深度优先搜索 - 广度优先搜索 - 宝岛探险
深度优先搜索 - 广度优先搜索 - 宝岛探险
《啊哈!算法》 - 啊哈磊
1. 宝岛探险
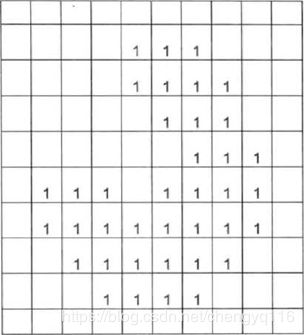
钓鱼岛由一个主岛和一些附属岛屿组成,下面这个 10*10 的二维矩阵就是钓鱼岛的航拍地图。图中数字表示海拔 0 表示海洋,1~9 都表示陆地。飞机将会降落在 (6, 8) 处,现在需要计算出飞机降落地所在岛的面积 (即有多少个格子)。此处我们把与降落点上、下、左、右相链接的陆地均视为同一岛屿。
1 2 1 0 0 0 0 0 2 3
3 0 2 0 1 2 1 0 1 2
4 0 1 0 1 2 3 2 0 1
3 2 0 0 0 1 2 4 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 5 3 0
0 1 2 1 0 1 5 4 3 0
0 1 2 3 1 3 6 2 1 0
0 0 3 4 8 9 7 5 0 0
0 0 0 3 7 8 6 0 1 2
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0
2. 广度优先搜索
其实就是从 (6, 8) 开始广度优先搜索。每次需要向上、下、左、右四个方向扩展,当扩展出的点大于 0 时就加入队列,直到队列扩展完毕。所有被加入到队列的点的总数就是小岛的面积。假设地图的大小不超过 50*50。
/*
============================================================================
Name : yongqiang.cpp
Author : Yongqiang Cheng
Version : Version 1.0.0
Copyright : Copyright (c) 2020 Yongqiang Cheng
Description : Hello World in C++, Ansi-style
============================================================================
*/
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int inference(int map[10][10], int H, int W, int start_hy, int start_xw)
{
int ret = 0;
int head = 0, tail = 0;
int queue_data[2500][2] = { 0 };
int book[10][10] = { 0 };
int dist[10][10] = { 0 };
int step = 0;
int next[4][2] = { {0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0} }; // right -> down -> left -> up - clockwise (height, width)
int area = 0;
queue_data[tail][0] = start_hy - 1; // height
queue_data[tail][1] = start_xw - 1; // width
tail++;
book[start_hy - 1][start_xw - 1] = 1;
dist[start_hy - 1][start_xw - 1] = step;
area++;
// 队列不为空时循环
while (head < tail)
{
int poph = queue_data[head][0];
int popw = queue_data[head][1];
head++; // 出队列
step = dist[poph][popw];
// 枚举 4 个方向
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
// 计算下一步的坐标
int th = 0, tw = 0;
th = poph + next[i][0];
tw = popw + next[i][1];
// 判断是否越界
if ((th < 0) || (th >= H) || (tw < 0) || (tw >= W))
{
continue;
}
// 判断是否走过或者是否陆地
if ((0 == book[th][tw]) && (map[th][tw] > 0))
{
// 入队
queue_data[tail][0] = th; // height
queue_data[tail][1] = tw; // width
tail++;
book[th][tw] = 1; // 标记已经走过
dist[th][tw] = step + 1;
area++;
}
}
}
for (int h = 0; h < H; h++)
{
for (int w = 0; w < W; w++)
{
cout << dist[h][w] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
ret = area;
return area;
}
int main()
{
clock_t start = 0, end = 0;
double cpu_time_used = 0;
const char input_txt[] = "D:\\visual_studio_workspace\\yongqiangcheng\\yongqiangcheng\\input.txt";
const char output_txt[] = "D:\\visual_studio_workspace\\yongqiangcheng\\yongqiangcheng\\output.txt";
freopen(input_txt, "r", stdin);
// freopen(output_txt, "w", stdout);
start = clock();
printf("Start of the program, start = %ld\n", start);
printf("Start of the program, start = %ld\n\n", start);
int case_num;
cin >> case_num;
for (int i = 1; i <= case_num; i++)
{
int H = 0, W = 0;
int start_hy = 0, start_xw = 0;
int map[10][10] = { 0 };
cin >> H >> W >> start_hy >> start_xw;
for (int h = 0; h < H; h++)
{
for (int w = 0; w < W; w++)
{
cin >> map[h][w];
}
}
int ret = inference(map, H, W, start_hy, start_xw);
cout << "CASE #" << i << " = " << ret << endl;
}
end = clock();
printf("\nEnd of the program, end = %ld\n", end);
printf("End of the program, end = %ld\n", end);
cpu_time_used = ((double)(end - start)) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
printf("Total time taken by CPU: %f\n", cpu_time_used);
printf("Exiting of the program...\n");
fclose(stdin);
// fclose(stdout);
return 0;
}
Start of the program, start = 0
Start of the program, start = 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 7 6 5 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 6 5 4 3 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 4 3 2 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 2 1 2 0
0 8 7 6 0 2 1 0 1 0
0 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 2 0
0 0 7 6 5 4 3 2 0 0
0 0 0 7 6 5 4 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
CASE #1 = 38
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 7 6 5 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 6 5 4 3 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 4 3 2 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 2 1 2 0
0 8 7 6 0 2 1 0 1 0
0 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 2 0
0 0 7 6 5 4 3 2 0 0
0 0 0 7 6 5 4 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
CASE #2 = 38
End of the program, end = 19
End of the program, end = 19
Total time taken by CPU: 0.019000
Exiting of the program...
