借鉴于[美团点评技术团队][2]
[2]: http://tech.meituan.com/java-hashmap.html
hashMap继承自AbstractMap抽象类
非线程安全,所以效率可能较高于Hashtable
其中键和值都是对象,并且不能包含重复键,但可以包含重复值
允许null的键和值
HashMap是Hashtable的轻量级实现
分析
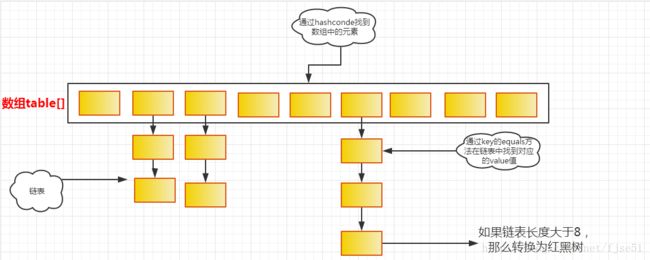
HashMap实际上是一个“链表散列”的数据结构,即数组和链表的结构,通过key的hashCode来计算Hash值,只要HashCode相同,计算出来的值也就一样,然后再计算数组下标,如果多个key对应到一个下标,就用链表串起来,新插入的在前面。在jdk1.8里 加入了红黑树的实现,当链表的长度大于8时,转换为红黑树的结构。
static class Node implements Map.Entry {
final int hash;//用于定位数组索引的位置
final K key;
V value;
Node next;//链表的下一个Node
Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
Node是HashMap的一个内部类,实现Map.Entry接口,本质就是一个映射(键值对)。
//threshold是HashMap所能容纳的最大数据量的Node(键值对)个数
int threshold; // 所能容纳的key-value对极限
final float loadFactor; // 负载因子
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; //默认负载因子
//默认的初始容量(容量为HashMap中桶的数目)是16,且实际容量必须是2的整数次幂。
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4;
final Node[] resize() {
Node[] oldTab = table;
......
else {
newCap = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
//默认使用0.75*16
newThr = (int)(DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
if (newThr == 0) {
float ft = (float)newCap * loadFactor;
newThr = (newCap < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && ft < (float)MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
(int)ft : Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
threshold = newThr;
......
}
也就是说,负载因子越大,也就是能容纳的键值对更多。这样空间利用率高了,但是冲突机会增大。
put方法实现:
put思路如下:
- 判断键值对数组table是否为空或者null,否则进行resize()扩容操作。
- 根据键值key计算hash得到插入索引index,如果table为空,直接新建新节点,转向步骤6判断扩容。
- 判断节点key存在,直接覆盖value。
- 判断table是否为treeNode红黑树,如果是红黑树,直接在树中插入键值对。
- 遍历table,链表长度大于8,就转换为红黑树,否则进行链表的插入操作,过程中发现相同的key直接进行覆盖value。
- 插入成功后,判断实际的size是否超过了最大的容量threshold,如果超过,进行扩容。
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
/**
*生成hash的方法
*/
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,boolean evict) {
Node[] tab; Node p; int n, i;
//判断table是否为空,
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;//创建一个新的table数组,并且获取该数组的长度
//根据键值key计算hash值得到插入的数组索引i,如果table[i]==null,直接新建节点添加
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {//如果对应的节点存在
Node e; K k;
//判断table[i]的首个元素是否和key一样,如果相同直接覆盖value
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
//判断table[i] 是否为treeNode,即table[i] 是否是红黑树,如果是红黑树,则直接在树中插入键值对
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
// 该链为链表
else {
//遍历table[i],判断链表长度是否大于TREEIFY_THRESHOLD(默认值为8),大于8的话把链表转换为红黑树,在红黑树中执行插入操作,否则进行链表的插入操作;遍历过程中若发现key已经存在直接覆盖value即可;
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
// 写入
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
// 插入成功后,判断实际存在的键值对数量size是否超多了最大容量threshold,如果超过,进行扩容
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
get方法实现:
get思路如下:
- table中的第一个节点,直接取出
- 通过key.equals()去查找对应的entry
若为链表,时间复杂度O(n),若为红黑树,则为O(logn)
public V get(Object key) {
Node e;
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;
}
final Node getNode(int hash, Object key) {
Node[] tab; Node first, e; int n; K k;
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
// 直接命中
if (first.hash == hash && // 每次都是校验第一个node
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return first;
// 未命中
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
// 在树中获取
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
return ((TreeNode)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
// 在链表中获取
do {
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
return null;
}
扩容机制:
我们分析下resize的源码,鉴于JDK1.8融入了红黑树,较复杂,为了便于理解我们仍然使用JDK1.7的代码,好理解一些
void resize(int newCapacity) { //传入新的容量
Entry[] oldTable = table; //引用扩容前的Entry数组
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { //扩容前的数组大小如果已经达到最大(2^30)了
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE; //修改阈值为int的最大值(2^31-1),这样以后就不会扩容了
return;
}
Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity]; //初始化一个新的Entry数组
transfer(newTable); //!!将数据转移到新的Entry数组里
table = newTable; //HashMap的table属性引用新的Entry数组
threshold = (int)(newCapacity * loadFactor);//修改阈值
}
void transfer(Entry[] newTable) {
Entry[] src = table; //src引用了旧的Entry数组
int newCapacity = newTable.length;
for (int j = 0; j < src.length; j++) { //遍历旧的Entry数组
Entry e = src[j]; //取得旧Entry数组的每个元素
if (e != null) {
if (e != null) {
src[j] = null;//释放旧Entry数组的对象引用(for循环后,旧的Entry数组不再引用任何对象)
do {
Entry next = e.next;
int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity); //!!重新计算每个元素在数组中的位置
e.next = newTable[i]; //标记[1]
newTable[i] = e; //将元素放在数组上
e = next; //访问下一个Entry链上的元素
} while (e != null);
}
}
}
其他
HashMap是非线程安全的,如果想得到线程安全的HashMap,可以通过Collections类的静态方法synchronizedMap获得线程安全的HashMap。
Map map = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap());
HashMap和ConcurrentHashMap的区别
ConcurrentHashMap引入一个"分段锁"的概念,将Map分成N个Segment,每一个Segment类似于HashTable,相当于每一个分段都进行了锁保护。默认是分成了16个。