springboot启动源码学习
一、springboot-Helloworld入门
第一个注解:@SpringBootApplication springboot 主配置类
具体如下:
@·····
@SpringBootConfiguration //表示这是一个springboot的配置类
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = {
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication {```}
进入@SpringBootConfiguration 注解?
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Configuration //配置类上来标注这个注解;表示配置类--配置文件
public @interface SpringBootConfiguration {
}
配置类也是一个组件@component, 如下:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component//spring 组件
public @interface Configuration {
第二个注解:@EnableAutoConfiguration :开启自动配置功能
两个组合注解
Ⅰ.@AutoconfigurationPackage
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
1).@AutoConfigurationPackage自动配置包 里面有一个 import
@Documented
@Inherited
@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class)
public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage {
//@import给容器中倒入一个组件,由XXX.class决定
}
2).打开Registrar.class类 里面有一个方法导入元数据
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata metadata,BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
register(registry, new PackageImport(metadata).getPackageName());
}
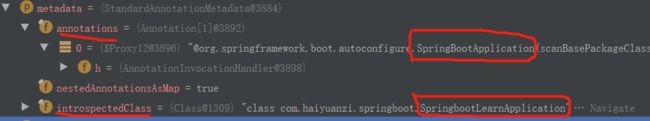
debug模式下获取元数据信息:annotations 是springbootApplication
introspectedClass(内省类) 自己命名的启动类
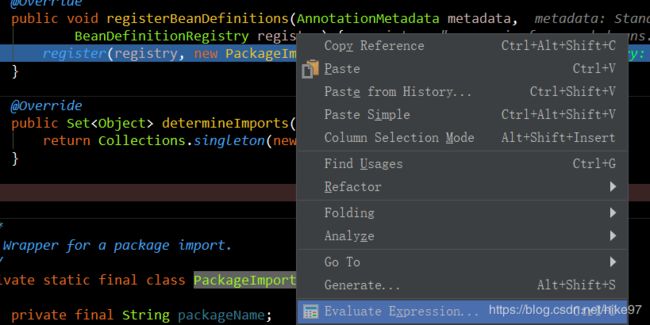
进行计算得到你定义的包名

综上所述,@autoconfiguration的作用就是:
将主配置类(@springbootApplication标注的类)的包及下面所有组件扫描到spring容器
Ⅱ、@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
给容器中导入组件 :AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class 中有一个selectImports方法
//将所需要的导入的组件以全类名的方式返回;这些组件就会被添加到容器中;
//会给容器中导入非常多的自动配置类(xxxAutoConfiguration);
//给容器中导入这个场景所需要的所有组件,并配置好这些组件;
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return NO_IMPORTS;
}
AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata = AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader
.loadMetadata(this.beanClassLoader);
AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry = getAutoConfigurationEntry(
autoConfigurationMetadata, annotationMetadata);
return StringUtils.toStringArray(autoConfigurationEntry.getConfigurations());
}
web-starter需要的21个组件
0 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.admin.SpringApplicationAdminJmxAutoConfiguration"
1 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CacheAutoConfiguration"
2 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.ConfigurationPropertiesAutoConfiguration"
3 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.MessageSourceAutoConfiguration"
4 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration"
5 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.HttpMessageConvertersAutoConfiguration"
6 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.codec.CodecsAutoConfiguration"
7 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.info.ProjectInfoAutoConfiguration"
8 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jackson.JacksonAutoConfiguration"
9 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jmx.JmxAutoConfiguration"
10 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.task.TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration"
11 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.task.TaskSchedulingAutoConfiguration"
12 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.validation.ValidationAutoConfiguration"
13 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.client.RestTemplateAutoConfiguration"
14 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.embedded.EmbeddedWebServerFactoryCustomizerAutoConfiguration"
15 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration"
16 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration"
17 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration"
18 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration"
19 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.MultipartAutoConfiguration"
20 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration"
21 = "org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.servlet.WebSocketServletAutoConfiguration"
有了自动配置类,免去手动编写注入功能组件 如何配置?
方法跟踪 getAutoConfigurationEntry()?
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
//··········
AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry = getAutoConfigurationEntry(
autoConfigurationMetadata, annotationMetadata);
//~~~~~~~~~~~~
}
中有以下代码:?
loadFactoryNames(EnableAutoConfiguration.class,this.beanClassLoader)
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(
getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), getBeanClassLoader());
中有两个参数:?