请按任意键继续. . .
2.1 D:\visual_studio_workspace\yongqiangcheng\yongqiangcheng\input.txt
input.txt 第一行是测试用例个数 2,后续依次为具体测试用例数据。
测试用例第一行前两个数 YH 和 XW,YH = 10 表示地图的行数,XW = 10 表示地图的列数。
测试用例第一行后两个数表示起始点坐标 (start_yh, start_xw),注意起始点为 (1, 1)。
接下来 YH = 10 行 XW = 10 列为地图,0 表示海洋,1~9 表示陆地。
2
10 10 6 8
1 2 1 0 0 0 0 0 2 3
3 0 2 0 1 2 1 0 1 2
4 0 1 0 1 2 3 2 0 1
3 2 0 0 0 1 2 4 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 5 3 0
0 1 2 1 0 1 5 4 3 0
0 1 2 3 1 3 6 2 1 0
0 0 3 4 8 9 7 5 0 0
0 0 0 3 7 8 6 0 1 2
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0
10 10 6 8
1 2 1 0 0 0 0 0 2 3
3 0 2 0 1 2 1 0 1 2
4 0 1 0 1 2 3 2 0 1
3 2 0 0 0 1 2 4 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 5 3 0
0 1 2 1 0 1 5 4 3 0
0 1 2 3 1 3 6 2 1 0
0 0 3 4 8 9 7 5 0 0
0 0 0 3 7 8 6 0 1 2
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0
从 (6, 8) 开始搜索,可以扩展出的点如下 (阴影部分)。
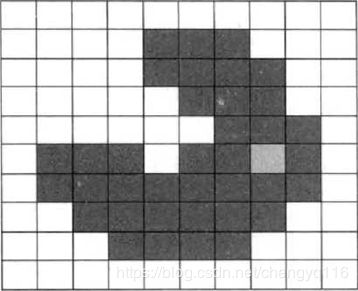
3. 深度优先搜索
/*
============================================================================
Name : yongqiang.cpp
Author : Yongqiang Cheng
Version : Version 1.0.0
Copyright : Copyright (c) 2020 Yongqiang Cheng
Description : Hello World in C++, Ansi-style
============================================================================
*/
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
void dfs(int map[10][10], int H, int W, int start_hy, int start_xw, int step, int book[10][10], int dist[10][10], int *area, int order[10][10])
{
int next[4][2] = { { 0, 1 },{ 1, 0 },{ 0, -1 },{ -1, 0 } }; // right -> down -> left -> up - clockwise (height, width)
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
int th = start_hy + next[k][0];
int tw = start_xw + next[k][1];
// 判断是否越界
if ((th < 0) || (th >= H) || (tw < 0) || (tw >= W))
{
continue;
}
if ((0 == book[th][tw]) && (map[th][tw] > 0))
{
book[th][tw] = 1;
dist[th][tw] = step + 1;
order[th][tw] = *area;
(*area)++;
dfs(map, H, W, th, tw, step + 1, book, dist, area, order);
}
}
return;
}
int inference(int map[10][10], int H, int W, int start_hy, int start_xw)
{
int ret = 0;
int step = 0;
int book[10][10] = { 0 };
int dist[10][10] = { 0 };
int order[10][10] = { 0 };
int area = 0;
start_hy = start_hy - 1;
start_xw = start_xw - 1;
book[start_hy][start_xw] = 1;
dist[start_hy][start_xw] = step;
order[start_hy][start_xw] = area;
area++;
dfs(map, H, W, start_hy, start_xw, step, book, dist, &area, order);
for (int h = 0; h < H; h++)
{
for (int w = 0; w < W; w++)
{
cout << setw(2) << dist[h][w] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
for (int h = 0; h < H; h++)
{
for (int w = 0; w < W; w++)
{
cout << setw(2) << book[h][w] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
for (int h = 0; h < H; h++)
{
for (int w = 0; w < W; w++)
{
cout << setw(2) << order[h][w] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
ret = area;
return area;
}
int main()
{
clock_t start = 0, end = 0;
double cpu_time_used = 0;
const char input_txt[] = "D:\\visual_studio_workspace\\yongqiangcheng\\yongqiangcheng\\input.txt";
const char output_txt[] = "D:\\visual_studio_workspace\\yongqiangcheng\\yongqiangcheng\\output.txt";
