Netty——基本使用介绍
1.为什么选择Netty
上一篇文章我们已经了解了Socket通信(IO/NIO/AIO)编程,对于通信模型已经有了一个基本的认识。其实上一篇文章中,我们学习的仅仅是一个模型,如果想把这些真正的用于实际工作中,那么还需要不断的完善、扩展和优化。比如经典的TCP读包写包问题,或者是数据接收的大小,实际的通信处理与应答的处理逻辑等等一些细节问题需要认真的去思考,而这些都需要大量的时间和经历,以及丰富的经验。所以想学好Socket通信不是件容易事,那么接下来就来学习一下新的技术Netty,为什么会选择Netty?因为它简单!使用Netty不必编写复杂的逻辑代码去实现通信,再也不需要去考虑性能问题,不需要考虑编码问题,半包读写等问题。强大的Netty已经帮我们实现好了,我们只需要使用即可。
Netty是最流行的NIO框架,它的健壮性、功能、性能、可定制性和可扩展性在同类框架都是首屈一指的。它已经得到成百上千的商业/商用项目验证,如Hadoop的RPC框架Avro、RocketMQ以及主流的分布式通信框架Dubbox等等。
2.Netty简介
Netty是基于Java NIO client-server的网络应用框架,使用Netty可以快速开发网络应用,例如服务器和客户端协议。Netty提供了一种新的方式来开发网络应用程序,这种新的方式使它很容易使用和具有很强的扩展性。Netty的内部实现是很复杂的,但是Netty提供了简单易用的API从网络处理代码中解耦业务逻辑。Netty是完全基于NIO实现的,所以整个Netty都是异步的。
网络应用程序通常需要有较高的可扩展性,无论是Netty还是其他的基于Java Nio的框架,都会提供可扩展性的解决方案。Netty中一个关键组成部分是它的异步特性,本片文章将讨论同步(阻塞)和异步(非阻塞)的IO来说明为什么使用异步代码解决扩展性问题以及如何使用异步。
3.Netty架构组成(借用一下网上的图片)
![]()
Netty实现原理浅析,写的很不错,感兴趣的可以看一下。
4.Helloworld入门
在学习Netty之前,先来回顾一下NIO的通信步骤:
①创建ServerSocketChannel,为其配置非阻塞模式。
②绑定监听,配置TCP参数,录入backlog大小等。
③创建一个独立的IO线程,用于轮询多路复用器Selector。
④创建Selector,将之前创建的ServerSocketChannel注册到Selector上,并设置监听标识位SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT。
⑤启动IO线程,在循环体中执行Selector.select()方法,轮询就绪的通道。
⑥当轮询到处于就绪状态的通道时,需要进行操作位判断,如果是ACCEPT状态,说明是新的客户端接入,则调用accept方法接收新的客户端。
⑦设置新接入客户端的一些参数,如非阻塞,并将其继续注册到Selector上,设置监听标识位等。
⑧如果轮询的通道标识位是READ,则进行读取,构造Buffer对象等。
⑨更细节的问题还有数据没发送完成继续发送的问题......
好啦,开始学习Netty了。先去http://netty.io/上下载所有的Netty包。
Netty通信的步骤:
①创建两个NIO线程组,一个专门用于网络事件处理(接受客户端的连接),另一个则进行网络通信的读写。
②创建一个ServerBootstrap对象,配置Netty的一系列参数,例如接受传出数据的缓存大小等。
③创建一个用于实际处理数据的类ChannelInitializer,进行初始化的准备工作,比如设置接受传出数据的字符集、格式以及实际处理数据的接口。
④绑定端口,执行同步阻塞方法等待服务器端启动即可。
强烈推荐读一读Netty官方翻译文档。
好了,说了那么多,下面就来HelloWorld入门吧!
