C#动态数据集合ObservableCollection的三种排序方式
WPF中对ListBox、ListView、TreeView等实现数据双向绑定经常会用到ObservableCollection
ObservableCollection
ObservableCollection没有自带的sort排序功能,而实际使用时我们经常需要对数据集合进行排序后再显示,比如按照ID从小到大排序,或者按照禁用状态排序(可用的排在前面)等等。下面新建一个控制台应用程序SortDemo:
1、新建商品类Goods
//商品类
public class Goods
{
public int Order { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public bool IsSoldOut { get; set; }
}2、第一种排序方式
ocGoods = new ObservableCollection
程序代码:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ObservableCollection ocGoods = new ObservableCollection();
ocGoods.Add(new Goods() { Order = 1, Name = "钢笔", IsSoldOut = true });
ocGoods.Add(new Goods() { Order = 2, Name = "羽毛球", IsSoldOut = false });
ocGoods.Add(new Goods() { Order = 3, Name = "毛巾", IsSoldOut = false });
ocGoods.Add(new Goods() { Order = 4, Name = "零食", IsSoldOut = true });
//按照IsSoldOut降序排列,即true在前面
ocGoods = new ObservableCollection(ocGoods.OrderByDescending(item => item.IsSoldOut));
foreach (Goods item in ocGoods)
{
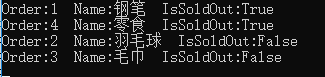
Console.WriteLine("Order:{0} Name:{1} IsSoldOut:{2}", item.Order, item.Name, item.IsSoldOut.ToString());
}
Console.ReadLine();
} 结果:
2、第二种排序方式
自己写一个Sort扩展方法:
public static class ObservableExtension
{
public static void Sort(this ObservableCollection collection) where T : IComparable
{
List sortedList = collection.OrderByDescending(x => x).ToList();//这里用降序
for (int i = 0; i < sortedList.Count(); i++)
{
collection.Move(collection.IndexOf(sortedList[i]), i);
}
}
} 调用的时候报错:
原来是Goods类没有实现IComparable
//商品类
public class Goods : IComparable
{
public int Order { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public bool IsSoldOut { get; set; }
public int CompareTo(Goods other)
{
return this.IsSoldOut.CompareTo(other.IsSoldOut);
}
} 程序代码:
namespace SortDemo
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ObservableCollection ocGoods = new ObservableCollection();
ocGoods.Add(new Goods() { Order = 1, Name = "钢笔", IsSoldOut = true });
ocGoods.Add(new Goods() { Order = 2, Name = "羽毛球", IsSoldOut = false });
ocGoods.Add(new Goods() { Order = 3, Name = "毛巾", IsSoldOut = false });
ocGoods.Add(new Goods() { Order = 4, Name = "零食", IsSoldOut = true });
ocGoods.Sort();//第二种方法
foreach (Goods item in ocGoods)
{
Console.WriteLine("Order:{0} Name:{1} IsSoldOut:{2}", item.Order, item.Name, item.IsSoldOut.ToString());
}
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
//商品类
public class Goods : IComparable
{
public int Order { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public bool IsSoldOut { get; set; }
public int CompareTo(Goods other)
{
return this.IsSoldOut.CompareTo(other.IsSoldOut);
}
}
public static class ObservableExtension
{
public static void Sort(this ObservableCollection collection) where T : IComparable
{
List sortedList = collection.OrderByDescending(x => x).ToList();//这里用降序
for (int i = 0; i < sortedList.Count(); i++)
{
collection.Move(collection.IndexOf(sortedList[i]), i);
}
}
}
} 3、第三种排序方式
第二种方式的实质是使用List的特性,那么如果直接用List的Sort排序特性,则不用单独再实现IComparable接口。这里的思路是建一个List
static void Main(string[] args)
{
List goodsList = new List();
goodsList.Add(new Goods() { Order = 1, Name = "钢笔", IsSoldOut = true });
goodsList.Add(new Goods() { Order = 2, Name = "羽毛球", IsSoldOut = false });
goodsList.Add(new Goods() { Order = 3, Name = "毛巾", IsSoldOut = false });
goodsList.Add(new Goods() { Order = 4, Name = "零食", IsSoldOut = true });
goodsList.Sort(delegate (Goods b1, Goods b2) { return Comparer.Default.Compare(b2.IsSoldOut, b1.IsSoldOut); });
ObservableCollection ocGoods = new ObservableCollection(goodsList);
foreach (Goods item in ocGoods)
{
Console.WriteLine("Order:{0} Name:{1} IsSoldOut:{2}", item.Order, item.Name, item.IsSoldOut.ToString());
}
Console.ReadLine();
}