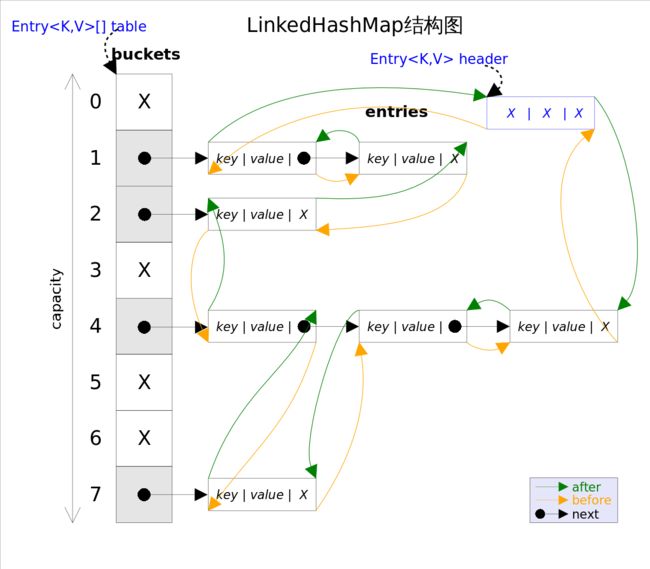
LinkedHashMap是HashMap的子类,与HashMap有着同样的存储结构,但它加入了一个双向链表的头结点,将所有put到LinkedHashMap的节点一一串成了一个双向循环链表,因此它保留了节点插入的顺序。可以按照访问顺序和插入顺序来进行排序。LruCahe就是基于LinkedHashMap来实现的。
(图片均来源于网络)
建议先阅读HashMap源码分析在来阅读此篇文章。
先看看结构图,这有助于我们阅读源码:
HashMap里面进行key value绑定的类是HashMapEntry,在LinkedHashMap则是LinkedHashMapEntry,它继承HashMapEntry的一个类并且重写recordAccess recordRemoval来进行重新指向进行排序,里面remove函数主要对自身在链表中进行移除,addBefore(LinkedHashMapEntry则是将自身插入到existingEntry之前。
/**
* LinkedHashMap entry.
*/
private static class LinkedHashMapEntry extends HashMapEntry {
// These fields comprise the doubly linked list used for iteration.
LinkedHashMapEntry before, after;
LinkedHashMapEntry(int hash, K key, V value, HashMapEntry next) {
super(hash, key, value, next);
}
/**
* Removes this entry from the linked list.
*/
// 对自身在链表中进行移除
private void remove() {
before.after = after;
after.before = before;
}
/**
* Inserts this entry before the specified existing entry in the list.
*/
//插入到LinkedHashMapEntry existingEntry之前
private void addBefore(LinkedHashMapEntry existingEntry) {
after = existingEntry;
before = existingEntry.before;
before.after = this;
after.before = this;
}
/**
* This method is invoked by the superclass whenever the value
* of a pre-existing entry is read by Map.get or modified by Map.set.
* If the enclosing Map is access-ordered, it moves the entry
* to the end of the list; otherwise, it does nothing.
*/
void recordAccess(HashMap m) {
LinkedHashMap lm = (LinkedHashMap)m;
if (lm.accessOrder) {
lm.modCount++;
remove();
addBefore(lm.header);
}
}
void recordRemoval(HashMap m) {
remove();
}
}
有了上面的概念来看LinkedHashMap的操作就相对比较容易了。
LinkedHashMap put的时候是调用HashMap的put函数,只是自身实现了addEntry() createEntry()来实现自身的逻辑
HashMap
/**
* Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map.
* If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old
* value is replaced.
*
* @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated
* @param value value to be associated with the specified key
* @return the previous value associated with key, or
* null if there was no mapping for key.
* (A null return can also indicate that the map
* previously associated null with key.)
*/
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {
inflateTable(threshold);
}
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = sun.misc.Hashing.singleWordWangJenkinsHash(key);
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
for (HashMapEntry e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
//调用子类LinkedHashMapEntry的recordAccess方法
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
//调用LinkedHashMap.addEntry方法
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
/**
* Adds a new entry with the specified key, value and hash code to
* the specified bucket. It is the responsibility of this
* method to resize the table if appropriate.
*
* Subclass overrides this to alter the behavior of put method.