服务器端:
public class Server {
private int port;
public Server(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
public void run() {
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); //用于处理服务器端接收客户端连接
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); //进行网络通信(读写)
try {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap(); //辅助工具类,用于服务器通道的一系列配置
bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) //绑定两个线程组
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) //指定NIO的模式
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer() { //配置具体的数据处理方式
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new ServerHandler());
}
})
/**
* 对于ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG的解释:
* 服务器端TCP内核维护有两个队列,我们称之为A、B队列。客户端向服务器端connect时,会发送带有SYN标志的包(第一次握手),服务器端
* 接收到客户端发送的SYN时,向客户端发送SYN ACK确认(第二次握手),此时TCP内核模块把客户端连接加入到A队列中,然后服务器接收到
* 客户端发送的ACK时(第三次握手),TCP内核模块把客户端连接从A队列移动到B队列,连接完成,应用程序的accept会返回。也就是说accept
* 从B队列中取出完成了三次握手的连接。
* A队列和B队列的长度之和就是backlog。当A、B队列的长度之和大于ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG时,新的连接将会被TCP内核拒绝。
* 所以,如果backlog过小,可能会出现accept速度跟不上,A、B队列满了,导致新的客户端无法连接。要注意的是,backlog对程序支持的
* 连接数并无影响,backlog影响的只是还没有被accept取出的连接
*/
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128) //设置TCP缓冲区
.option(ChannelOption.SO_SNDBUF, 32 * 1024) //设置发送数据缓冲大小
.option(ChannelOption.SO_RCVBUF, 32 * 1024) //设置接受数据缓冲大小
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true); //保持连接
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind(port).sync();
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Server(8379).run();
}
}
ServerHandler类:
public class ServerHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
//do something msg
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf)msg;
byte[] data = new byte[buf.readableBytes()];
buf.readBytes(data);
String request = new String(data, "utf-8");
System.out.println("Server: " + request);
//写给客户端
String response = "我是反馈的信息";
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("888".getBytes()));
//.addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
}客户端:
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(workerGroup)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new ClientHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1", 8379).sync();
future.channel().writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("777".getBytes()));
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
} ClientHandler类:
public class ClientHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
try {
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
byte[] data = new byte[buf.readableBytes()];
buf.readBytes(data);
System.out.println("Client:" + new String(data).trim());
} finally {
ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg);
}
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
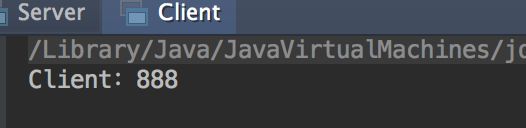
}运行结果:
5.TCP粘包、拆包问题
熟悉TCP编程的可能都知道,无论是服务器端还是客户端,当我们读取或者发送数据的时候,都需要考虑TCP底层的粘包/拆包机制。
TCP是一个“流”协议,所谓流就是没有界限的遗传数据。大家可以想象一下,如果河水就好比数据,他们是连成一片的,没有分界线,TCP底层并不了解上层业务数据的具体含义,它会根据TCP缓冲区的具体情况进行包的划分,也就是说,在业务上一个完整的包可能会被TCP分成多个包进行发送,也可能把多个小包封装成一个大的数据包发送出去,这就是所谓的粘包/拆包问题。
解决方案:
①消息定长,例如每个报文的大小固定为200个字节,如果不够,空位补空格。
②在包尾部增加特殊字符进行分割,例如加回车等。
③将消息分为消息头和消息体,在消息头中包含表示消息总长度的字段,然后进行业务逻辑的处理。
Netty中解决TCP粘包/拆包的方法:
①分隔符类:DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder(自定义分隔符)
②定长:FixedLengthFrameDecoder
6.Netty编解码技术
通常我们也习惯将编码(Encode)成为序列化,它将数据序列化为字节数组,用于网络传输、数据持久化或者其他用途。反之,解码(Decode)/反序列化(deserialization)
把从网络、磁盘等读取的字节数组还原成原始对象(通常是原始对象的拷贝),以方便后续的业务逻辑操作。进行远程跨进程服务调用时(例如RPC调用),需要使用特定的编解码技术,对需要进行网络传输的对象做编码或者解码,以便完成远程调用。
主流的编解码框架:
①JBoss的Marshalling包
②google的Protobuf
③基于Protobuf的Kyro
④MessagePack框架
上代码,一读就懂,注意红色字体部分。
服务器端:
public class Server {
public Server(int port) {