//1.EnableAutoConfiguration.class
protected Class<?> getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass() {
return EnableAutoConfiguration.class;
}
//2.类加载器 this.beanClassLoader
protected ClassLoader getBeanClassLoader() {
return this.beanClassLoader;
}
下面看一下loadFactoryNames()方法
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryClass, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
String factoryClassName = factoryClass.getName();
return loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryClassName, Collections.emptyList());
}
?
/**
loadSpringFactories方法
*/
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
MultiValueMap<String, String> result = cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
try {
Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null ?
classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) :
ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION));
//````省略后续代码
//打开FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION
public static final String FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories";
/**根据路径找到spring.factories文件
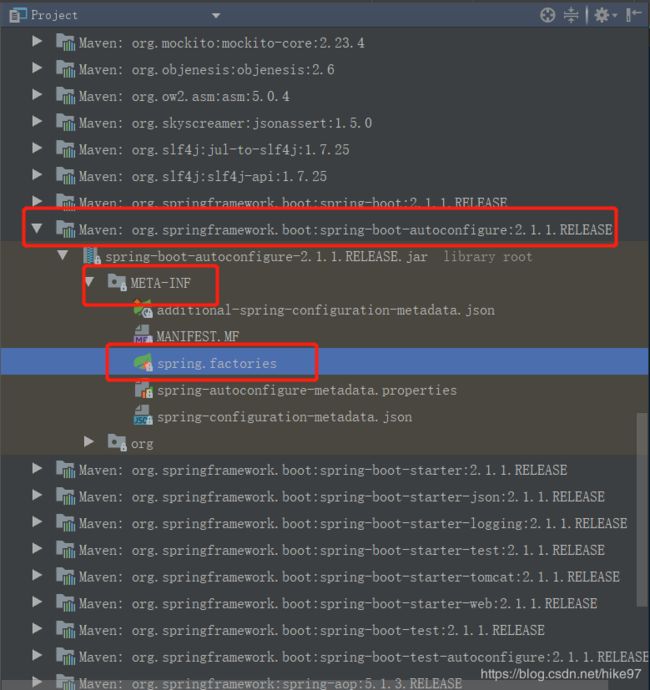
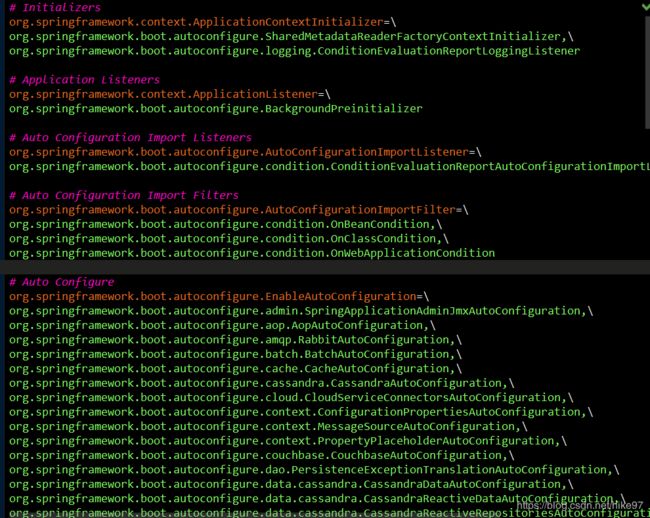
综上所述:springboot 在启动的时候从类路径下的META-INF/spring.factories中获取
EnableAutoConfiguration指定的值并作为自动配置类导入容器中,进行自动配置工作。
例如:WebMvcAutoConfiguration中的一些配置:?
