POI导出Excel——模板类的封装
一 说明
前阵子做OA系统,遇到了将表格导出为Excel文件的需求。poi生成Excel的时候,一般是每个excel书写一个模板类,很是麻烦,此篇博客希望提供一种思路,用于快速创建excel模板类,并增加代码的复用性。很多地方可能做的不够好,有不妥的地方,请不吝赐教,大家一起进步!
二 目录结构
如下图所示,有四个包inter,test,utils,write;
其中,inter放接口,test测试文件,utils工具类,write放写好的excel的模板。
三 Constant——常量类
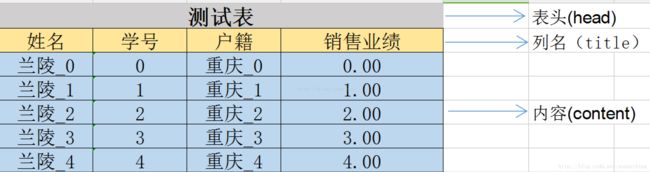
下图是本例导出的样图。要说明的是,将Excel分成了三个部分来构造,分别是head(表头),title(列名),content(内容);三个部分单独构造,互不影响。
Constant类预先定义好了一些基本的常量。如字体大小,对齐方式,字体样式单元格高度等。
poi中,很多方法中都需要传入了short类型的参数。所以,为了方便对传入的short值的控制,我在Constant中定义了一个short类型的常量SHORT_NULL,当传入这个常量的时候,不进行任何操作。
public class Constant {
//传入此变量,表示不进行操作
public static final short SHORT_NULL = -200;
public static final short alignment_cell = CellStyle.ALIGN_CENTER;
public static final short verticalAlignment_cell = CellStyle.VERTICAL_CENTER;
public static final short forgroundColor_cell = SHORT_NULL;
public static final short fontHeightInpoint_font_head = (short)12;
public static final short fontHeightInpoint_font_title = (short)11;
public static final short fontHeightInpoint_font_content = (short)11;
public static final short fillPattern = HSSFCellStyle.SOLID_FOREGROUND;
public static final short boldWeight_head = Font.BOLDWEIGHT_BOLD;
public static final short boldWeight_title = Font.BOLDWEIGHT_NORMAL;
public static final short boldWeight_content = Font.BOLDWEIGHT_NORMAL;
public static final byte charset = Font.DEFAULT_CHARSET;
public static final short fontColor_font = Font.COLOR_NORMAL;
public static final short border_style = CellStyle.BORDER_THIN;
public static final String fontName_head = "宋体";
public static final String fontName_title = "宋体";
public static final String fontName_content = "宋体";
public static final float rowHeight = 23;
......
}
四 ExcelUtils——工具类
我封装的方法不是很多,这里只贴出来一部分。
public class ExcelUtils {
public static void setCellStyleBorder(CellStyle style,short left,
short top,short right,short bottom){
if(left != Constant.SHORT_NULL){
style.setBorderLeft(left);
}
if(top != Constant.SHORT_NULL){
style.setBorderTop(left);
}
if(right != Constant.SHORT_NULL){
style.setBorderRight(right);
}
if(bottom != Constant.SHORT_NULL){
style.setBorderBottom(bottom);
}
}
/**
* 自动列宽
* @param size
* @param sheet
*/
public static void fitColumn(int size,Sheet sheet){
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
sheet.autoSizeColumn(i, true);
}
} ......
