.res<-residuals(b)
shapiro.test(b.res)
##
## Shapiro-Wilk normality test
##
## data: b.res
## W = 0.9766, p-value = 0.459
从结果来看,p值是0.459,模型残差符合正态分布
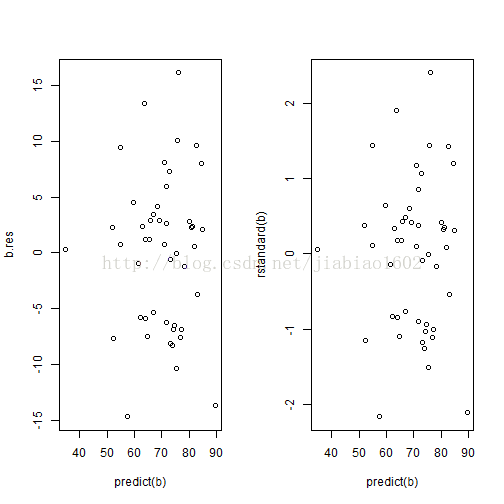
接下来,画出回归值与残差的残差图(应该符合均匀分布,即残差不管回归值如何,都具有相同分布)
par(mfrow=c(1,2))
# 画出残差图
plot(b.res~predict(b))
# 画出标准残差图
plot(rstandard(b)~predict(b))
par(mfrow=c(1,1))
从残差图来看,效果不太明显.
其实,可以直接画出残差图
par(mfrow=c(2,2))
plot(b)
# 先查看各变量间的散点图
pairs(swiss, panel = panel.smooth, main = "swiss data",
col = 3 + (swiss$Catholic > 50))

# 利用全部变量建立多元线性回归
a=lm(Fertility ~ . , data = swiss)
summary(a)
##
## Call:
## lm(formula = Fertility ~ ., data = swiss)
##
## Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -15.274 -5.262 0.503 4.120 15.321
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
## (Intercept) 66.9152 10.7060 6.25 1.9e-07 ***
## Agriculture -0.1721 0.0703 -2.45 0.0187 *
## Examination -0.2580 0.2539 -1.02 0.3155
## Education -0.8709 0.1830 -4.76 2.4e-05 ***
## Catholic 0.1041 0.0353 2.95 0.0052 **
## Infant.Mortality 1.0770 0.3817 2.82 0.0073 **
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## Residual standard error: 7.17 on 41 degrees of freedom
## Multiple R-squared: 0.707, Adjusted R-squared: 0.671
## F-statistic: 19.8 on 5 and 41 DF, p-value: 5.59e-10
# 从结果看,Education变量的p值一颗星就都没有,说明对模型极不显著。
# R中提供了add1 drop1函数来针对线性模型进行变量的增减处理
drop1(a)
## Single term deletions
##
## Model:
## Fertility ~ Agriculture + Examination + Education + Catholic +
## Infant.Mortality
## Df Sum of Sq RSS AIC
##
## Agriculture 1 308 2413 195
## Examination 1 53 2158 190
## Education 1 1163 3268 209
## Catholic 1 448 2553 198
## Infant.Mortality 1 409 2514 197
# 从结果看,去掉Education这个变量后,AIC最小,所以下一步可以剔除该变量进行建模。
b=update(a,.~.-Education)
summary(b)
##
## Call:
## lm(formula = Fertility ~ Agriculture + Examination + Catholic +
## Infant.Mortality, data = swiss)
##
## Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -23.919 -3.553 -0.649 6.596 14.177
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
## (Intercept) 59.6027 13.0425 4.57 4.2e-05 ***
## Agriculture -0.0476 0.0803 -0.59 0.55669
## Examination -0.9680 0.2528 -3.83 0.00042 ***
## Catholic 0.0261 0.0384 0.68 0.50055
## Infant.Mortality 1.3960 0.4626 3.02 0.00431 **
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## Residual standard error: 8.82 on 42 degrees of freedom
## Multiple R-squared: 0.545, Adjusted R-squared: 0.501
## F-statistic: 12.6 on 4 and 42 DF, p-value: 8.27e-07
#从接下来的结果看,有两个变量不显著,R平方也仅有0.53,模型效果极不理想。需要进一步进行研究。