package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet;
//rest风格中的方法过滤器
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(HiddenHttpMethodFilter.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.mvc.hiddenmethod.filter", name = "enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
public OrderedHiddenHttpMethodFilter hiddenHttpMethodFilter() {
return new OrderedHiddenHttpMethodFilter();
}
//视图解析器
@Bean
@ConditionalOnBean(ViewResolver.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "viewResolver", value = ContentNegotiatingViewResolver.class)
public ContentNegotiatingViewResolver viewResolver(BeanFactory beanFactory) {
ContentNegotiatingViewResolver resolver = new ContentNegotiatingViewResolver();
resolver.setContentNegotiationManager(
beanFactory.getBean(ContentNegotiationManager.class));
// ContentNegotiatingViewResolver uses all the other view resolvers to locate
// a view so it should have a high precedence
resolver.setOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE);
return resolver;
}
小结:三个注解
@SpringBootConfiguration 实际上是@configuration 实际上是一个component-->配置类
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@AutoConfigurationPackage() ?@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class)-->定位配置包,加载用户写的组件
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)-->自动装配默认组件
javaEE 整体整合解决方案和自动配置都在spring-boot-autoconfigure:X.X.XRELEASE中
二、springbootMVC自动配置及拓展原理
官方文档
https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/2.1.1.RELEASE/reference/htmlsingle/#boot-features-developing-web-applications
28.1.1 Spring MVC Auto-configuration
Spring Boot provides auto-configuration for Spring MVC that works well with most applications.
The auto-configuration adds the following features on top of Spring’s defaults:
- Inclusion of ContentNegotiatingViewResolver and BeanNameViewResolver beans.
- 自动配置了ViewResolver(视图解析器:根据方法的返回值得到视图对象(View),视图对象决定如何渲染(转发?重定向?))
- @Bean
@ConditionalOnBean(ViewResolver.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "viewResolver", value = ContentNegotiatingViewResolver.class)
public ContentNegotiatingViewResolver viewResolver(BeanFactory beanFactory) {
ContentNegotiatingViewResolver resolver = new ContentNegotiatingViewResolver();
resolver.setContentNegotiationManager( beanFactory.getBean(ContentNegotiationManager.class));
resolver.setOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE);
return resolver
}
?
- //ContentNegotiatingViewResolver中的resolveViewName()方法
@Override
@Nullable
public View resolveViewName(String viewName, Locale locale) throws Exception {
//~~~~~省略~~~~~~~
if (requestedMediaTypes != null) {
//第一步:获取备选视图对象
List<View> candidateViews = getCandidateViews(viewName, locale, requestedMediaTypes);
//第二步:选择最适合的视图对象
View bestView = getBestView(candidateViews, requestedMediaTypes, attrs);
if (bestView != null) {
return bestView;
}
}
//~~~~~省略~~~~~~~
}
/*进入getCandidateViews()方法*/
- /**
* 作用:组合所有视图解析器 关键字this.viewResolver
*/
private List<View> getCandidateViews(String viewName, Locale locale, List<MediaType> requestedMediaTypes)
throws Exception {
List<View> candidateViews = new ArrayList<>();
if (this.viewResolvers != null) {
for (ViewResolver viewResolver : this.viewResolvers) {
View view = viewResolver.resolveViewName(viewName, locale);
if (view != null) {
candidateViews.add(view);
}
/*~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~省略~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~*/
return candidateViews;
}
- /**
初始化方法,容器工厂类获取所有的视图解析器
*/
@Override
protected void initServletContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
Collection<ViewResolver> matchingBeans = BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(obtainApplicationContext(),ViewResolver.class).values();
/*~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~省略~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~*/
}
- 如何定制:我们可以自己给容器中添加一个视图解析器
- /**在配置类下注入一个视图解析器*/
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootLearnApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootLearnApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
public ViewResolver myViewResolver(){
return new MyViewResolver ();
}
public static class MyViewResolver implements ViewResolver{
@Nullable
@Override
public View resolveViewName (String viewName, Locale locale) throws Exception {
return null;
}
}
}
- 开启debug模式:位置:dispatcherServlet的doDispatch()方法
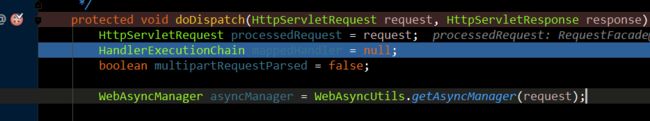
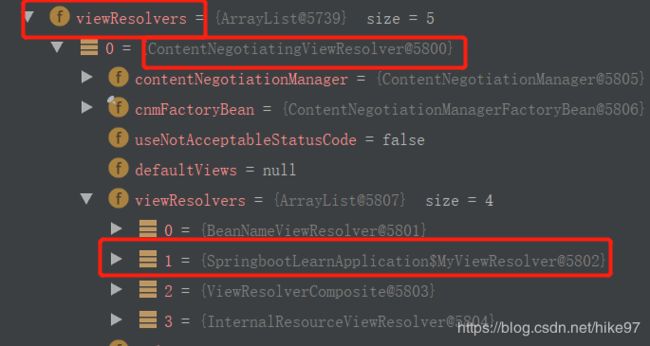
- 发现确实注入了自定义的视图解析器
- Support for serving static resources, including support for WebJars (covered later in this document)).
