前言
最近有很多朋友问我这个AIDL怎么用,也许由于是工作性质的原因,很多人都没有使用过aidl,所以和他们讲解完以后,感觉对方也是半懂不懂的,所以今天我就从浅到深的分析一下这个aidl具体是怎么用的,希望对大家有帮助。
作为一名合格Android开发人员,如果没听过Service,那就有点说不过去了啊,Service是Android四大组件之一,它是不依赖于用户界面的,就是因为Service不依赖与用户界面,所以我们常常用于进行一些耗时的操作,比如:下载数据等;
有些朋友可能是从事开发工作的时间不是特别的长,所以觉得Service相对与另外两个组件activity、broadcast receiver来说,使用可能并不是特别的多,所以对Service来说,理解不是特别的深入,只是有一个大概的概念,今天就和一块来走一下Service,希望能够帮助到大家对Service有更深入的理解。
Service基本用法——本地服务
我们知道服务分为本地服务和远程服务,而本地服务由于它的启动方式不一样,所以生命周期也就不一样,对Service生命周期不熟悉的朋友,自行去百度一下啊。好了,那么我们分别看一下两种不同的启动方式。我们先创建好Service:
ServiceTest.java
1 package com.example.administrator.servicetestaidl; 2 3 import android.app.Service; 4 import android.content.Intent; 5 import android.os.IBinder; 6 import android.support.annotation.IntDef; 7 import android.util.Log; 8 9 public class ServiceTest extends Service { 10 11 12 @Override 13 public void onCreate() { 14 super.onCreate(); 15 Log.d("ServiceTest"," -----> onCreate"); 16 } 17 18 19 @Override 20 public int onStartCommand(Intent intent,int flags, int startId) { 21 22 Log.d("ServiceTest"," -----> onStartCommand"); 23 24 return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId); 25 } 26 27 28 @Override 29 public void onDestroy() { 30 super.onDestroy(); 31 32 Log.d("ServiceTest"," -----> onDestroy"); 33 34 } 35 36 @Override 37 public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) { 38 // TODO: Return the communication channel to the service. 39 throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not yet implemented"); 40 } 41 }
在看看MainActivity的代码:
1 package com.example.administrator.servicetestaidl; 2 3 import android.app.Activity; 4 import android.content.Intent; 5 import android.os.Bundle; 6 import android.view.View; 7 import android.widget.Button; 8 9 public class MainActivity extends Activity { 10 private Button startService, stopService; 11 12 13 @Override 14 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { 15 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 16 setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); 17 18 startService = (Button) findViewById(R.id.start_service); 19 stopService = (Button) findViewById(R.id.stop_service); 20 21 22 /** 23 * 开启服务 24 */ 25 startService.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { 26 @Override 27 public void onClick(View v) { 28 Intent startService = new Intent(MainActivity.this,ServiceTest.class); 29 startService(startService); 30 31 } 32 }); 33 34 35 /** 36 * 停止服务 37 */ 38 stopService.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { 39 @Override 40 public void onClick(View v) { 41 Intent stopService = new Intent(MainActivity.this,ServiceTest.class); 42 stopService(stopService); 43 } 44 }); 45 46 47 } 48 }
布局activity_main
1 23 android:layout_width="match_parent" 4 android:layout_height="match_parent" 5 android:orientation="vertical"> 6 7 <Button 8 android:id="@+id/start_service" 9 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 10 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 11 android:text="开启服务" /> 12 13 <Button 14 android:id="@+id/stop_service" 15 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 16 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 17 android:text="停止服务" /> 18 19
配置文件AndroidManifest.xml
1 23 package="com.example.administrator.servicetestaidl"> 4 5 <application 6 android:allowBackup="true" 7 android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher" 8 android:label="@string/app_name" 9 android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round" 10 android:supportsRtl="true" 11 android:theme="@style/AppTheme"> 12 13 19 20 <service 21 android:name=".ServiceTest" 22 android:enabled="true" 23 android:exported="true"> 24 25 2614 1815 16 17
