Python控制语句
Python 控制语句
利用布尔值做决定程序的执行方向.
| 布尔运算符 | 运算结果为True or Flase |
|---|---|
| < | 小于 |
| > | 大于 |
| <= | 小于等于 |
| >= | 大于等于 |
| == | 等于 |
| != | 不等于 |
| and | 逻辑与 |
| or | 逻辑或 |
| not | 逻辑非 |
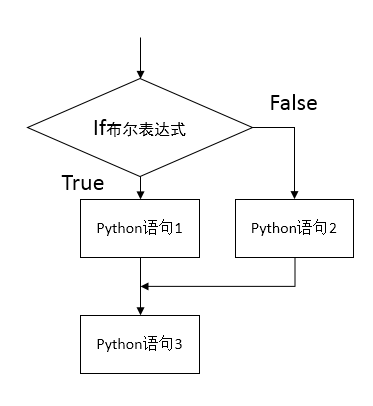
1 选择语句 if
1.1 if 基本语句
Python中if语句基本语法:
if booleanExpression:
# suite of Python statemants
# rest of the Python program
- Python中缩进对代码块非常重要. 有相同的缩进量, 表示当前语句属于并列结构, 没有嵌套.
# suite of Python statements与# rest of the Python program缩进不一样, 代码执行也不一样.- 注意
if语句后的冒号:
1.2 if-else 语句
if booleanExpression:
# suite executed for a True boolean result
else:
# suite executed for a False boolean result
# rest of the Pthon program
- 注意
if语句后和else语句后的冒号.
在Python命令行下实现:
>>> points = 10
>>> seconds = 20
>>> if points > seconds:
...: print "Lead is safe."
...: else:
...: print "Lead is not safe."
Lead is not safe.
- 注意连续语句的输入.
else:语句需要左顶格,else:与if语句属于两个同级语句块, 所以缩进位置一样, 切勿将else:纳入if的语句块下.- 两次回车, 表示程序输入完成.
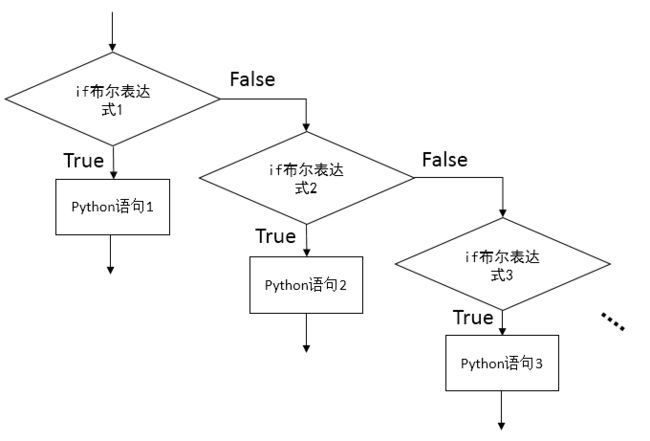
1.3 if-elif-else 语句
if booleanExpression1:
# suit1
elif booleanExpression2:
# suit2
elif booleanExpression3:
# suit3
else:
# suitLast
if、elif和else属于相同缩进.
1.4 经典算法实现
这是一个在NBA中经典的垃圾时间算法, 由体育作家Bill James 提出.
Bill James 的算法是基于他多年观看篮球比赛的经验来判定当前领先的优势是不是不可超越, 算法描述如下:
- 获取领先一队的分数.
- 减去3分.
- 如果目前是领先队控球, 那么加上0.5分; 如果是落后队控球, 减去0.5分(结果小于0, 则变成0).
- 计算平方后的结果.
- 如果得到的结果比当前比赛剩下的时间秒数更大, 那么这个领先队是安全的(或无法超越的, 也就是说当前已经进入了垃圾时间).
下面用Python实现这个算法:
# Bill James' Safe Lead Calculator
# From http://www.slate.com/id/2185975
# 1. Take the number of points one team is ahead.
pointsStr = raw_input("Enter the lead in points: ")
points = int(pointsStr)
# 2. Subreact three.
points = points - 3
# 3. Add a half-ppoint if the ream that ahead has the ball,
# and subtract a half-point if the other team has the ball.
has_ball = raw_input("Does the lead team have the ball (Yea or No): ")
if has_ball == 'Yes':
points = points + 0.5
else:
points = points - 0.5
# (Number less than zero become zero)
if points < 0:
points = 0
# 4. Square that.
points = points ** 2
# 5. If the result is greater that the number of secinds left in the game,
# the lead is safe.
seconds = int(raw_input("Enter the number of secinds remaining: "))
if points > seconds:
print "Lead is safe."
else:
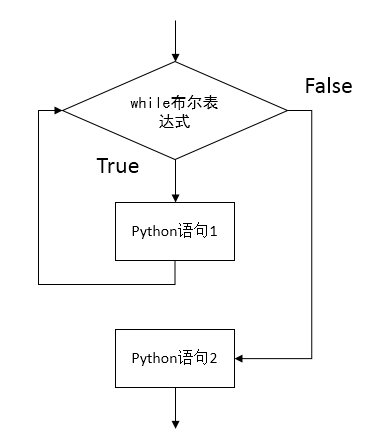
print "Lead is not safe."2 循环语句 while
while booleanExpression:
# while suite
# rest of the Python program一个简单的例子:
x_int = 0
while x_int < 10:
print x_int, # 逗号表示在一行输出
x_int = x_int + 1
print
print "Final value of x_int: ", x_int
>>> 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 93 循环语句 for
Python 中for 语句的语法:
for anElement in object:
# for suit
anElement是与for循环相关的变量, 会将集合object中元素的值逐一赋值给anElement.- 注意
for语句后的冒号:
一个简单的例子:
>>> for theChar in "hi mom":
...: print theChar
...