freopen(input_txt, "r", stdin);
// freopen(output_txt, "w", stdout);
start = clock();
printf("Start of the program, start = %ld\n", start);
printf("Start of the program, start = %ld\n\n", start);
int case_num;
cin >> case_num;
for (int i = 1; i <= case_num; i++)
{
int H = 0, W = 0;
int start_hy = 0, start_xw = 0;
int map[10][10] = { 0 };
cin >> H >> W >> start_hy >> start_xw;
for (int h = 0; h < H; h++)
{
for (int w = 0; w < W; w++)
{
cin >> map[h][w];
}
}
int ret = inference(map, H, W, start_hy, start_xw);
cout << "CASE #" << i << " = " << ret << endl;
}
end = clock();
printf("\nEnd of the program, end = %ld\n", end);
printf("End of the program, end = %ld\n", end);
cpu_time_used = ((double)(end - start)) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
printf("Total time taken by CPU: %f\n", cpu_time_used);
printf("Exiting of the program...\n");
fclose(stdin);
// fclose(stdout);
return 0;
}
Start of the program, start = 0
Start of the program, start = 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 25 24 23 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 26 21 22 23 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 20 19 18 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 16 17 18 0
0 18 19 20 0 16 15 0 1 0
0 17 16 15 14 13 14 3 2 0
0 0 17 10 11 12 5 4 0 0
0 0 0 9 8 7 6 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0
0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0
0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0
0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0
0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 28 27 26 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 29 23 24 25 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 22 21 20 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 17 18 19 0
0 35 36 37 0 16 15 0 1 0
0 34 32 31 30 13 14 3 2 0
0 0 33 10 11 12 5 4 0 0
0 0 0 9 8 7 6 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
CASE #1 = 38
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 25 24 23 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 26 21 22 23 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 20 19 18 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 16 17 18 0
0 18 19 20 0 16 15 0 1 0
0 17 16 15 14 13 14 3 2 0
0 0 17 10 11 12 5 4 0 0
0 0 0 9 8 7 6 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0
0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0
0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0
0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0
0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 28 27 26 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 29 23 24 25 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 22 21 20 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 17 18 19 0
0 35 36 37 0 16 15 0 1 0
0 34 32 31 30 13 14 3 2 0
0 0 33 10 11 12 5 4 0 0
0 0 0 9 8 7 6 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
CASE #2 = 38
End of the program, end = 78
End of the program, end = 78
Total time taken by CPU: 0.078000
Exiting of the program...
请按任意键继续. . .