*/
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
//扩容
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {
resize(2 * table.length);
hash = (null != key) ? sun.misc.Hashing.singleWordWangJenkinsHash(key) : 0;
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);
}
//增加新的key value 调用LinkedHashMap.createEntry
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
}
LinkedHashMap
/**
* This override alters behavior of superclass put method. It causes newly
* allocated entry to get inserted at the end of the linked list and
* removes the eldest entry if appropriate.
*/
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
// Previous Android releases called removeEldestEntry() before actually
// inserting a value but after increasing the size.
// The RI is documented to call it afterwards.
// **** THIS CHANGE WILL BE REVERTED IN A FUTURE ANDROID RELEASE ****
//得到需要移除的对象
// Remove eldest entry if instructed
LinkedHashMapEntry eldest = header.after;
//需要移除的对象是否是自身
if (eldest != header) {
boolean removeEldest;
size++;
try {
//得到是否移除的对象的标识
removeEldest = removeEldestEntry(eldest);
} finally {
size--;
}
if (removeEldest) {
//调用HashMap的removeEntryForKey进行移除
removeEntryForKey(eldest.key);
}
}
//调用HashMap的addEntry
super.addEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
}
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry eldest) {
return false;
}
/**
* Like addEntry except that this version is used when creating entries
* as part of Map construction or "pseudo-construction" (cloning,
* deserialization). This version needn't worry about resizing the table.
*
* Subclass overrides this to alter the behavior of HashMap(Map),
* clone, and readObject.
*/
//增加新的key value
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
HashMapEntry e = table[bucketIndex];
table[bucketIndex] = new HashMapEntry<>(hash, key, value, e);
size++;
}
我们主要看LinkedHashMap里面的东西,涉及到HashMap的就不重复说了。
如果key已经在该LinkedHashMap里面put了,那么将会重新进行赋值,并且调用LinkedHashMapEntry.recordAccess()进行排序,排序方式如果是访问顺序(accessOrder==true),将会将其在链表中移除,然后添加到链尾部。最后在返回oldValue。
如果key不存在,则会调用LinkedHashMap.addEntry,先得到需要移除的对象,就是header.after,接着判断需要移除的对象是否是自身,如果不是自生并且removeEldestEntry()函数返回的是true的话,那么将会调用HashMap的removeEntryForKey移除。移除这里后面在讲。
接着调用HashMap.addEntry进行扩容,在调用LinkedHashMap.createEntry,这一步就是重新new一个HashMapEntry,添加到链尾就可以了。
如图所示:
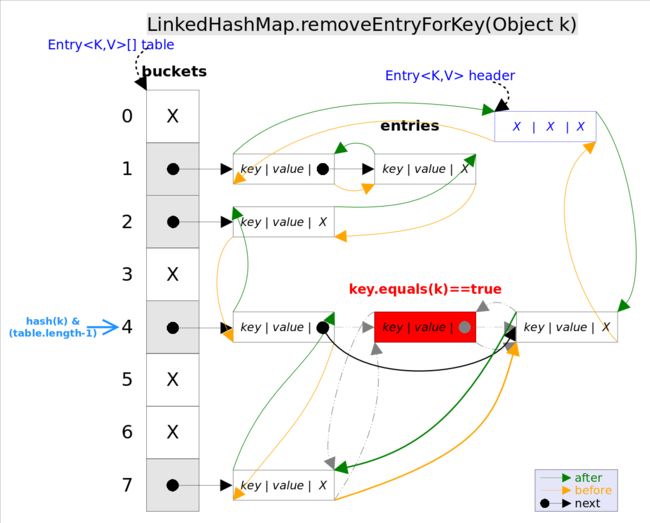
remove过程也是调用HashMap.remove,然后调用LinkedHashMapEntry.recordRemoval函数来进行删除
/**
* Removes the mapping for the specified key from this map if present.
*
* @param key key whose mapping is to be removed from the map
* @return the previous value associated with key, or
* null if there was no mapping for key.
* (A null return can also indicate that the map
* previously associated null with key.)
*/
public V remove(Object key) {
Entry e = removeEntryForKey(key);
return (e == null ? null : e.getValue());
}
/**
* Removes and returns the entry associated with the specified key
* in the HashMap. Returns null if the HashMap contains no mapping
* for this key.