}
五 DefaultStyle——默认样式类
目的在于,在创建模板的时候,尽量让通用的样式可复用。
- 本类封装了一些常用的样式,比如。表头/内容/列名的字体,单元格的样式,行高等;
- 如果每个单元格都单独new一个font,很占内存;
- poi中对Font字体的个数的支持是有限制的;
- DefaultStyle中的content部分的字体样式中,常用的是货币,日期,百分比,普通文本样式;本类默认提供了这四种样式;
贴出部分代码:
public class DefaultStyle{
private HSSFWorkbook book;
//表头
private Font default_head_font;
private HSSFCellStyle default_head_style;
//标题
private Font default_title_font;
private HSSFCellStyle default_title_style;
//内容
private Font default_content_font;
private HSSFCellStyle default_content_style_text;
private HSSFCellStyle default_content_style_money;
private HSSFCellStyle default_content_style_date;
private HSSFCellStyle default_content_style_percent;
//行高
private float default_rowHeight = Constant.rowHeight;
//边框样式
private short default_border_style = Constant.border_style;
public DefaultStyle(HSSFWorkbook book) {
this.book = book;
}
public HSSFWorkbook getBook() {
return book;
}
public void setBook(HSSFWorkbook book) {
this.book = book;
}
public Font getDefault_head_font() {
if(this.default_head_font == null){
this.default_head_font = ExcelUtils.createFont(book,
Constant.fontName_head,Constant.SHORT_NULL,
Constant.fontHeightInpoint_font_head,
Constant.fontColor_font);
}
return default_head_font;
}
public void setDefault_head_font(Font default_head_font) {
this.default_head_font = default_head_font;
}
public HSSFCellStyle getDefault_head_style() {
if(this.default_head_style == null){
this.default_head_style = ExcelUtils.createCellStyle(
book,getDefault_head_font(),
Constant.alignment_cell,
Constant.verticalAlignment_cell,
Constant.SHORT_NULL,Constant.SHORT_NULL);
}
return default_head_style;
}
public void setDefault_head_style(HSSFCellStyle default_head_style) {
this.default_head_style = default_head_style;
}
public Font getDefault_title_font() {
if(this.default_title_font == null){
this.default_title_font = ExcelUtils.createFont(book,
Constant.fontName_title, Constant.SHORT_NULL,
Constant.fontHeightInpoint_font_title,
Constant.boldWeight_title,
Constant.fontColor_font);
}
return default_title_font;
}
public void setDefault_title_font(Font default_title_font) {
this.default_title_font = default_title_font;
}
public HSSFCellStyle getDefault_title_style() {
if(this.default_title_style == null){
this.default_title_style = ExcelUtils.createCellStyle(book,
Constant.verticalAlignment_cell,
Constant.SHORT_NULL,Constant.SHORT_NULL);
ExcelUtils.setCellStyleBorder(default_title_style,
Constant.border_style,
Constant.border_style,
Constant.border_style);
}
return default_title_style;
}
}
六 IWriteExcel ——接口类
正如之前所说,excel分为三个部分构建(head,title,content),IWriteExcel 自然需要包含这三个方法。但是大家发现多了一个方法(onInitRowProperties)。为啥呢?这是因为像行高、列宽呀这些行级别的属性都是通过Sheet来控制的,而行高,列宽,对于一张excel表来说,基本上一开始就确定好了 。所以,在导出excel之前先初始化了这些属性。
除了onInitRowProperties方法外的其他三个方法,它们的返回值都是int类型。因为接口的方法我在后边是按顺序执行的.执行顺序为:
onInitRowProperties–>onCreateHeadRow–>onCreateTitleRow–>onCreateContent
- 首先,对于一张excel工作表,从第0行开始调用onCreateHeadRow,表头占用多少行不用管,自己去实现即可。
- 接下来,你要告诉onCreateTitleRow方法,它可以从哪一行开始写入数据;
- 同理,onCreateContent也需要知道自己能够从哪一行开始写入数据;
- 所以,每执行完一个方法,返回下一个可以写入的行的index即可;
不同的模板类的实现可能不一样。假如我们实现了一个模板类A。如果另一个模板类B样式与A差不多,如果只有列名部分不一样,那我们可以直接继承自模版A,然后重写onCreateTitleRow()方法即可,这就省去了
重新构建excel其他部分的功夫。
public interface IWriteExcel {
/**
* 初始化行级别的属性(行高。列宽)
* @param sheet
* @param excelData
* @param defaultStyle
*/
public void onInitRowProperties(HSSFWorkbook book,HSSFSheet sheet,
WriteExcelData excelData,
DefaultStyle defaultStyle);
/**
* 创建列名行
* @param sheet
* @param excelData
* @param defaultStyle
* @param allColumnSize
* @param currentIndex