- 静态资源文件夹路径,webjars
- Automatic registration of Converter, GenericConverter, and Formatter beans.
- Converter➡转换器:将页面提交的文本转换成实体类的相关属性
- Formatter➡格式化器:2017/12/17===Date;
-
@Bean @Override public FormattingConversionService mvcConversionService() { WebConversionService conversionService = new WebConversionService( this.mvcProperties.getDateFormat()); addFormatters(conversionService); return conversionService; } //自己添加的格式化转换器,我们只需放在容器中即可 ? @Override public void addFormatters(FormatterRegistry registry) { for (Converter<?, ?> converter : getBeansOfType(Converter.class)) { registry.addConverter(converter); } for (GenericConverter converter : getBeansOfType(GenericConverter.class)) { registry.addConverter(converter); } for (Formatter<?> formatter : getBeansOfType(Formatter.class)) { registry.addFormatter(formatter); } }
- Support for HttpMessageConverters (covered later in this document).
- springmvc 用来转换Http请求和响应的;User-json
- messageConverters从容器中确定:获取所有的HttpMessageConverters`;
- 自己给容器中添加HttpMessageConverter,只需将自己的组件注册容器中
- (@Bean,@Component)
- Automatic registration of MessageCodesResolver (covered later in this document).
-
- @Override public MessageCodesResolver getMessageCodesResolver() { if (this.mvcProperties.getMessageCodesResolverFormat() != null) { DefaultMessageCodesResolver resolver = new DefaultMessageCodesResolver(); resolver.setMessageCodeFormatter( this.mvcProperties.getMessageCodesResolverFormat()); return resolver; } return null; } 进入getMessageCodesResolverFormat()方法? - public DefaultMessageCodesResolver.Format getMessageCodesResolverFormat() { return this.messageCodesResolverFormat; } 点击Format? - public enum Format implements MessageCodeFormatter { /** * Prefix the error code at the beginning of the generated message code. e.g.: * {@code errorCode + "." + object name + "." + field} */ PREFIX_ERROR_CODE { @Override public String format(String errorCode, @Nullable String objectName, @Nullable String field) { return toDelimitedString(errorCode, objectName, field); } }, /** * Postfix the error code at the end of the generated message code. e.g.: * {@code object name + "." + field + "." + errorCode} */ POSTFIX_ERROR_CODE { @Override public String format(String errorCode, @Nullable String objectName, @Nullable String field) { return toDelimitedString(objectName, field, errorCode); } }; - 可见MessageCodesResolver用于生成错误代码生成规则的 - Static index.html support. 静态首页访问
- Custom Favicon support (covered later in this document).
- Automatic use of a ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer bean (covered later in this document).
protected ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer getConfigurableWebBindingInitializer() {
try {
//由此代码可见:我们可以配置一个ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer来替换默认的;
return this.beanFactory.getBean(ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer.class);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
//如果找不到会调用父类方法?
return super.getConfigurableWebBindingInitializer();
}
}
- /**
* Return the {@link ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer} to use for
* initializing all {@link WebDataBinder} instances.
初始化web绑定数据的实例
*/
protected ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer getConfigurableWebBindingInitializer() {
ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer initializer = new ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer();
initializer.setConversionService(mvcConversionService());
initializer.setValidator(mvcValidator());
MessageCodesResolver messageCodesResolver = getMessageCodesResolver();
if (messageCodesResolver != null) {
initializer.setMessageCodesResolver(messageCodesResolver);
}
return initializer;
}
- webDataBinder的作用:请求数据转换为javaBean;
If you want to keep Spring Boot MVC features and you want to add additional MVC configuration (interceptors, formatters, view controllers, and other features), you can add your own @Configuration class of type WebMvcConfigurer but without @EnableWebMvc.
If you wish to provide custom instances of RequestMappingHandlerMapping, RequestMappingHandlerAdapter, or ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver, you can declare a WebMvcRegistrationsAdapter instance to provide such components.
If you want to take complete control of Spring MVC, you can add your own @Configuration annotated with @EnableWebMvc.
