lodash
获取地址
文档地址
中文api地址
一.“Array” 方法:
_.compact(array)
作用:创建一个新数组,包含原数组中所有的非假值元素。例如false, null, 0, "", undefined, 和 NaN 都是被认为是“假值”。
例如:
var arr = [2, 2, 1, 3, 2, 4, 22, false, 0, 100]
arr = _.compact(arr);
console.log(arr) //[2, 2, 1, 3, 2, 4, 22, 100]
_.uniq(array)
作用:去重,创建一个去重后的array数组副本。使用了 SameValueZero 做等值比较。只有第一次出现的元素才会被保留。
例如:
var arr = [2, 2, 1, 3, 2, 4, 22, false, 0, 100]
arr = _.uniq(arr);
console.log(arr) //[2, 1, 3, 4, 22, false, 0, 100]
很多情况可以将 _.compact和_.uniq配合使用,已得到一个去重的,去除假值的数据
针对数组对象去重:
场景:需要将数组对象中TeamId属性值相同的去重
var arr = [{'TeamId',1},{'TeamId',3},{'TeamId',2},{'TeamId',4},{'TeamId',1}]
var newarr = _.uniqBy(arr , 'TeamId');
_.uniqBy([2.1, 1.2, 2.3], Math.floor);
// => [2.1, 1.2]
// The `_.property` iteratee shorthand.
_.uniqBy([{ 'x': 1 }, { 'x': 2 }, { 'x': 1 }], 'x');
// => [{ 'x': 1 }, { 'x': 2 }]
_.findIndex(array, [predicate=_.identity], [fromIndex=0])
作用:该方法类似_.find,区别是该方法返回第一个通过 predicate 判断为真值的元素的索引值(index),而不是元素本身。
参数
array(Array): 要搜索的数组。[predicate=_.identity](Array|Function|Object|string): 这个函数会在每一次迭代调用。[fromIndex=0](number): The index to search from.
返回值
(number): 返回找到元素的 索引值(index),否则返回 -1。
var users = [
{ 'user': 'barney', 'active': false },
{ 'user': 'fred', 'active': false },
{ 'user': 'pebbles', 'active': true }
];
_.findIndex(users, function(o) { return o.user == 'barney'; });
// => 0
// The `_.matches` iteratee shorthand.
_.findIndex(users, { 'user': 'fred', 'active': false });
// => 1
// The `_.matchesProperty` iteratee shorthand.
_.findIndex(users, ['active', false]);
// => 0
// The `_.property` iteratee shorthand.
_.findIndex(users, 'active');
// => 2
_.findLastIndex(array, [predicate=_.identity], [fromIndex=array.length-1])
这个方式类似 _.findIndex, 区别是它是从右到左的迭代集合array中的元素。 找到最后一个,从后往前找
_.indexOf(array, value, [fromIndex=0])
作用:使用 SameValueZero 等值比较,返回首次 value 在数组array中被找到的 索引值, 如果 fromIndex 为负值,将从数组array尾端索引进行匹配。
参数
array(Array): 需要查找的数组。value(*): 需要查找的值。[fromIndex=0](number): 开始查询的位置。
返回值
(number): 返回 值value在数组中的索引位置, 没有找到为返回-1。
_.indexOf([1, 2, 1, 2], 2);
// => 1
// Search from the `fromIndex`.
_.indexOf([1, 2, 1, 2], 2, 2);
// => 3
if (_.indexOf(hero_data.raceIdList, race_data.raceId) === -1) {//等于-1说明没有找到这一项
arr.push(2)
}
_.lastIndexOf(array, value, [fromIndex=array.length-1])
作用:这个方法类似 _.indexOf ,区别是它是从右到左遍历array的元素。
参数
array(Array): 要搜索的数组。value(*): 要搜索的值。[fromIndex=array.length-1](number): 开始搜索的索引值。
返回值
(number): 返回匹配值的索引值,否则返回 -1。
_.lastIndexOf([1, 2, 1, 2], 2);
// => 3
// Search from the `fromIndex`.