* @return
*/
public int onCreateTitleRow(HSSFWorkbook book,HSSFSheet sheet,
WriteExcelData excelData,DefaultStyle defaultStyle,
int allColumnSize,int currentIndex);
/**
* 创建表头行
* @param sheet
* @param excelData
* @param defaultStyle
* @param allColumnSize
* @param currentIndex
* @return
*/
public int onCreateHeadRow(HSSFWorkbook book,HSSFSheet sheet,
WriteExcelData excelData,DefaultStyle defaultStyle,
int allColumnSize,int currentIndex);
/**
* 创建表格内容部分
* @param sheet
* @param excelData
* @param defaultStyle
* @param allColumnSize
* @param currentIndex
* @return
*/
public int onCreateContent(HSSFWorkbook book,HSSFSheet sheet,
WriteExcelData excelData,DefaultStyle defaultStyle,
int allColumnSize,int currentIndex);
}
七 WriteExcelData——封装数据类
这是一个封装的数据资源类,我们就是从这里面取出数据,经过一些列操作后,写入到excel中去。
- sheetName,headName:工作表名、表头名;
- fieldsWidths:列宽数组,预先定义excel好每一列的宽度。
- titleNames:列名数组,每一列的列名。titleNames的数据顺序要与fieldsWidths的顺序一致(分别对应着每个列的列名和列宽)。
- maps:数据源,是一个Map集合,因为公司前端接收list数据;我懒得为导出excel单独写一个查询方法;所以,我直接用的之前的查询方法;但是这个改成list当然也可以。只是在后面的时候的时候取数据的方法不一样而已;
- tableFields:要输入的数据,也就是map中的key。这里的key应当要与titleNames和fieldsWidths保持对应关系;也许你会问?为什么要单独传入一个tableFields呢?其实我之前也没想传这个变量。因为后来我们的需求发生了变化:公司需要我们实现excel的个性化导出,具体要导出哪些列,让用户自己去选择;而且,不能简单地将map中的所有key对应的value导出,因为可能有些用户没有查看所有列的权限。所以,tableFields就起到了这样的作用。
简单来说就是,maps就是最终你要导出到excel的实际数据,用list来表示,一个Map表示一行数据。而titleNames、fieldsWidths则是用来表示哪一列应该显示什么数据(是什么标题),这一列的宽度应该是多少。而最终的显示结果是通过tableFields与titleNames来共同控制的。
比如,
titleNames[0]的值为”姓名”,说明第一列要显示的是姓名,
tableFields[0]的值为”name”,说明应该map中对应的key为”name”,
此时,
Map map = maps[0];
String showName = map .getValue(“name”);
所以,第一行中的第一列要显示的数据就是showName了;
下面给出数据类的定义:
public class WriteExcelData {
private String sheetName;//工作簿名
private String headName;//表头名
private int[] fieldsWidths;//列宽
private String[] titleNames;//列名
private String[] tableFileds;//要显输出maps中的哪些数据(哪些key-value)
public WriteExcelData() {
}
public WriteExcelData(String sheetName, String headName,
int[] fieldsWidths, String[] titleNames,
String[] tableFileds, List八 AbstractExcel ——导出Excel的模板抽象类
理论上所有的Excel模板类都应该继承自这个类。这个类的作用主要是进行一些初始化操作,并且引导正确的方法调用顺序。
成员变量包括了上述的DefaultStyle默认样式类和WriteExcelData数据类。还包含了IWriteExcel类,而IWriteExcel类需要AbstractExcel自己去创建。
导出excel的时候,我们只需要在构造方法中传入一个WriteExcelData,并且手动传入一个IWriteExcel实例即可,然手直接调用write()方法即可。
public abstract class AbstractExcel {
public DefaultStyle config;
private WriteExcelData datas;
private HSSFWorkbook book;
private HSSFSheet sheet;
protected int cellSize;//列的长度
private int dataSize;//内容部分的数据长度
private int currentIndex;//当前写入到的行
private IWriteExcel writeExcel;
public AbstractExcel(WriteExcelData datas) {
this.datas = datas;
if(datas.getTableFileds() != null){
this.cellSize = datas.getTableFileds().length;
}
if(datas.getMaps() != null){
this.dataSize = datas.getMaps().size();
}
}
private void init(){
book = new HSSFWorkbook();
String sheetName = datas.getSheetName();
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(sheetName)){
sheet = book.createSheet();
}else{
sheet = book.createSheet(sheetName);
}
config = new DefaultStyle(this.book);
}
public void destroy(){
sheet = null;
book = null;
if(datas!=null){
List maps = datas.getMaps();
if(maps != null){
maps.clear();
}
}
datas = null;
}
public abstract IWriteExcel createWriteExcel();
public void write(OutputStream os) throws IOException{
init();
writeExcel = createWriteExcel();
int rowLength = datas.getTitleNames().length;
writeExcel.onInitRowProperties(book,sheet, datas, config);
currentIndex = writeExcel.onCreateHeadRow(book,sheet, datas, config, rowLength, currentIndex);