3. Floodfill 漫水填充法 (种子填充法)
如果想知道这个地图中有多少个独立的小岛,只需要对地图上的每一个大于 0 的点都进行一遍深度优先搜索即可。因为等于 0 的点是海洋,小于 0 的点是已经被染色的小岛,我们可以从 (1, 1) 开始,一直枚举到 (n, m),对每个点进行尝试染色。
/*
============================================================================
Name : yongqiang.cpp
Author : Yongqiang Cheng
Version : Version 1.0.0
Copyright : Copyright (c) 2020 Yongqiang Cheng
Description : Hello World in C++, Ansi-style
============================================================================
*/
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
void dfs(int map[10][10], int H, int W, int start_hy, int start_xw, int step, int book[10][10], int dist[10][10], int num)
{
int next[4][2] = { { 0, 1 },{ 1, 0 },{ 0, -1 },{ -1, 0 } }; // right -> down -> left -> up - clockwise (height, width)
map[start_hy][start_xw] = num;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
int th = start_hy + next[k][0];
int tw = start_xw + next[k][1];
// 判断是否越界
if ((th < 0) || (th >= H) || (tw < 0) || (tw >= W))
{
continue;
}
if ((0 == book[th][tw]) && (map[th][tw] > 0))
{
book[th][tw] = 1;
dist[th][tw] = step + 1;
dfs(map, H, W, th, tw, step + 1, book, dist, num);
}
}
return;
}
int inference(int map[10][10], int H, int W)
{
int ret = 0;
int step = 0;
int book[10][10] = { 0 };
int dist[10][10] = { 0 };
int num = 0;
for (int start_hy = 0; start_hy < H; start_hy++)
{
for (int start_xw = 0; start_xw < W; start_xw++)
{
if (map[start_hy][start_xw] > 0)
{
num--;
book[start_hy][start_xw] = 1;
dist[start_hy][start_xw] = step;
dfs(map, H, W, start_hy, start_xw, step, book, dist, num);
}
}
}
for (int h = 0; h < H; h++)
{
for (int w = 0; w < W; w++)
{
cout << setw(2) << dist[h][w] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
for (int h = 0; h < H; h++)
{
for (int w = 0; w < W; w++)
{
cout << setw(2) << book[h][w] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
ret = -num;
return ret;
}
int main()
{
clock_t start = 0, end = 0;
double cpu_time_used = 0;
const char input_txt[] = "D:\\visual_studio_workspace\\yongqiangcheng\\yongqiangcheng\\input.txt";
const char output_txt[] = "D:\\visual_studio_workspace\\yongqiangcheng\\yongqiangcheng\\output.txt";
freopen(input_txt, "r", stdin);
// freopen(output_txt, "w", stdout);
start = clock();
printf("Start of the program, start = %ld\n", start);
printf("Start of the program, start = %ld\n\n", start);
int case_num;
cin >> case_num;
for (int i = 1; i <= case_num; i++)
{
int H = 0, W = 0;
int start_hy = 0, start_xw = 0;
int map[10][10] = { 0 };
cin >> H >> W >> start_hy >> start_xw;
for (int h = 0; h < H; h++)
{
for (int w = 0; w < W; w++)
{
cin >> map[h][w];
}
}
int ret = inference(map, H, W);
cout << "CASE #" << i << " = " << ret << endl;
}
end = clock();
printf("\nEnd of the program, end = %ld\n", end);
printf("End of the program, end = %ld\n", end);
cpu_time_used = ((double)(end - start)) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
printf("Total time taken by CPU: %f\n", cpu_time_used);
printf("Exiting of the program...\n");
fclose(stdin);
// fclose(stdout);
return 0;
}
Start of the program, start = 0
Start of the program, start = 0
0 1 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
1 0 3 0 0 1 2 0 3 2
2 0 4 0 27 26 3 4 0 3
3 4 0 0 0 25 24 5 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 23 6 7 0
0 25 26 27 0 23 22 23 8 0
0 24 23 22 21 20 21 10 9 0
0 0 24 17 18 19 12 11 0 0
0 0 0 16 15 14 13 0 0 1
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0
1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1
1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1
1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1
1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0
0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0
0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0
0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0
0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0
CASE #1 = 4
0 1 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
1 0 3 0 0 1 2 0 3 2
2 0 4 0 27 26 3 4 0 3
3 4 0 0 0 25 24 5 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 23 6 7 0
0 25 26 27 0 23 22 23 8 0
0 24 23 22 21 20 21 10 9 0
0 0 24 17 18 19 12 11 0 0
0 0 0 16 15 14 13 0 0 1
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0
1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1
1 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1
1 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 1
1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0
0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0
0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0
0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0
0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0
CASE #2 = 4
End of the program, end = 51
End of the program, end = 51
Total time taken by CPU: 0.051000
Exiting of the program...
请按任意键继续. . .
其实这就是求一个图中独立子图的个数。这个算法就是 Floodfill 漫水填充法 (种子填充法)。Floodfill 在计算机图形学中有着非常广泛的运用,比如图像分割、物体识别等等。Windows下画图软件的油漆桶工具就是基于这个算法的,当你需要给某个密闭区域涂色或者更改某个密闭区域的颜色时,程序自动选中与种子点周边颜色相同的区域,接着将该区域替换成指定的颜色。Photoshop 的魔术棒选拝工具也可以基于这个算法实现,具体的算法是:查找种子点周边的点,将与种子点颜色相近的点 (可以设置一个阈值) 入队作为新种子,并对新入队的种子也进行同样的扩展操作,这样就选取了和最初种子相近颜色的区域。
References
《啊哈!算法》 - 啊哈磊