_.lastIndexOf([1, 2, 1, 2], 2, 2);
// => 1
二.“集合” 方法(“Collection” Methods):
_.flatMap(collection, [iteratee=_.identity])
作用:创建一个扁平化(注:同阶数组)的数组,这个数组的值来自collection(集合)中的每一个值经过 iteratee(迭代函数) 处理后返回的结果,并且扁平化合并。 iteratee 调用三个参数: (value, index|key, collection)。
参数
collection(Array|Object): 一个用来迭代遍历的集合。[iteratee=_.identity](Array|Function|Object|string): 每次迭代调用的函数。
返回
(Array): 返回新扁平化数组。
例如:想得到一个新数组,由一个数组对象中所有的hero_id组成
var arr = [
{ TFTID: "175", hero_id: "1" },
{ TFTID: "175", hero_id: "2" },
{ TFTID: "175", hero_id: "4" },
{ TFTID: "175", hero_id: "5" },
{ TFTID: "175", hero_id: "7" },
{ TFTID: "175", hero_id: "7" }
];
var newarr = _.flatMap(arr, function test(n){
return n.hero_id});
console.log(arr)
console.log(newarr) //获取到所有的hero_id ["1", "2", "4", "5", "7", "7"]
如果需求是将这些数组对象中的没个对象,添加一个type=1,则可以这样写:
var arr = [
{ TFTID: "175", hero_id: "1" },
{ TFTID: "175", hero_id: "2" },
{ TFTID: "175", hero_id: "4" },
{ TFTID: "175", hero_id: "5" },
{ TFTID: "175", hero_id: "7" },
{ TFTID: "175", hero_id: "7" }
];
var newarr = _.flatMap(arr, function (n){
n['type']=1;
return n
});
console.log(arr)
console.log(newarr)
_.flatMap配合_.find的使用规则:相当于双重遍历的效果,将chessId等于hero_id_list某项的对象存为一个新数组
var hero_id_list = ['6', '1', '2', '9', '7', '8']
var hero_data_all = [
{ 'chessId': '6', 'type': 1 },
{ 'chessId': '1', 'type': 1 },
{ 'chessId': '2', 'type': 1 },
{ 'chessId': '9', 'type': 1 },
{ 'chessId': '7','type': 1 },
{ 'chessId': '8','type': 1 },
{ 'chessId': '11','type': 1 },
{ 'chessId': '81','type': 1 }
]
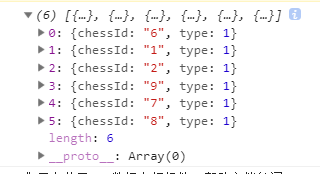
var hero_data_List = _.flatMap(hero_id_list, function(hero_id) {
//找到这个英雄id对应英雄数据
return _.find(hero_data_all, { chessId: '' + hero_id });
});
console.log(hero_data_List)得到的结果是:
_.sample(collection)
作用:从collection(集合)中获得一个随机元素。
例如:随机取数组【1,2,3,4】中的一项
_.sample([1, 2, 3, 4]);
// => 2
如果需要取的是数组对象中的某个属性值作为随机元素,则:
var arr = [
{ TFTID: "175", hero_id: "1" },
{ TFTID: "171", hero_id: "2" },
{ TFTID: "170", hero_id: "4" },
{ TFTID: "172", hero_id: "5" },
{ TFTID: "173", hero_id: "7" },
{ TFTID: "174", hero_id: "7" }
];
arr = _.sample(arr).TFTID
console.log(arr)
_.find(collection, [predicate=_.identity], [fromIndex=0])
作用:遍历 collection(集合)元素,返回 predicate(断言函数)第一个返回真值的第一个元素。predicate(断言函数)调用3个参数: (value, index|key, collection)。
参数
collection(Array|Object): 一个用来迭代的集合。[predicate=_.identity](Array|Function|Object|string): 每次迭代调用的函数。[fromIndex=0](number): 开始搜索的索引位置。
返回
(*): 有的话则返回第一个返回真值的第一个元素;无的话则返回 undefined。
例子:
var users = [
{ 'user': 'barney', 'age': 36, 'active': true },
{ 'user': 'fred', 'age': 40, 'active': false },
{ 'user': 'pebbles', 'age': 1, 'active': true }
];
_.find(users, function(o) { return o.age < 40; });
// => object for 'barney' 'age': 36
// The `_.matches` iteratee shorthand.
_.find(users, { 'age': 1, 'active': true });
// => object for 'pebbles'
// The `_.matchesProperty` iteratee shorthand.
_.find(users, ['active', false]);
// => object for 'fred'
// The `_.property` iteratee shorthand.
_.find(users, 'active');
// => object for 'barney'
默认第三个参数不传,都是从集合的0项开始从头往后找,如果想要从后往前找的话,在加一个参数:
这里加上了users.length-1,则从后往前找
var users = [
{ 'user': 'barney', 'age': 36, 'active': true },
{ 'user': 'fred', 'age': 40, 'active': false },
{ 'user': 'pebbles', 'age': 1, 'active': true }
];
_.find(users, function(o) { return o.age < 40; },users.length-1);
// => object for 'pebbles' 'age': 1
_.findLast(collection, [predicate=_.identity], [fromIndex=collection.length-1])
作用:这个方法类似_.find ,不同之处在于,_.findLast是从右至左遍历collection (集合)元素的。
参数
collection(Array|Object): 一个用来迭代的集合。[predicate=_.identity](Array|Function|Object|string): 每次迭代调用的函数。[fromIndex=collection.length-1](number): 开始搜索的索引位置。
返回
(*): 返回匹配元素,否则返回 undefined。
_.findLast([1, 2, 3, 4], function(n) {
return n % 2 == 1;
});
// => 3