上面的代码很简单,并不难理解,在页面上加两个按钮,一个是启动服务,一个是销毁服务的,并且我们在ServiceTest里面的几个方法都加上了log,那我们点击开启服务,看看Log,如图:
然后我们多次点击开启服务,如图:
我们看到,后面即使多点几下这个开启服务,但是也只会调onStartCommand方法,onCreate方法并不会重复调用,那是因为我们点击Service,由于该service已经存在,所以并不会重新创建,所以onCreate方法只会调用一次。
我们还可以到手机的应用程序管理界面来检查一下Service是不是正在运行,如下图所示:
那当我们点击停止服务按钮呢,看看log:如图
![]()
这时候说明了服务已经销毁了。
有些朋友可能注意到了,我们刚刚那种启动服务的方式,好像除了对Service进行开启和销毁以外,很难在activity里进行对Service进行控制,什么意思呢?举个例子,如果说
我现在用Service进行下载某些东西,我现在在Service写有下载这两个东西的方法,方法a,方法b,那么我怎样在activity里面控制什么时候调用方法a,什么时候调用方法b呢,如果
按照原本的启动方式,好像并不好实现,或者说灵活性很差,那么有没有办法办到呢,接着看Service另一种启动方式
在前面我们有一个方法一直都没有动onBind方法,我们就从这个方法入手,先看ServiceTest代码:
1 package com.example.administrator.servicetestaidl; 2 3 import android.app.Service; 4 import android.content.Intent; 5 import android.os.Binder; 6 import android.os.IBinder; 7 import android.support.annotation.IntDef; 8 import android.util.Log; 9 10 public class ServiceTest extends Service { 11 12 13 @Override 14 public void onCreate() { 15 super.onCreate(); 16 Log.d("ServiceTest"," -----> onCreate"); 17 } 18 19 20 @Override 21 public int onStartCommand(Intent intent,int flags, int startId) { 22 23 Log.d("ServiceTest"," -----> onStartCommand"); 24 25 return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId); 26 } 27 28 29 @Override 30 public void onDestroy() { 31 super.onDestroy(); 32 33 Log.d("ServiceTest"," -----> onDestroy"); 34 35 } 36 37 @Override 38 public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) { 39 40 return new Mybind(); 41 } 42 43 44 class Mybind extends Binder{ 45 public void getString(){ 46 Log.d("ServiceTest"," -----> getString"); 47 } 48 } 49 50 51 52 }
在ServiceTest中增加了一个内部类Mybind,并且在Mybind中增加一个getString方法,在方法中打印log,然后在onBind方法中返回Mybind对象。
再看看MainActivity的代码
1 package com.example.administrator.servicetestaidl; 2 3 import android.app.Activity; 4 import android.content.ComponentName; 5 import android.content.Intent; 6 import android.content.ServiceConnection; 7 import android.os.Bundle; 8 import android.os.IBinder; 9 import android.view.View; 10 import android.widget.Button; 11 12 public class MainActivity extends Activity { 13 14 private Button startService,stopService,bindService,unbindService; 15 private ServiceTest.Mybind mybind; 16 17 18 private ServiceConnection connection = new ServiceConnection() { 19 @Override 20 public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) { 21 mybind = (ServiceTest.Mybind) service; 22 mybind.getString(); //获取到getString方法 23 } 24 25 @Override 26 public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) { 27 28 } 29 }; 30 31 32 33 34 @Override 35 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { 36 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 37 setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); 38 39 startService = (Button) findViewById(R.id.start_service); 40 stopService = (Button) findViewById(R.id.stop_service); 41 bindService = (Button) findViewById(R.id.bind_service); 42 unbindService = (Button) findViewById(R.id.unbind_service); 43 44 45 /** 46 * 开启服务 47 */ 48 startService.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { 49 @Override 50 public void onClick(View v) { 51 Intent startService = new Intent(MainActivity.this,ServiceTest.class); 52 startService(startService); 53 54 } 55 }); 56 57 58 /** 59 * 停止服务 60 */ 61 stopService.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { 62 @Override 63 public void onClick(View v) { 64 Intent stopService = new Intent(MainActivity.this,ServiceTest.class); 65 stopService(stopService); 66 } 67 }); 68 69 /** 70 * 绑定服务 71 */ 72 bindService.