currentIndex = writeExcel.onCreateTitleRow(book,sheet, datas, config, rowLength, currentIndex);
currentIndex = writeExcel.onCreateContent(book,sheet, datas, config, rowLength, currentIndex);
book.write(os);
}}
九 SimpleExcel ——最简单的AbstractExcel实现类
SimpleExcel 继承自AbstractExcel ,并且实现了IWriteExcel接口。此外,还定义了一个IcellValueTransformer接口——单元格内容转化器,可将单元格的值进行处理以后再输出,也可以重新设置单元格的样式;
public class SimpleExcel extends AbstractExcel implements IWriteExcel{
/**
* 单元格内容转化器,可以单元格的值进行处理,或者重新设置单元格的样式
* @author sonnyching
*
*/
public interface IcellValueTransformer{
/**
* 将单元格的内容转化
* @param defaultStyle 默认样式
* @param cell 要转化的单元格
* @param mapKey map中的key
* @param value 单元格中最初的数据
*/
public void transformCellValue(DefaultStyle defaultStyle,HSSFCell cell,String mapKey,T value);
}
private IcellValueTransformer transformer;
public SimpleExcel(WriteExcelData datas) {
super(datas);
}
@Override
public IWriteExcel createWriteExcel() {
return this;
}
@Override
public void onInitRowProperties(HSSFWorkbook book, HSSFSheet sheet,
WriteExcelData excelData, DefaultStyle defaultStyle) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
@Override
public int onCreateTitleRow(HSSFWorkbook book, HSSFSheet sheet,
WriteExcelData excelData, DefaultStyle defaultStyle,
int allColumnSize, int currentIndex) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return 0;
}
@Override
public int onCreateHeadRow(HSSFWorkbook book, HSSFSheet sheet,
WriteExcelData excelData, DefaultStyle defaultStyle,
int allColumnSize, int currentIndex) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return 0;
}
@Override
public int onCreateContent(HSSFWorkbook book, HSSFSheet sheet,
WriteExcelData excelData, DefaultStyle defaultStyle,
int allColumnSize, int currentIndex) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return 0;
}
public void setTransformer(IcellValueTransformer transformer) {
this.transformer = transformer;
}
}
1. onCreateRowProperties()的实现
新建一个私有方法来调用。若没有传入列宽数组,则自动调整列宽。
private void autoInitRowProperties(HSSFWorkbook book,HSSFSheet sheet,
WriteExcelData excelData,DefaultStyle defaultStyle){
int[] columnWidths = excelData.getFieldsWidths();
sheet.setDefaultRowHeightInPoints(defaultStyle.getDefault_rowHeight());//默认行高
try {
if(columnWidths == null){
ExcelUtils.fitColumn(super.cellSize, sheet);
}else{
for (int i = 0; i < super.cellSize; i++) {
sheet.setColumnWidth(i, columnWidths[i]*256);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
//throw new IllegalAccessException("列宽数组与列的数量不一致");
}
}
2. onCreateHeadRow()的实现
同样新建一个私有方法。也很简单。默认将表头部分在水平方向进行了合并,合并的列数正好是所有列
的个数。如果不需要表头,直接返回0就可以了。mergeCells(Sheet sheet,int startRow,int endRow,int starColumn,int endColumn)我自己封装的方法,传
入要合并的区域值即可。
private int autoCreateHeadRow(HSSFWorkbook book, HSSFSheet sheet,
WriteExcelData excelData, DefaultStyle defaultStyle,
int allColumnSize, int currentIndex){
String headName = excelData.getHeadName();
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(headName) ){
return currentIndex;
}
try {
HSSFRow headRow = sheet.createRow(currentIndex);
//合并
HSSFCell cell = headRow.createCell(0);
cell.setCellStyle(super.config.getDefault_head_style());
cell.setCellValue(headName);
ExcelUtils.mergeCells(sheet, 0, 0, 0, super.cellSize - 1);
return ++currentIndex;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return currentIndex;
}
3)onCreateTitleRow()的实现
也就是将列名数组中的数据挨个取粗来用而已。默认一个列名只占一行,且没有单元格合并。
tips:随着表格复杂度的增加,列名可能会出现好几个单元格合并,列名不仅仅占一行的情况。这时我们只
需要重写此方法即可。原理一样。
private int autoCreateTitleRow(HSSFWorkbook book, HSSFSheet sheet,
WriteExcelData excelData, DefaultStyle defaultStyle,