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = newNioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = newNioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = newServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.handler(newLoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))
.childHandler(newChannelInitializer
@Override
protected voidinitChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(MarshallingCodeCFactory.buildMarshallingDecoder());
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(MarshallingCodeCFactory.buildMarshallingEncoder());
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new ServerHandler());
}
})
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG,1024)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_RCVBUF, 32 * 1024)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_SNDBUF, 32 * 1024)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true);
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind(port).sync();
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Server(8765);
}
}
ServerHandler类:
public classServerHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public voidexceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
@Override
public voidchannelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
super.channelActive(ctx);
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContextctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
Request request = (Request) msg;
System.out.println("Server:"+ request.getId() + "," + request.getName() + "," +request.getReqeustMessag());
Response response = new Response();
response.setId(request.getId());
response.setName("response "+ request.getId());
response.setResponseMessage("响应内容:" +request.getReqeustMessag());
byte[] unGizpData =GzipUtils.unGzip(request.getAttachment());
char separator = File.separatorChar;
FileOutputStream outputStream = newFileOutputStream(System.getProperty("user.dir") + separator +"recieve" + separator + "1.png");
outputStream.write(unGizpData);
outputStream.flush();
outputStream.close();
ctx.writeAndFlush(response);
}
}
客户端:
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = newNioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(workerGroup)
.handler(newLoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(newChannelInitializer
@Override
protected voidinitChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(MarshallingCodeCFactory.buildMarshallingEncoder());
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(MarshallingCodeCFactory.buildMarshallingDecoder());
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new ClientHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture future =bootstrap.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.01", 8765)).sync();
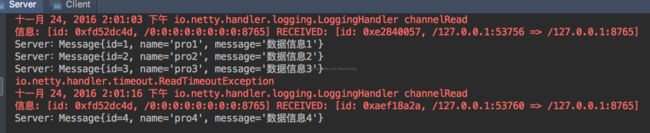
for(int i=1; i<=5; i++) {
Request request = newRequest();
request.setId(i);
request.setName("pro"+ i);
request.setReqeustMessag("数据信息" + i);
//传输图片
char separator =File.separatorChar;
File file = newFile(System.getProperty("user.dir") + separator + "source"+ separator + "2.jpg");
FileInputStream inputStream = newFileInputStream(file);
byte[] data = newbyte[inputStream.available()];
inputStream.read(data);
inputStream.close();
byte[] gzipData =GzipUtils.gzip(data);
request.setAttachment(gzipData);
future.channel().writeAndFlush(request);
}
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
ClientHandler类:
public classClientHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
@Override
public voidexceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
super.exceptionCaught(ctx, cause);
}
@Override
public voidchannelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
super.channelActive(ctx);
}
@Override
public voidchannelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
Response response = (Response) msg;
System.out.println("Client:"+ response.getId() + "," + response.getName() + "," +response.getResponseMessage());
}
}
Marshalling工具类:
public final classMarshallingCodeCFactory {
/**
* 创建Jboss Marshalling解码器MarshallingDecoder
* @return MarshallingDecoder
*/
public static MarshallingDecoderbuildMarshallingDecoder() {
//首先通过Marshalling工具类的精通方法获取Marshalling实例对象 参数serial标识创建的是java序列化工厂对象。
final MarshallerFactorymarshallerFactory =Marshalling.getProvidedMarshallerFactory("serial");
//创建了MarshallingConfiguration对象,配置了版本号为5
final MarshallingConfigurationconfiguration = new MarshallingConfiguration();
configuration.setVersion(5);
//根据marshallerFactory和configuration创建provider
UnmarshallerProvider provider= new DefaultUnmarshallerProvider(marshallerFactory, configuration);
//构建Netty的MarshallingDecoder对象,俩个参数分别为provider和单个消息序列化后的最大长度
MarshallingDecoder decoder =new MarshallingDecoder(provider, 1024 * 1024);
return decoder;
}
/**
* 创建Jboss Marshalling编码器MarshallingEncoder
* @return MarshallingEncoder
*/
public static MarshallingEncoderbuildMarshallingEncoder() {
final MarshallerFactorymarshallerFactory =Marshalling.getProvidedMarshallerFactory("serial");
final MarshallingConfigurationconfiguration = new MarshallingConfiguration();
configuration.setVersion(5);
MarshallerProvider provider =new DefaultMarshallerProvider(marshallerFactory, configuration);
//构建Netty的MarshallingEncoder对象,MarshallingEncoder用于实现序列化接口的POJO对象序列化为二进制数组
MarshallingEncoder encoder =new MarshallingEncoder(provider);
return encoder;
}
}
Gizp压缩与解压缩工具类:
public classGzipUtils {
public static byte[] gzip(byte[] val)throws IOException {
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = newByteArrayOutputStream(val.length);
GZIPOutputStream gos = null;
try {
gos = new GZIPOutputStream(bos);
gos.write(val, 0, val.length);
gos.finish();
gos.flush();
bos.flush();
val = bos.toByteArray();
} finally {
if (gos != null)
gos.close();
if (bos != null)
bos.close();
}
return val;
}
public static byte[] unGzip(byte[] buf)throws IOException {
GZIPInputStream gzi = null;
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = null;
try {
gzi = new GZIPInputStream(newByteArrayInputStream(buf));
bos = newByteArrayOutputStream(buf.length);
int count = 0;
byte[] tmp = new byte[2048];
while ((count = gzi.read(tmp)) !=-1) {
bos.write(tmp, 0, count);
}
buf = bos.toByteArray();
} finally {
if (bos != null) {
bos.flush();
bos.close();
}
if (gzi != null)
gzi.close();
}
return buf;
}
}
7.最佳实践
(1)数据通信
我们需要了解在真正项目中如何使用Netty,大体上对于一些参数设置都是根据服务器性能决定的。我们需要考虑的问题是两台机器(甚至多台)使用Netty怎样进行通信。
大体上分为三种:
①使用长连接通道不断开的形式进行通信,也就是服务器和客户端的通道一直处于开启状态,如果服务器性能足够好,并且客户端数量也比较上的情况下,推荐这种方式。
②一次性批量提交数据,采用短连接方式。也就是说先把数据保存到本地临时缓存区或者临时表,当达到界值时进行一次性批量提交,又或者根据定时任务轮询提交,
这种情况的弊端是做不到实时性传输,对实时性要求不高的应用程序中推荐使用。
③使用一种特殊的长连接,在某一指定时间段内,服务器与某台客户端没有任何通信,则断开连接。下次连接则是客户端向服务器发送请求的时候,再次建立连接。
在这里将介绍使用Netty实现第三种方式的连接,但是我们需要考虑两个因素:
①如何在超时(即服务器和客户端没有任何通信)后关闭通道?关闭通道后又如何再次建立连接?
②客户端宕机时,我们无需考虑,下次重启客户端之后就可以与服务器建立连接,但服务器宕机时,客户端如何与服务器端通信?
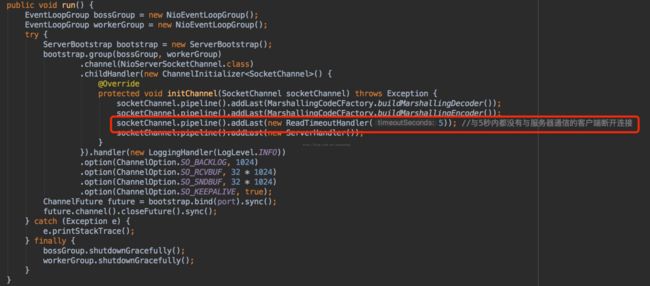
服务器端:增加了红色框部分
客户端(注意红色字体部分):
public class Client {
private static class SingleHodler {
static final Client client = newClient();
}
public static Client getInstance() {
return SingleHodler.client;
}
private EventLoopGroup workerGroup;
private Bootstrap bootstrap;
private ChannelFuture future;
private Client() {
workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(workerGroup)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(newChannelInitializer
@Override
protected voidinitChannel(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws Exception {
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(MarshallingCodeCFactory.buildMarshallingEncoder());