拓展springmvc:既保留了原来的配置 也用于我们拓展的配置
@Configuration
public class MyMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addViewControllers (ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
registry.addViewController ("/hello").setViewName ("success");
}
}
原理:为什么能拓展?
1)、WebMvcAutoConfiguration是SpringMVC的自动配置类
/**
该类中有一个静态类WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter
--注意与WebMvcConfigurerAdapter(2.X已经废弃)的区别
此类也是实现了webMVcConfiger,进行了webmvc方法的自动装配,
这不是重点,我们来查看Import的类:EnableWebMvcConfiguration.class
*/
@Configuration
@Import(EnableWebMvcConfiguration.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ WebMvcProperties.class, ResourceProperties.class })
@Order(0)
public static class WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter
implements WebMvcConfigurer, ResourceLoaderAware {
/*继承了DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration*/
@Configuration
public static class EnableWebMvcConfiguration extends DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration {
?
//该类中有如下方法:
//Autowired标注在方法上就意味着:从容器中获取所有的WebMvcConfigurer
private final WebMvcConfigurerComposite configurers = new WebMvcConfigurerComposite();
@Autowired(required = false)
public void setConfigurers(List<WebMvcConfigurer> configurers) {
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(configurers)) {
//赋值到configures中
this.configurers.addWebMvcConfigurers(configurers);
}
}
// 点进 (configurers)类
class WebMvcConfigurerComposite implements WebMvcConfigurer {
private final List<WebMvcConfigurer> delegates = new ArrayList<>();
//一个参考实现;将所有的WebMvcConfigurer相关配置都来一起调用;
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
for (WebMvcConfigurer delegate : this.delegates) {
delegate.addViewControllers(registry);
}
}
3)、容器中所有的WebMvcConfigurer都会一起起作用;
4)、我们的配置类也会被调用;
效果:SpringMVC的自动配置和我们的扩展配置都会起作用;
3、全面接管SpringMVC;
SpringBoot对SpringMVC的自动配置不需要了,所有都是我们自己配置;所有的SpringMVC的自动配置都失效了
我们需要在配置类中添加@EnableWebMvc即可;
为什么全面接管,自动配置会失效?
@Import(DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration.class)
public @interface EnableWebMvc {
}
@Configuration
public class DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class, WebMvcConfigurer.class })
//容器中没有这个组件的时候,这个自动配置类才生效
//配置了EnableWebMvc会导入 DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration 他是属于【WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class】范畴的 所以自动配置失效
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class)
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 10)
@AutoConfigureAfter({ DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.class,
TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration.class, ValidationAutoConfiguration.class })
public class WebMvcAutoConfiguration {
综上所述,@EnableWebMvc将WebMvcConfigurationSupport组件导入进来,导入的WebMvcConfigurationSupport只是SpringMVC最基本的功能;
三、如何修改SpringBoot的默认配置模式:
1)、SpringBoot在自动配置很多组件的时候,先看容器中有没有用户自己配置的(@Bean @Component)如果有就用用户配置的,如果没有,才自动配置;如果有些组件可以有多个(ViewResolver)将用户配置的和自己默认的组合起来;
2)、在SpringBoot中会有非常多的xxxConfigurer帮助我们进行扩展配置
3)、在SpringBoot中会有很多的xxxCustomizer帮助我们进行定制配置)
四、springboot的启动运行流程
Ⅰ.启动流程:DEBUG–SpringApplication.run方法
1、创建springApplication对象
//run方法 执行了SpringApplication()的有参构造对象的run方法方法跟踪如下:
public SpringApplication(Class<?>... primarySources) {
this(null, primarySources);
}
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