...
h
i
m
o
m
>>>4 Python中什么是相等?
4.1 is & ==
在Python中有两种不同的相等:
- 两个不同名字变量关联同一个对象值, 但ID不一样.(值相等但ID不相等)
- 两个不同名字变量与同一个ID的对象关联.(值相等且ID相等)
例如:
float1 = 2.5
float2 = 2.5
float3 = float2float1和float2有相同的对象值, 但是对象值的ID不一样, Python中每创建一个变量关联一个值, 均会创建一个新的ID.float2和float3有相同的对象值和相同的ID. Python中的赋值语句不会创建新的ID.
针对上述两种相等, Python有两条语句==和is检查相等.
==检查对象值是否相等, 不检查ID.is检查是否关联同一个对象, 检查ID.
例如:
>>> float1 = 2.5
>>> float2 = 2.5
>>> float3 =float2
>>> float1 == float2 #只检查值对象值,不检查ID
True
>>> float1 is float2 #检查ID
False
>>> float2 is float3
True4.2 浮点数的相等
计算机是无法精确计算得到理想值, 在大部分情况下都需要近似计算, 那么在处理浮点数的时候, 就很有可能因为省略了一些小数点后面的数, 而造成本来完全等价的两个浮点数不想等.
例如:
>>> u = 11111113
>>> v = -11111111
>>> w = 7.51111111
>>> (u + v) + w
>9.5111111099999999
>>> u + (v + w)
>9.5111111104488373
>>> (u + v) + w == u + (v + w)
False在加法的结合律中 (u + v) + w 和 u + (v + w)是完全等价的, 但是在程序中无法做到精确相等, 所以需要近似相等, 引入math模块中的fabs函数(绝对值函数), 来衡量两个值的接近程度, 当接近程度<我们规定的一个阀值(这个阀值通常为0.0000001)时, 我们认为他们相等.
>>> import math
>>> u = 11111113
>>> v = -11111111
>>> w = 7.51111111
>>> x = (u + v) + w
>>> y = u + (v + w)
>>> x == y
False
>>> math.fabs(x - y) < 0.0000001
True在进行浮点数的相等运算时, 后一种方法才是正确的选择, 不然程序将会得到意想不到的错误, 而且很难查找.
5 continue & break
continue语句表示: 跳过后面的执行语句, 继续当前循环.
- 这是不推荐被采用的, 易造成程序可读性很差. 如果需要用到
continue则需要调整算法.
- 这是不推荐被采用的, 易造成程序可读性很差. 如果需要用到
break语句表示: 无条件跳出当前循环.
- 在
while循环中运用较多.
- 在
6 延伸
6.1 基于对象调用函数
# sum up a serise of numbers
# make sure input is only numbers
print "Allow the user to enter a series of integers. Um the integers"
print "Ignore non-numberic input. End input with a '.'"
#initialize the input number and the sum
theNumStr = raw_input("Number: ")
theSum = 0
# Stop if a period (.) is entered
# remember, the Num is a string until we cinvert it
while theNumStr != '.':
if not theNumStr.isdigit():
print "Error, only numbers please"
theNumStr = raw_input("Number: ")
continue
theSum += int(theNumStr)
theNumStr = raw_input("Number: ")
print "The sum is : ", theSum
isdigit方法用于检查一个字符串是否只包含数字, 返回一个布尔值.- 这是一种基于对象调用函数, 叫 ‘点调用’. 用句号将对象和方法联系起来, 通常形式
someObject.aMethod(arguments), 表示调用someObject上的方法aMethod.
6.2 冰雹数序列
冰雹数序列由Collatz先生在1937年提出, 所以又名 Collatz猜想, 至今未解, 该猜想的内容是:
- 给定一个初值, 按下列公式运算, 直到收敛为1.
- 如果数字是偶数, 除以2.
- 如果数字是奇数, 乘以3, 再加1.
- 当数等于1时, 退出运算.
# Generate a Hailstone sequence
numString = raw_input("Enter a positive integer: ")
num = int(numString)
count = 0
print "Starting with number: ",num
print "Sequence is: ",
while num > 1: # stop when the sequence reaches 1
if num % 2:
num = num * 3 + 1
else:
num = num / 2
print num, ",",
count += 1
else:
print # blank line foe nicer output
print "Sequence is ", count,"numbers long"6.3 用pylab对数据绘图
import pylab
listOfInts = []
for counter in range(10):
listOfInts.append(counter * 2)
print listOfInts
print len(listOfInts)
# now polt the list
pylab.plot(listOfInts)
pylab.show()# plot a sine wave from 0 to 4pi
import math
import pylab
#initialize the two lists and the counting variable num. Note is a float
y_values = []
x_values = []
num = 0.0
#collect bath num and the sine of num is a list
while num < math.pi * 4:
y_values.append(math.sin(num))
x_valuse.append(num)
num += 0.1
# plot the x and y values as rad circles
pylab.plot(x_values, y_values, 'ro')
pylab.show()
- 颜色: 第一个小写字母为颜色,
r红色,b蓝色,g绿色,k黑色- 标记: 第二个元素为字符,
o圆圈,.点,x叉,+加.
ro表示: 红色圆圈.