# 幸好R有step函数,可以对模型进行变量自动筛选,根据AIC最小原则进行
b=step(a,direction="backward")
## Start: AIC=190.7
## Fertility ~ Agriculture + Examination + Education + Catholic +
## Infant.Mortality
##
## Df Sum of Sq RSS AIC
## - Examination 1 53 2158 190
##
## - Agriculture 1 308 2413 195
## - Infant.Mortality 1 409 2514 197
## - Catholic 1 448 2553 198
## - Education 1 1163 3268 209
##
## Step: AIC=189.9
## Fertility ~ Agriculture + Education + Catholic + Infant.Mortality
##
## Df Sum of Sq RSS AIC
##
## - Agriculture 1 264 2422 193
## - Infant.Mortality 1 410 2568 196
## - Catholic 1 957 3115 205
## - Education 1 2250 4408 221
summary(b)
##
## Call:
## lm(formula = Fertility ~ Agriculture + Education + Catholic +
## Infant.Mortality, data = swiss)
##
## Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -14.676 -6.052 0.751 3.166 16.142
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
## (Intercept) 62.1013 9.6049 6.47 8.5e-08 ***
## Agriculture -0.1546 0.0682 -2.27 0.0286 *
## Education -0.9803 0.1481 -6.62 5.1e-08 ***
## Catholic 0.1247 0.0289 4.31 9.5e-05 ***
## Infant.Mortality 1.0784 0.3819 2.82 0.0072 **
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## Residual standard error: 7.17 on 42 degrees of freedom
## Multiple R-squared: 0.699, Adjusted R-squared: 0.671
## F-statistic: 24.4 on 4 and 42 DF, p-value: 1.72e-10
接下来,对建模的变量和模型进行回归诊断的研究
首先,对自变量进行正态性检验
shapiro.test(swiss$Agriculture)
##
## Shapiro-Wilk normality test
##
## data: swiss$Agriculture
## W = 0.9664, p-value = 0.193
shapiro.test(swiss$Examination)
##
## Shapiro-Wilk normality test
##
## data: swiss$Examination
## W = 0.9696, p-value = 0.2563
shapiro.test(swiss$Education)
##
## Shapiro-Wilk normality test
##
## data: swiss$Education
## W = 0.7482, p-value = 1.312e-07
shapiro.test(swiss$Catholic)
##
## Shapiro-Wilk normality test
##
## data: swiss$Catholic
## W = 0.7463, p-value = 1.205e-07
shapiro.test(swiss$Infant.Mortality)
##
## Shapiro-Wilk normality test
##
## data: swiss$Infant.Mortality
## W = 0.9776, p-value = 0.4978
对各变量的正态性检验结果来看,变量Education和Catholic的p值小于0.05,故这两个变量数据不符合正态性分布。
现在,对模型的残差也进行正态性检验(回归模型的残差也要符合正态分布)
b.res<-residuals(b)
shapiro.test(b.res)
##
## Shapiro-Wilk normality test
##
## data: b.res
## W = 0.9766, p-value = 0.459
从结果来看,p值是0.459,模型残差符合正态分布
接下来,画出回归值与残差的残差图(应该符合均匀分布,即残差不管回归值如何,都具有相同分布)
par(mfrow=c(1,2))
# 画出残差图
plot(b.res~predict(b))
# 画出标准残差图
plot(rstandard(b)~predict(b))

par(mfrow=c(1,1))
从残差图来看,效果不太明显.
其实,可以直接画出残差图
par(mfrow=c(2,2))
plot(b)
par(mfrow=c(1,1))