Python+wxPython+OpenCV 界面图片浏览和处理
程序资源链接:点击打开链接
一、环境:
(一开始考虑的就是跨平台,所以Python代码能在Windows和Linux下面运行,唯一的要求是wxPython版本要在3.0以上,因为wxPython+matplotlib使用要求,其他任意,python2和3的区别只要改一下print函数就可以了)
因为基本上环境都兼容,只好说一说我自己的环境了。
Windows下:
1、Python+OpenCV环境配置:这个在Windows下超级简单,读者可以自行百度,唯一要提的就是连接OpenCV的wheel要和Python匹配。(我是Python3.5+OpenCV3.1.0)
2、wxPthon+Python配置:官网下载wxPython:点击打开链接,比如我是Python3.5,要下带cp35的,如果是Python2.7,要下cp27的。我下的是:wxPython-4.0.1-cp35-cp35m-win_amd64.whl。
将文件放置到Python安装目录的Scripts下,如我的是:D:\SoftWare\Python\Python\Scripts,利用pip命令进行安装,相信配置过Python+OpenCV,这里也会很简单(pip install wxPython-4.0.1-cp35-cp35m-win_amd64.whl)。
Linux下:
1、Python+OpenCV环境配置:我是CentOS7的环境(Ubuntun的别担心,也能跑),终端下输入python --version,python的默认版本是2.7.5,输入
pkg-config --modversion opencv 查看opencv版本OpenCV默认是2.4.5的,可以自行升级OpneCV,我升级到了OpnCV3.2.0,本来Python我也升级了,但是实验室的那个老师硬要我用2.7,那就又降
回了2.7,这里连接Python和OpenCV要用命令:pip install opencv-python
2、wxPthon+Python配置:官网下载对应Linux操作系统的wheel,点击打开链接,解压,进入目录,同样使用pip install进行安装,不用下包去编译,
如果你升级了Python,那么相应的pip命令也要升级,这个自行百度。
二、程序
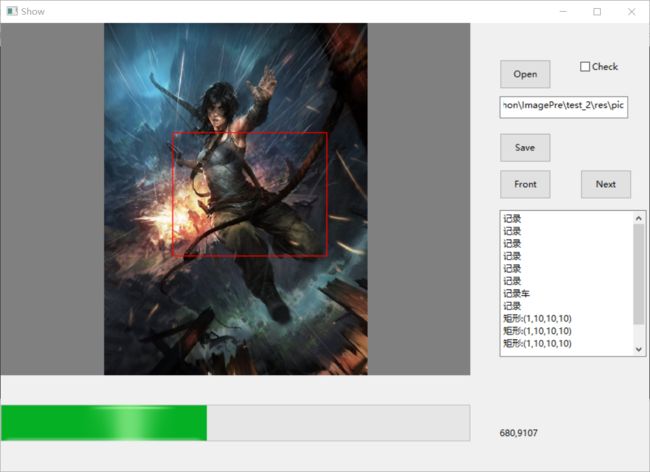
先上图:
Windows下:
Linux下:
1、下面贴一下界面初始化的代码,注释用的是英文,不难,慢慢看,简单来说就是创建一个画布,
我们可以在画布上画矩形,显示图片,这个画布是嵌入到wxPython的面板panel里的。
参考过:点击打开链接,还有一些不记得了,百度 wxPython matplotlib就会出现一大堆资料
这里贴一下自己找的wxPython的使用教程:点击打开链接
def __init__(self, parent, pathToImage=None):
# Use English dialog
self.locale = wx.Locale(wx.LANGUAGE_ENGLISH)
# Initialise the parent
wx.Panel.__init__(self, parent)
# Intitialise the matplotlib figure
#self.figure = plt.figure(facecolor='gray',figsize=(10.5, 8))
self.figure = Figure(facecolor='gray',figsize=(10.5, 8))
# Create an axes, turn off the labels and add them to the figure
self.axes = plt.Axes(self.figure,[0,0,1,1])
self.axes.set_axis_off()
self.figure.add_axes(self.axes)
self.panel=wx.Panel(self,-1,pos=(10,10),size=(1390,940))
# Add the figure to the wxFigureCanvas
self.canvas = FigureCanvas(self.panel, -1, self.figure)
# Height,width
#self.picSize=wx.TextCtrl(self,-1,"",pos=(1100,800),size=(100,30),style=wx.TE_READONLY)
# Check box
self.check=wx.CheckBox(self.panel,-1,u"批量处理全部图片",pos=(1080,50),size=(100,20))
self.check.Bind(wx.EVT_CHECKBOX,self.onCheck)
# StaticText
wx.StaticText(self.panel,-1,u"图像文件所在目录:",pos=(1080,90))
# Show dialog path
self.pathText=wx.TextCtrl(self.panel,-1,"",pos=(1080,130),size=(190,30))
# Add Button
self.openBtn=wx.Button(self.panel,-1,u">>",pos=(1280,130),size=(90,30))
self.frontBtn=wx.Button(self.panel,-1,u"上一张",pos=(1080,830),size=(90,50))
self.saveBtn=wx.Button(self.panel,-1,u"保存本帧结果",pos=(1190,830),size=(100,50))
self.nextBtn=wx.Button(self.panel,-1,u"下一张",pos=(1300,830),size=(90,50))
self.workBtn=wx.Button(self.panel,-1,u"开始处理/暂停处理",pos=(1080,760),size=(290,40))
# Progress Bar
self.gauge=wx.Gauge(self.panel,-1,1000,(10,830),(1050,50))
#self.gauge.SetValue(2)
# StaticText
wx.StaticText(self.panel,-1,u"耗时:",pos=(1080,723))
# Show time
self.timeText=wx.TextCtrl(self.panel,-1,"",pos=(1140,720),size=(230,30),style=wx.TE_READONLY)
# Attach button with function
self.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON,self.load,self.openBtn)