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(MarshallingCodeCFactory.buildMarshallingDecoder());
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(newReadTimeoutHandler(5)); //5秒后未与服务器通信,则断开连接。
socketChannel.pipeline().addLast(new ClientHandler());
}
});
}
public void connect() {
try {
future =bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1", 8765).sync();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public ChannelFuture getFuture() {
if(future == null ||!future.channel().isActive()) {
this.connect();
}
return future;
}
public static void main(String[] args)throws InterruptedException {
Client client = getInstance();
ChannelFuture future = client.getFuture();
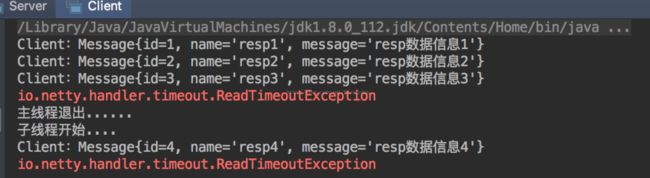
for(int i=1; i<=3; i++) {
Message message = new Message(i,"pro" + i, "数据信息" + i);
future.channel().writeAndFlush(message);
Thread.sleep(4000); //休眠4秒后再发送数据
}
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
System.out.println("子线程开始....");
ChannelFuture f =client.getFuture();
Message message = newMessage(4, "pro" + 4, "数据信息" + 4);
f.channel().writeAndFlush(message);
f.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}).start();
System.out.println("主线程退出......");
}
}
其他的类与之前的一样,没有变化。
运行结果:
(2)心跳检测
我们使用Socket通信一般经常会处理多个服务器之间的心跳检测,一般来讲我们去维护服务器集群,肯定要有一台或多台服务器主机(Master),然后还应该有N台(Slave),那么我们的主机肯定要时时刻刻知道自己下面的从服务器的各方面情况,然后进行实时监控的功能。这个在分布式架构里交做心跳检测或者心跳监控。最佳处理方案是使用一些通信框架进行实现,Netty就可以做这样的事。
这个例子需要使用Sigar,不熟悉的可以看这篇文章。
Server
public class Server {
public Server(int port) {
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = newNioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = newNioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = newServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.group(bossGroup,workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(newChannelInitializer
@Override
protected voidinitChannel(SocketChannel sc) throws Exception {
sc.pipeline().addLast(MarshallingCodeCFactory.buildMarshallingEncoder());
sc.pipeline().addLast(MarshallingCodeCFactory.buildMarshallingDecoder());
sc.pipeline().addLast(new ServerHeartBeatHandler());
}
})
.handler(newLoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 1024);
ChannelFuture future =bootstrap.bind(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", port)).sync();
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Server(8765);
}
}
ServerHeartBeatHandler类:
public classServerHeartBeatHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
private static Map
private static final String SUCCESS_KEY ="auth_success_key";
static {
AUTH_IP_MAP.put("192.168.3.176","1234");
}
private boolean auth(ChannelHandlerContextctx, Object msg) {
String[] rets = ((String)msg).split(",");
String auth = AUTH_IP_MAP.get(rets[0]);
if(auth != null &&auth.equals(rets[1])) {
ctx.writeAndFlush(SUCCESS_KEY);
return true;
} else {
ctx.writeAndFlush("authfailure!").addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);
return false;
}
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContextctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
if(msg instanceof String) {
auth(ctx, msg);
} else if(msg instanceof RequestInfo) {
RequestInfo info = (RequestInfo)msg;
System.out.println("----------------------------------------------");
System.out.println("当前主机ip:" +info.getIp());
System.out.println("当前主机cpu:情况");
Map
System.out.println("总使用率:" + cpuMap.get("combined"));
System.out.println("用户使用率:" +cpuMap.get("user"));
System.out.println("系统使用率:" +cpuMap.get("sys"));
System.out.println("等待率:" +cpuMap.get("wait"));
System.out.println("空闲率:" +cpuMap.get("idle"));
System.out.println("当前主机memory情况:");
Map
System.out.println("内存总量:" +memMap.get("total"));