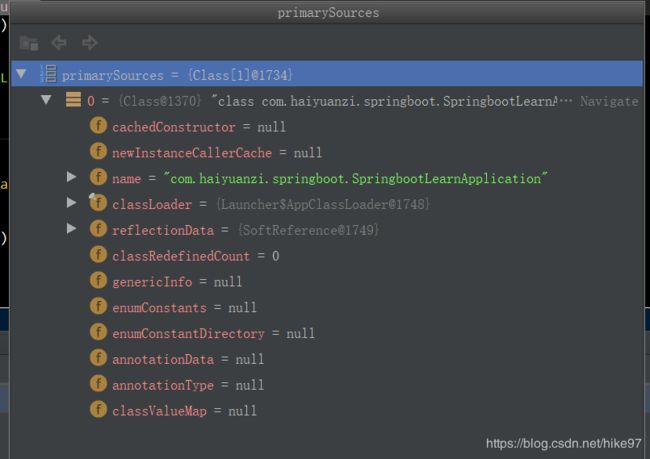
//1.先将主配置类中添加到primarySource中
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
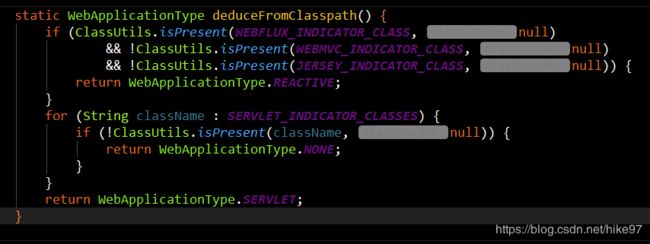
//2.决定web应用环境 因为springboot 2.X 加入了react编程
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
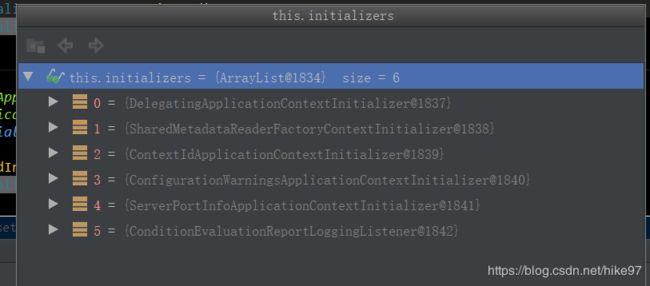
//3.从类路径下找到META‐INF/spring.factories配置的所有ApplicationContextInitializer;然后保存起来
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(
ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
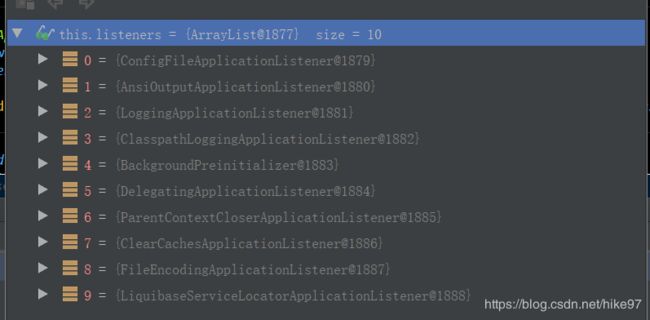
//4.从类路径下找到META‐INF/spring.factories配置的所有ApplicationListener;然后保存起来
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
//5.从多个配置类中找到有main方法的主配置类
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、代码如下、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、、
private Class<?> deduceMainApplicationClass() {
try {
StackTraceElement[] stackTrace = new RuntimeException().getStackTrace();
for (StackTraceElement stackTraceElement : stackTrace) {
if ("main".equals(stackTraceElement.getMethodName())) {
return Class.forName(stackTraceElement.getClassName());
}
}
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// Swallow and continue
}
return null;
}
2️⃣。webApplicationType
2、运行run方法
一:环境准备
二:创建IOC容器
几个重要的事件回调机制
配置在META-INF/spring.factories
ApplicationContextInitializer
SpringApplicationRunListener
只需要放在ioc容器中
ApplicationRunner
CommandLineRunner
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
//1.开启停止的监听
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
//2.声明ioc容器
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
//3.awt相关配置
configureHeadlessProperty();
//4.获取SpringApplicationRunListener;从类路径下META‐INF/spring.factories(见详细分析)
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
//5.回调所有的获取SpringApplicationRunListener.starting()方法
listeners.starting();
详细分析一:获取SpringApplicationRunListener。
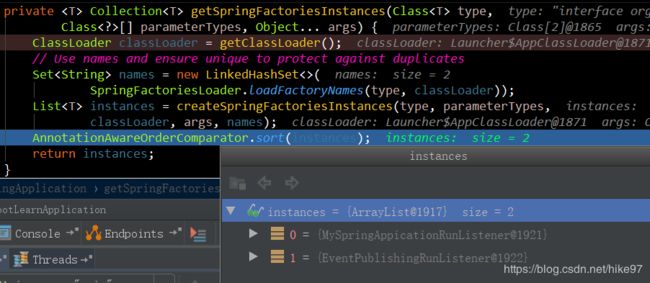
private SpringApplicationRunListeners getRunListeners(String[] args) {
Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[] { SpringApplication.class, String[].class };
return new SpringApplicationRunListeners(logger, getSpringFactoriesInstances(
SpringApplicationRunListener.class, types, this, args));
}
如上图,通过反射机制获取到EventPublishingRunListener的实例(MySpringApplicationRunListner为本人编写 ,可忽略)
然后调用listeners.run()方法
循环遍历listener的starting()方法
try {
//6.封装命令行参数
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(
args);
//7.准备环境
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners,
applicationArguments);
–prepareEnvirenment()方法
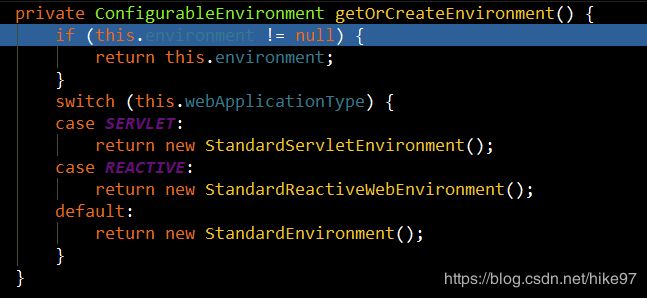
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// Create and configure the environment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();//SERVLET REACT
//配置这些环境
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
//7.1 创建环境完成后回调SpringApplicationRunListener.environmentPrepared();表示环境准备完成
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
//2.X多的方法
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
//1.5.6为isWebEnvironment 可能由于加入react的原因
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader())
.convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment, deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
//2.0新增
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
//8.打印springBoot的图标
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