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { 73 @Override 74 public void onClick(View v) { 75 Intent bindService = new Intent(MainActivity.this,ServiceTest.class); 76 bindService(bindService,connection,BIND_AUTO_CREATE); 77 } 78 }); 79 80 /** 81 * 解绑服务 82 */ 83 unbindService.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { 84 @Override 85 public void onClick(View v) { 86 unbindService(connection); 87 } 88 }); 89 } 90 }
主页面布局:activity_main
1 23 android:layout_width="match_parent" 4 android:layout_height="match_parent" 5 android:orientation="vertical"> 6 7 <Button 8 android:id="@+id/start_service" 9 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 10 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 11 android:text="开启服务" /> 12 13 <Button 14 android:id="@+id/stop_service" 15 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 16 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 17 android:text="停止服务" /> 18 19 <Button 20 android:id="@+id/bind_service" 21 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 22 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 23 android:text="绑定服务" /> 24 25 <Button 26 android:id="@+id/unbind_service" 27 android:layout_width="wrap_content" 28 android:layout_height="wrap_content" 29 android:text="解绑服务" /> 30 31
可以看到,这里我们首先创建了一个ServiceConnection的匿名类,在里面重写了onServiceConnected()方法和onServiceDisconnected()方法,这两个方法分别会在Activity与Service建立关联和解除关联的时候调用。在onServiceConnected()方法中,我们又通过向下转型得到了MyBind的实例,有了这个实例,Activity和Service之间的关系就变得非常紧密了。现在我们可以在Activity中根据具体的场景来调用MyBind中的任何public方法,即实现了Activity指挥Service干什么Service就去干什么的功能。
当我们点击绑定服务的时候,结果如下,如图
点击解绑服务的时候,结果如下,如图
![]()
注意:Service 是运行在后台,没有可视化的页面,我们很多时候会把耗时的操作放在Service中执行,但是注意,Service是运行在主线程的,不是在子线程中,
Service和Thread没有半毛钱的关系,所以如果在Service中执行耗时操作,一样是需要开起线程,否则会引起ANR,这个需要区别开来。
好了~~~本地服务基本到这就结束,在后面我会将本地服务这部分代码的链接发出来,需要的可以进行下载~~
远程服务 —— AIDL
AIDL(Android Interface Definition Language)是Android接口定义语言的意思,它可以用于让某个Service与多个应用程序组件之间进行跨进程通信,从而可以实现多个应用程序共享同一个Service的功能。实际上实现跨进程之间通信的有很多,
比如广播,Content Provider,但是AIDL的优势在于速度快(系统底层直接是共享内存),性能稳,效率高,一般进程间通信就用它。
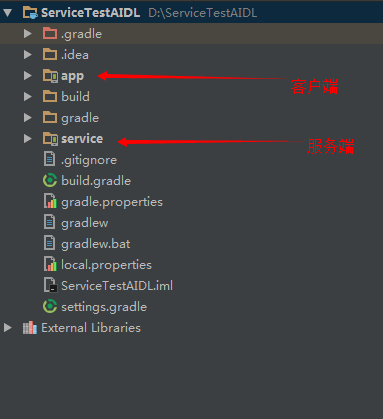
既然是跨进程,那必须的有两个应用,一个是service端,一个是client端,然后实现客户端从服务端获取数据。那么我们创建一个服务端,项目结构如图所示:
服务端
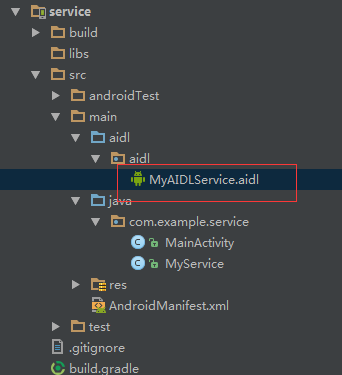
我们在服务端下建立一个MyAIDLService.aidl文件,目录结构为如图所示:
然后,我们在MyAIDLService下增加一个获取字符串的方法。代码如下:(注:刚刚建立的aidl文件中存在一个方法,那个方法可以忽略,可以删掉不要)
1 // MyAIDLService.aidl 2 package aidl; 3 4 // Declare any non-default types here with import statements 5 6 interface MyAIDLService { 7 //获取String数据 8 String getString(); 9 }
创建完aidl文件以后,我们build一下项目,然后会在build - >generated ->source ->aidl->debug下会生成一个aidl文件,那说明AIDL文件已经编译成功。
接着建立一个MyService类,代码如下:
1 package com.example.service; 2 3 import android.app.Service; 4 import android.content.Intent; 5 import android.os.Binder; 6 import android.os.IBinder; 7 import android.os.RemoteException; 8 import android.util.Log; 9 10 import java.util.Map; 11 12 import aidl.MyAIDLService; 13 14 public class MyService extends Service { 15 16 @Override 17 public void onCreate() { 18 super.onCreate(); 19 } 20 21 22 @Override 23 public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) { 24 return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId); 25 } 26 27 28 @Override 29 public void onDestroy() { 30 super.onDestroy(); 31 } 32 33 @Override 34 public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) { 35 return new Mybind(); 36 } 37 38 class Mybind extends MyAIDLService.Stub { 39 40 @Override 41 public String getString() throws RemoteException { 42 String string = "我是从服务起返回的"; 43 44 return string; 45 } 46 } 47 }