System.out.println("当前内存使用量:" +memMap.get("used"));
System.out.println("当前内存剩余量:" +memMap.get("free"));
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------------");
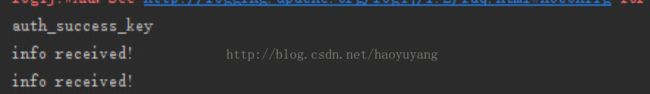
ctx.writeAndFlush("inforeceived!");
} else {
ctx.writeAndFlush("connectfailure").addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);
}
}
}
Client类:
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = newNioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap bootstrap = newBootstrap();
bootstrap.group(workerGroup)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.handler(newChannelInitializer
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannelsc) throws Exception {
sc.pipeline().addLast(MarshallingCodeCFactory.buildMarshallingDecoder());
sc.pipeline().addLast(MarshallingCodeCFactory.buildMarshallingEncoder());
sc.pipeline().addLast(new ClientHeartBeatHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture future =bootstrap.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 8765)).sync();
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
ClientHeartBeatHandler类:
public classClientHeartBeatHandler extends ChannelHandlerAdapter {
private ScheduledExecutorService scheduled= Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);
private ScheduledFuture heartBeat;
private InetAddress address;
private static final String SUCCESS_KEY ="auth_success_key";
@Override
public voidchannelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
address = InetAddress.getLocalHost();
String ip = address.getHostAddress();
String key = "1234";
String auth = ip + "," + key;
ctx.writeAndFlush(auth);
}
@Override
public voidexceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
if(heartBeat != null) {
heartBeat.cancel(true);
heartBeat = null;
}
ctx.fireExceptionCaught(cause);
}
@Override
public voidchannelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
try {
if(msg instanceof String) {
String data = (String) msg;
if(SUCCESS_KEY.equals(data)) {
heartBeat =scheduled.scheduleWithFixedDelay(new HeartBeatTask(ctx), 0, 5,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println(msg);
} else {
System.out.println(msg);
}
}
} finally {
ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg);
}
}
private class HeartBeatTask implements Runnable{
private final ChannelHandlerContextctx;
publicHeartBeatTask(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
this.ctx = ctx;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
RequestInfo requestInfo = newRequestInfo();
requestInfo.setIp(address.getHostAddress());
Sigar sigar = new Sigar();
CpuPerc cpuPerc =sigar.getCpuPerc();
Map
cpuPercMap.put("combined",cpuPerc.getCombined());
cpuPercMap.put("user", cpuPerc.getUser());
cpuPercMap.put("sys",cpuPerc.getSys());
cpuPercMap.put("wait", cpuPerc.getWait());
cpuPercMap.put("idle",cpuPerc.getIdle());
Mem mem = sigar.getMem();
Map
memoryMap.put("total", mem.getTotal() / (1024 * 1024));
memoryMap.put("used",mem.getUsed() / (1024 * 1024));
memoryMap.put("free",mem.getFree() / (1024 * 1024));
requestInfo.setCpuPercMap(cpuPercMap);
requestInfo.setMemoryMap(memoryMap);
ctx.writeAndFlush(requestInfo);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
RequestInfo类:
public classRequestInfo implements Serializable {
private String ip ;
private Map
private Map
//.. other field
public String getIp() {
return ip;
}
public void setIp(String ip) {
this.ip = ip;
}
public Map
return cpuPercMap;
}
public voidsetCpuPercMap(Map
this.cpuPercMap = cpuPercMap;
}
public Map
return memoryMap;
}
public void setMemoryMap(Map
this.memoryMap = memoryMap;
}
}
MarshallingCodeCFactory类就不贴出来了,跟之前的一样。
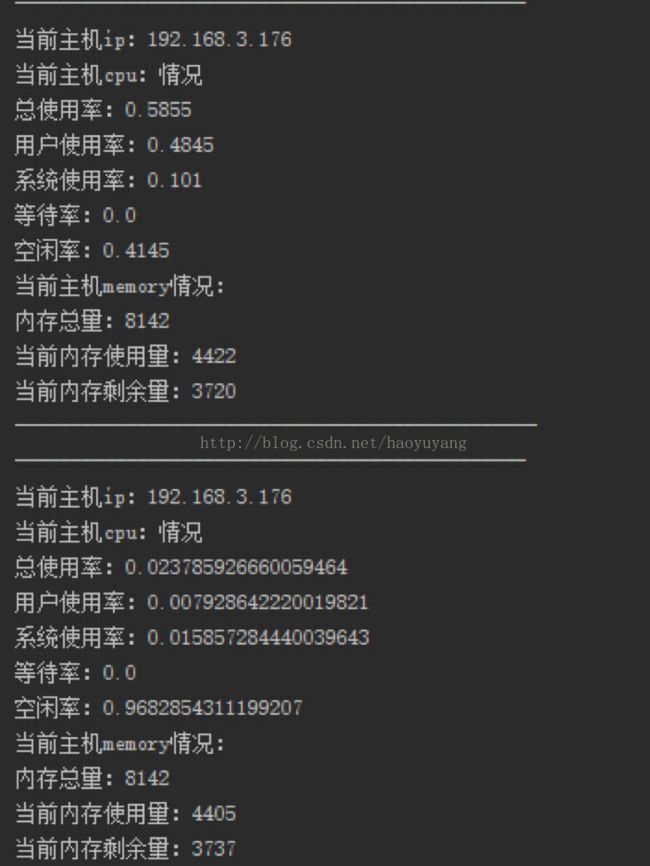
运行结果:
每5秒发送一次数据到服务器端,这样主服务器就可以知道每台从服务器的状态了。当然,这只是一个简单的小例子,真实环境中肯定需要更严格的校验。