//9.创建applicationContext上下文;
context = createApplicationContext();
//10.异常报告
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(
SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
//11.准备上下文环境;
//11.1 将environment保存到ioc中;而且applyInitializers();
//11.2 applyInitializers():回调之前保存的所有的ApplicationContextInitializer的initialize方法
//11.3 回调所有的SpringApplicationRunListener的contextPrepared();
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments,
printedBanner);
//11.4 prepareContext运行完成以后回调所有的SpringApplicationRunListener的contextLoaded();
–prepareContext()方法 ?
private void prepareContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context,
ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {
//保存之前准备的环境
context.setEnvironment(environment);
//ioc容器后置处理 注册小组件
postProcessApplicationContext(context);
applyInitializers(context);
//applyInitializers方法执行完,监听器调用contextPrepared方法(),和之前的start() prepreparedEnvironment()一样循环调用
listeners.contextPrepared(context);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
logStartupProfileInfo(context);
}
// Add boot specific singleton beans
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
//注册命令行主类
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments);
if (printedBanner != null) {
//banner注册
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
}
if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) {
((DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory)
.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);
}
// Load the sources
//获取所有资源
Set<Object> sources = getAllSources();
Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]));
//paredContext方法,进行完毕 调用listener的contextLoaded()方法
listeners.contextLoaded(context);
}
–applyInitializers()方法 将之前初始化的springApplicatio对象中的initializers进行循环遍历回调initialize()方法
//12.刷新容器;ioc容器初始化(如果是web应用还会创建嵌入式的Tomcat);Spring注解版
//扫描,创建,加载所有组件的地方;
refreshContext(context);
?
–refresh()方法 ioc容器初始化
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
//初始化单实例bean
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
//13.从ioc容器中获取所有的ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner进行回调
//14.ApplicationRunner先回调,CommandLineRunner再回调(1.5.9源码)
/*
*2.X版本改变了已经:在后边回调
*/
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)
.logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
//finish(1.5.9) 改为started()
listeners.started(context);
//回调 ApplicationRunner先回调,CommandLineRunner再回调
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
?
–callRunners()方法
private void callRunners(ApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) {
List<Object> runners = new ArrayList<>();
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(ApplicationRunner.class).values());
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(CommandLineRunner.class).values());
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(runners);
for (Object runner : new LinkedHashSet<>(runners)) {
if (runner instanceof ApplicationRunner) {
callRunner((ApplicationRunner) runner, args);
}
if (runner instanceof CommandLineRunner) {
callRunner((CommandLineRunner) runner, args);
}
}
}
try {
//springboot 2.x 多了一个回调listeners的running()方法
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
//所有的listeners回调完毕
//15.整个SpringBoot应用启动完成以后返回启动的ioc容器;
return context;
}
五、自定义starter
自定义starter的一些问题:
1、这个场景需要使用到的依赖是什么?