int allColumnSize, int currentIndex){
HSSFRow titleRow = sheet.createRow(currentIndex);
String[] rowNames = excelData.getTitleNames();
for (int i = 0; i < super.cellSize; i++) {
String value = rowNames[i];
HSSFCell cell = titleRow.createCell(i);
cell.setCellStyle(super.config.getDefault_title_style());
cell.setCellValue(value==null?"":value);
}
return ++currentIndex;
}
4)onCreateContent()的实现
内容部分的导出。其实也就是遍历list数据源的数据而已。当然,无用的列是不需要导出的,用tableFileds数组来确定。这里还要判断是否传入了IcellValueTransformer单元格转化器,如果,传入了,就要使用转化器转化后再输出。
private int autoCreateContent(HSSFWorkbook book, HSSFSheet sheet,
WriteExcelData excelData, DefaultStyle defaultStyle,
int allColumnSize, int currentIndex){
String[] fileds = excelData.getTableFileds();
List maps = excelData.getMaps();
for (int i = 0; i < maps.size(); i++) {
//创建行
HSSFRow row = sheet.createRow(currentIndex);
//创建列
Map map = maps.get(i);
for (int j = 0; j < super.cellSize; j++) {
Object obj = map.get(fileds[j]);
HSSFCell cell = row.createCell(j);
//设置单元格的格式
if(transformer != null){
transformer.transformCellValue(defaultStyle, cell, fileds[j], obj);
}else{
defaultTransformCellValue(defaultStyle, cell, fileds[j], obj);
}
}
currentIndex++;
}
return currentIndex;
}
private void defaultTransformCellValue(DefaultStyle defaultStyle,
HSSFCell cell,String mapKey,T value){
short border = defaultStyle.getDefault_border_style();
HSSFCellStyle style_text = defaultStyle.getDefault_content_style_text();
ExcelUtils.setCellStyleBorder(style_text, border, border, border, border);
cell.setCellStyle(style_text);
if(value==null){
cell.setCellValue("");
return ;
}
if(value instanceof Boolean){
cell.setCellValue((Boolean)value);
}else if(value instanceof Double){
cell.setCellValue((Double)value);
}else if(value instanceof Float){
cell.setCellValue((Float)value);
}else if(value instanceof RichTextString){
cell.setCellValue((RichTextString)value);
}else{
cell.setCellValue(value.toString());
}
}
十 测试
public class Test{
//构造假数据
public static List getDatas(){
List datas = new ArrayList<>();
Map map = null;
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
map = new HashMap();
map.put("name", "兰陵_"+i);
map.put("num", ""+i);
map.put("place", "重庆_"+i);
map.put("sum", i);
datas.add(map);
}
return datas;
}
//设置 单元格数据/样式 转换器
pulic IcellValueTransformer getTranformaer(){
return new IcellValueTransformer() {
@Override
public void transformCellValue(DefaultStyle defaultStyle,
HSSFCell cell, String mapKey, T value) {
if("sum".equals(mapKey)){
HSSFCellStyle money = defaultStyle.getDefault_content_style_money();
cell.setCellStyle(money);
System.out.println(Double.valueOf(value.toString()));
cell.setCellValue(Double.valueOf(value.toString()));
}else{
HSSFCellStyle text = defaultStyle.getDefault_content_style_text();
cell.setCellStyle(text);
cell.setCellValue(value.toString());
}
}
};
}
//调用
public static void main(String[] args) {
List maps = getDatas();
String sheetName = "Test ExcelExport";
String headName = "测试表";
int[] fieldsWidths = new int[]{10,10,10,20};
String[] titleNames = new String[]{"姓名","学号","户籍","销售业绩"};
String[] tableFileds = new String[]{"name","num","place","sum"};
WriteExcelData datas = new WriteExcelData(sheetName, headName, fieldsWidths,
titleNames, tableFileds, maps);
SimpleExcel excel = new SimpleExcel(datas);
excel.setTransformer(getTranformaer());//根据业务需要,加不加这个都行
try {
String fileName = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("C:/develop/"+fileName+".xls");
excel.write(os);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
代码一起打包上传了。
代码地址 戳这里 ——> poi导出excel封装