*/
final Entry removeEntryForKey(Object key) {
if (size == 0) {
return null;
}
int hash = (key == null) ? 0 : sun.misc.Hashing.singleWordWangJenkinsHash(key);
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
HashMapEntry prev = table[i];
HashMapEntry e = prev;
while (e != null) {
HashMapEntry next = e.next;
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
modCount++;
size--;
if (prev == e)
table[i] = next;
else
prev.next = next;
//调用LinkedHashMapEntry.recordRemoval
e.recordRemoval(this);
return e;
}
prev = e;
e = next;
}
return e;
}
LinkedHashMapEntry中:
/**
* Removes this entry from the linked list.
*/
private void remove() {
before.after = after;
after.before = before;
}
void recordRemoval(HashMap m) {
remove();
}
很简单,就是进行一个指向。如图所示:
get
/**
* Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped,
* or {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key.
*
* More formally, if this map contains a mapping from a key
* {@code k} to a value {@code v} such that {@code (key==null ? k==null :
* key.equals(k))}, then this method returns {@code v}; otherwise
* it returns {@code null}. (There can be at most one such mapping.)
*
*
A return value of {@code null} does not necessarily
* indicate that the map contains no mapping for the key; it's also
* possible that the map explicitly maps the key to {@code null}.
* The {@link #containsKey containsKey} operation may be used to
* distinguish these two cases.
*/
public V get(Object key) {
//调用HashMap的getEntry
LinkedHashMapEntry e = (LinkedHashMapEntry)getEntry(key);
if (e == null)
return null;
e.recordAccess(this);
return e.value;
}
通过HashMap.getEntry获取对应的值,然后调用LinkedHashMapEntry.recordAccess排序。
有了LinkedHashMap的基础我们来看LruCache的源码就很好理解了
put
/**
* Caches {@code value} for {@code key}. The value is moved to the head of
* the queue.
*
* @return the previous value mapped by {@code key}.
*/
public final V put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null || value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null || value == null");
}
V previous;
synchronized (this) {
putCount++;
//根据key, value获取大小,我们需要重写sizeOf自行赋值
size += safeSizeOf(key, value);
//加入到LinkedHashMap
previous = map.put(key, value);
//如果key已经存在了previous 就!=null 就移除刚加的大小
if (previous != null) {
size -= safeSizeOf(key, previous);
}
}
if (previous != null) {
//重写移除的逻辑
entryRemoved(false, key, previous, value);
}
//根据maxSize去除多余的元素
trimToSize(maxSize);
return previous;
}
remove
/**
* Removes the entry for {@code key} if it exists.
*
* @return the previous value mapped by {@code key}.
*/
public final V remove(K key) {
if (key == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null");
}
V previous;
synchronized (this) {
//从LinkedHashMap中移除
previous = map.remove(key);
if (previous != null) {
size -= safeSizeOf(key, previous);
}
}
if (previous != null) {
entryRemoved(false, key, previous, null);
}
return previous;
}
get
/**
* Returns the value for {@code key} if it exists in the cache or can be
* created by {@code #create}. If a value was returned, it is moved to the
* head of the queue. This returns null if a value is not cached and cannot
* be created.
*/
public final V get(K key) {
if (key == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null");
}
V mapValue;
synchronized (this) {
//从LinkedHashMap中取出元素
mapValue = map.get(key);
if (mapValue != null) {
hitCount++;
return mapValue;
}
missCount++;
}
/*
* Attempt to create a value. This may take a long time, and the map
* may be different when create() returns. If a conflicting value was
* added to the map while create() was working, we leave that value in
* the map and release the created value.
*/
//如果没有这个key,那么你可以重写create来创建一个新的value
V createdValue = create(key);
if (createdValue == null) {
return null;
}
//新的创建的value 添加到LinkedHashMap
synchronized (this) {
createCount++;
mapValue = map.put(key, createdValue);
if (mapValue != null) {
// There was a conflict so undo that last put
map.put(key, mapValue);
} else {
size += safeSizeOf(key, createdValue);
}
}
if (mapValue != null) {
entryRemoved(false, key, createdValue, mapValue);
return mapValue;
} else {
trimToSize(maxSize);
return createdValue;
}
}
参考链接:
Java容器框架分析(七)——LinkedHashSet与LinkedHashMap
【Java集合源码剖析】LinkedHashmap源码剖析
水平有限,文中有什么不对或者有什么建议希望大家能够指出,谢谢!