2、如何编写自动配置
@Configuration //指定这个类是一个配置类
@ConditionalOnXXX //在指定条件成立的情况下自动配置类生效
@AutoConfigureAfter //指定自动配置类的顺序
@Bean //给容器中添加组件
@ConfigurationPropertie结合相关xxxProperties类来绑定相关的配置
@EnableConfigurationProperties //让xxxProperties生效加入到容器中
自动配置类要能加载
将需要启动就加载的自动配置类,配置在META‐INF/spring.factories
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.admin.SpringApplicationAdminJmxAutoConfiguration,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration,\
3、模式:
启动器只用来做依赖导入;
专门来写一个自动配置模块;
启动器依赖自动配置;别人只需要引入启动器(starter)
mybatis-spring-boot-starter;自定义启动器名-spring-boot-starter
4.步骤
4.1创建starter(普通maven工程)
pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
<groupId>com.atguigu.startergroupId>
<artifactId>atguigu-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOTversion>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.atguigu.startergroupId>
<artifactId>atguigu-spring-boot-autoconfigurerartifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOTversion>
dependency>
dependencies>
project>
4.2创建spring-boot基础工程 --atguigu-spring-boot-autoconfigurer
pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parentartifactId>
<version>2.1.1.RELEASEversion>
<relativePath/>
parent>
<groupId>com.atguigu.startergroupId>
<artifactId>atguigu-spring-boot-autoconfigurerartifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOTversion>
<name>atguigu-spring-boot-autoconfigurername>
<description>Demo project for Spring Bootdescription>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8java.version>
properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starterartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
dependency>
dependencies>
project>
4.3 创建 helloService 组件 引入了helloProperties
package com.atguigu.starter;
import lombok.Data;
/**
* @author hike97 許せ サスケ これで最後だ
* @create 2019-01-02 16:25
* @desc
**/
@Data
public class HelloService {
private HelloProperties properties;
public String sayHello(String msg){
return properties.getPrefix ()+":"+msg+":"+properties.getSuffix ();
}
}
?
package com.atguigu.starter;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
/**
* @author hike97 許せ サスケ これで最後だ
* @create 2019-01-02 16:26
* @desc
**/
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.hello")
@Data
public class HelloProperties {
private String prefix;
private String suffix;
}
4.4创建自动装配类HelloServiceAutoConfiguration
package com.atguigu.starter;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnWebApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @author hike97 許せ サスケ これで最後だ
* @create 2019-01-02 16:36
* @desc
**/
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnWebApplication//web环境下有效
@EnableConfigurationProperties(HelloProperties.class)
public class HelloServiceAutoConfiguration {
@Autowired
HelloProperties helloProperties;
@Bean
public HelloService helloService(){
HelloService service = new HelloService ();
service.setProperties (helloProperties);
return service;
}
}
META-INF/spring.factories
# Auto Configure
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
com.atguigu.starter.HelloServiceAutoConfiguration
maven操作:打包autoconfigures 打包starters
应用:在springboot web 项目中添加自定义starters 依赖
com.atguigu.starter
atguigu-spring-boot-starter
1.0-SNAPSHOT
在控制层 引入 service
package com.haiyuanzi.springboot.controller;
import com.atguigu.starter.HelloService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @author hike97 許せ サスケ これで最後だ
* @create 2019-01-02 16:46
* @desc
**/
@RestController
public class TestStartController {
@Autowired
HelloService helloService;
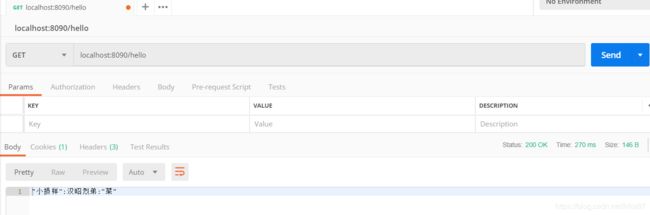
@GetMapping(value = "/hello" ,produces="text/plain;charset=UTF-8")
public String sayHello(){
return helloService.sayHello ("汉昭烈弟");
}
}
在配置文件中引用properties
server.port=8090
spring.hello.prefix="小损样"
spring.hello.suffix="菜"