self.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON,self.save,self.saveBtn)
self.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON,self.front,self.frontBtn)
self.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON,self.next,self.nextBtn)
self.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON,self.work,self.workBtn)
self.area_text = wx.TextCtrl(self, -1, u'小轿车',pos=(1080,175),size=(290,535),style=(wx.TE_MULTILINE))
self.area_text.AppendText('\n大货车')
self.area_text.AppendText('\n大货车')
self.area_text.AppendText('\n大货车')
self.area_text.AppendText('\n大货车')
self.area_text.AppendText('\n大货车')
self.area_text.AppendText('\n大货车')
self.area_text.AppendText('\n大货车')
self.area_text.AppendText('\n矩形:(1,10,10,10)')
self.area_text.AppendText('\n矩形:(1,10,10,10)')
self.area_text.AppendText('\n矩形:(1,10,10,10)')
self.area_text.AppendText('\n矩形:(1,10,10,10)')
self.area_text.AppendText('\n矩形:(1,10,10,10)')
# Initialise the rectangle
self.rect = Rectangle((0,0), 0, 0, facecolor='None', edgecolor='red')
self.x0 = None
self.y0 = None
self.x1 = None
self.y1 = None
self.axes.add_patch(self.rect)
# The list of the picture(absolute path)
self.fileList=[]
# Picture name
self.picNameList=[]
# Picture index in list
self.count=0
# Cut from the picture of the rectangle
self.cut_img=None
# Connect the mouse events to their relevant callbacks
self.canvas.mpl_connect('button_press_event', self._onPress)
self.canvas.mpl_connect('button_release_event', self._onRelease)
self.canvas.mpl_connect('motion_notify_event', self._onMotion)
# Lock to stop the motion event from behaving badly when the mouse isn't pressed
self.pressed = False2、显示图片:这里读入图片是用OpenCV的imread()实现的,用putText()把图像的宽高写在图像上,注意别写画布上,不然想清除就难了。
# Show Picture
def setImage(self, pathToImage):
'''Sets the background image of the canvas'''
# Clear the rectangle in front picture
self.axes.text(100,100,'',None)
self.rect.set_width(0)
self.rect.set_height(0)
self.rect.set_xy((0, 0))
self.canvas.draw()
# Load pic by OpenCV
image=cv2.imread(pathToImage)
self.imageSize = image.shape
print pathToImage
print "It's width and height:"
print self.imageSize
print "------------------------"
# OpenCV add text on pic
str1='(%s,%s)' % (str(self.imageSize[0]),str(self.imageSize[1]))
#rev=wx.StaticText(self,-1,str1,(670,400))
cv2.putText(image,str1,(10,200), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1,(255,0,0),2)
# Add the image to the figure and redraw the canvas. Also ensure the aspect ratio of the image is retained.
self.axes.imshow(image,aspect='auto')
self.canvas.draw()3、鼠标交互截矩形:
简单思路就是绑定鼠标左、右键,检测到鼠标按下且移动就在画布上画矩形,直到释放鼠标。
4、程序入口:
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Create an demo application
app = wx.App()
# Create a frame and a RectangleSelectorPanel
frame = wx.Frame(None, -1,"Show Demo",size=(1400,950))
panel = MyDialog(frame)
# Start the demo app
frame.Show()
app.MainLoop()三、总结
最后我得感谢一下那些我参考过代码的作者,因为做的时候浏览了很多资料,记不住具体的作者,只好在这里一起感谢了。
资源链接:点击打开链接