代码看起来是不是很熟悉,唯一不一样的就是原来在本地服务的时候内部类继承的是Binder,而现在继承的是MyAIDLService.Stub,继承的是我们刚刚建立的aidl文件,然后实现我们刚刚的定义的
getString()方法,在这里,我们只是返回一句话,"我是从服务起返回的"~~~~~~~~~~~
客户端
首先将刚刚在服务端创建的MyAIDLService原封不动的复制到客户端来。(注意:路径要一模一样)。接着我们在客户端的MainActivity中加两个按钮,并且和服务端进行相连,代码如下:
MainActivity
1 package com.example.administrator.servicetestaidl; 2 3 import android.app.Activity; 4 import android.content.ComponentName; 5 import android.content.Intent; 6 import android.content.ServiceConnection; 7 import android.os.Bundle; 8 import android.os.IBinder; 9 import android.os.RemoteException; 10 import android.view.View; 11 import android.widget.Button; 12 import android.widget.TextView; 13 14 import aidl.MyAIDLService; 15 16 public class MainActivity extends Activity { 17 18 private Button bindService,unbindService; 19 private TextView tvData; 20 private MyAIDLService myAIDLService; 21 22 23 private ServiceConnection connection = new ServiceConnection() { 24 @Override 25 public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) { 26 myAIDLService = MyAIDLService.Stub.asInterface(service); 27 try { 28 String str = myAIDLService.getString(); 29 tvData.setText(str); 30 } catch (RemoteException e) { 31 e.printStackTrace(); 32 } 33 } 34 35 @Override 36 public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) { 37 myAIDLService = null; 38 } 39 }; 40 41 42 43 44 @Override 45 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { 46 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 47 setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); 48 49 bindService = (Button) findViewById(R.id.bind_service); 50 unbindService = (Button) findViewById(R.id.unbind_service); 51 tvData = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv_data); 52 53 54 /** 55 * 绑定服务 56 */ 57 bindService.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { 58 @Override 59 public void onClick(View v) { 60 Intent intent = new Intent(); 61 intent.setAction("com.example.service.MyService"); 62 //从 Android 5.0开始 隐式Intent绑定服务的方式已不能使用,所以这里需要设置Service所在服务端的包名 63 intent.setPackage("com.example.service"); 64 bindService(intent, connection, BIND_AUTO_CREATE); 65 66 67 68 } 69 }); 70 71 /** 72 * 解绑服务 73 */ 74 unbindService.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { 75 @Override 76 public void onClick(View v) { 77 unbindService(connection); 78 } 79 }); 80 } 81 }
大家是不是感觉和连接本地服务的代码差不多,没错,这里只需要注意两个地方,一个是绑定服务的时候,因为从 Android 5.0开始 隐式Intent绑定服务的方式已不能使用,所以这里需要设置Service所在服务端的包名
那么这个action是怎么来的呢,我们回来服务端的AndroidManifest.xml,代码如下
1 23 package="com.example.service"> 4 5 <application 6 android:allowBackup="true" 7 android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher" 8 android:label="@string/app_name" 9 android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round" 10 android:supportsRtl="true" 11 android:theme="@style/AppTheme"> 12 13 19 20 <service 21 android:name=".MyService" 22 > 2314 1815 16 17 24 26 27 28 29 3025
另一个需要注意的就是获取MyAIDLService对象是通过MyAIDLService.Stub.asInterface(service);这里大家需要注意一下的。
不过还有一点需要说明的是,由于这是在不同的进程之间传递数据,Android对这类数据的格式支持是非常有限的,
基本上只能传递Java的基本数据类型、字符串、List或Map等。那么如果我想传递一个自定义的类该怎么办呢?这就必须要让这个类去实现Parcelable接口,
并且要给这个类也定义一个同名的AIDL文件。这部分内容并不复杂,而且和Service关系不大,所以就不再详细进行讲解了,感兴趣的朋友可以自己去查阅一下相关的资料。
注意:从服务器复制过来的aidl文件不能直接放到Java文件夹下面,必须建立一个aidl文件夹存放,否则会编译不成功
好了,到这里,基本上就结束了,附上一张效果图:
最后附上源码链接
本地服务源码:https://github.com/343661629/nativeService
远程服务源码:https://github.com/343661629/remoteService