1 import numpy as np
2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
3 from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer
4 from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
5 #initialize parameters(w,b)
6 def initialize_parameters(layer_dims):
7 """
8 :param layer_dims: list,每一层单元的个数(维度)
9 :return:dictionary,存储参数w1,w2,...,wL,b1,...,bL
10 """
11 np.random.seed(3)
12 L = len(layer_dims)#the number of layers in the network
13 parameters = {}
14 for l in range(1,L):
15 # parameters["W" + str(l)] = np.random.randn(layer_dims[l],layer_dims[l-1])*0.01
16 parameters["W" + str(l)] = np.random.randn(layer_dims[l], layer_dims[l-1])*np.sqrt(2/layer_dims[l-1]) # he initialization
17 # parameters["W" + str(l)] = np.zeros((layer_dims[l], layer_dims[l - 1])) #为了测试初始化为0的后果
18 # parameters["W" + str(l)] = np.random.randn(layer_dims[l], layer_dims[l - 1]) * np.sqrt(1 / layer_dims[l - 1]) # xavier initialization
19 parameters["b" + str(l)] = np.zeros((layer_dims[l],1))
20 return parameters
21 def relu(Z):
22 """
23 :param Z: Output of the linear layer
24 :return:
25 A: output of activation
26 """
27 A = np.maximum(0,Z)
28 return A
29 #implement the activation function(ReLU and sigmoid)
30 def sigmoid(Z):
31 """
32 :param Z: Output of the linear layer
33 :return:
34 """
35 A = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-Z))
36 return A
37
38 def forward_propagation(X, parameters):
39 """
40 X -- input dataset, of shape (input size, number of examples)
41 parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters "W1", "b1", "W2", "b2",...,"WL", "bL"
42 W -- weight matrix of shape (size of current layer, size of previous layer)
43 b -- bias vector of shape (size of current layer,1)
44 :return:
45 AL: the output of the last Layer(y_predict)
46 caches: list, every element is a tuple:(W,b,z,A_pre)
47 """
48 L = len(parameters) // 2 # number of layer
49 A = X
50 caches = [(None,None,None,X)] # 第0层(None,None,None,A0) w,b,z用none填充,下标与层数一致,用于存储每一层的,w,b,z,A
51 # calculate from 1 to L-1 layer
52 for l in range(1,L):
53 A_pre = A
54 W = parameters["W" + str(l)]
55 b = parameters["b" + str(l)]
56 z = np.dot(W,A_pre) + b #计算z = wx + b
57 A = relu(z) #relu activation function
58 caches.append((W,b,z,A))
59 # calculate Lth layer
60 WL = parameters["W" + str(L)]
61 bL = parameters["b" + str(L)]
62 zL = np.dot(WL,A) + bL
63 AL = sigmoid(zL)
64 caches.append((WL,bL,zL,AL))
65 return AL, caches
66 #calculate cost function
67 def compute_cost(AL,Y):
68 """
69 :param AL: 最后一层的激活值,即预测值,shape:(1,number of examples)
70 :param Y:真实值,shape:(1, number of examples)
71 :return:
72 """
73 m = Y.shape[1]
74 # cost = -1.0/m * np.sum(Y*np.log(AL)+(1-Y)*np.log(1.0 - AL))#py中*是点乘
75 # cost = (1. / m) * (-np.dot(Y, np.log(AL).T) - np.dot(1 - Y, np.log(1 - AL).T)) #推荐用这个,上面那个容易出错
76 cost = 1. / m * np.nansum(np.multiply(-np.log(AL), Y) +
77 np.multiply(-np.log(1 - AL), 1 - Y))
78 #从数组的形状中删除单维条目,即把shape中为1的维度去掉,比如把[[[2]]]变成2
79 cost = np.squeeze(cost)
80 # print('=====================cost===================')
81 # print(cost)
82 return cost
83
84 # derivation of relu
85 def relu_backward(Z):
86 """
87 :param Z: the input of activation
88 :return:
89 """
90 dA = np.int64(Z > 0)
91 return dA
92
93 def backward_propagation(AL, Y, caches):
94 """
95 Implement the backward propagation presented in figure 2.
96 Arguments:
97 X -- input dataset, of shape (input size, number of examples)
98 Y -- true "label" vector (containing 0 if cat, 1 if non-cat)
99 caches -- caches output from forward_propagation(),(W,b,z,pre_A)
100
101 Returns:
102 gradients -- A dictionary with the gradients with respect to dW,db
103 """
104 m = Y.shape[1]
105 L = len(caches) - 1
106 # print("L: " + str(L))
107 #calculate the Lth layer gradients
108 prev_AL = caches[L-1][3]
109 dzL = 1./m * (AL - Y)
110 # print(dzL.shape)
111 # print(prev_AL.T.shape)
112 dWL = np.dot(dzL, prev_AL.T)
113 dbL = np.sum(dzL, axis=1, keepdims=True)
114 gradients = {"dW"+str(L):dWL, "db"+str(L):dbL}
115 #calculate from L-1 to 1 layer gradients
116 for l in reversed(range(1,L)): # L-1,L-3,....,1
117 post_W= caches[l+1][0] #要用后一层的W
118 dz = dzL #用后一层的dz
119
120 dal = np.dot(post_W.T, dz)
121 z = caches[l][2]#当前层的z
122 dzl = np.multiply(dal, relu_backward(z))
123 prev_A = caches[l-1][3]#前一层的A
124 dWl = np.dot(dzl, prev_A.T)
125 dbl = np.sum(dzl, axis=1, keepdims=True)
126
127 gradients["dW" + str(l)] = dWl
128 gradients["db" + str(l)] = dbl
129 dzL = dzl #更新dz
130 return gradients
131
132 def update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate):
133 """
134 :param parameters: dictionary, W,b
135 :param grads: dW,db
136 :param learning_rate: alpha
137 :return:
138 """
139 L = len(parameters) // 2
140 for l in range(L):
141 parameters["W" + str(l + 1)] = parameters["W" + str(l + 1)] - learning_rate * grads["dW" + str(l+1)]
142 parameters["b" + str(l + 1)] = parameters["b" + str(l + 1)] - learning_rate * grads["db" + str(l+1)]
143 return parameters
144
145
146 def random_mini_batches(X, Y, mini_batch_size = 64, seed=1):
147 """
148 Creates a list of random minibatches from (X, Y)
149 Arguments:
150 X -- input data, of shape (input size, number of examples)
151 Y -- true "label" vector (1 for blue dot / 0 for red dot), of shape (1, number of examples)
152 mini_batch_size -- size of the mini-batches, integer
153
154 Returns:
155 mini_batches -- list of synchronous (mini_batch_X, mini_batch_Y)
156 """
157 np.random.seed(seed)
158 m = X.shape[1] # number of training examples
159 mini_batches = []
160
161 # Step 1: Shuffle (X, Y)
162 permutation = list(np.random.permutation(m))
163 shuffled_X = X[:, permutation]
164 shuffled_Y = Y[:, permutation].reshape((1, m))
165
166 # Step 2: Partition (shuffled_X, shuffled_Y). Minus the end case.
167 num_complete_minibatches = m // mini_batch_size # number of mini batches of size mini_batch_size in your partitionning
168 for k in range(0, num_complete_minibatches):
169 mini_batch_X = shuffled_X[:, k * mini_batch_size: (k + 1) * mini_batch_size]
170 mini_batch_Y = shuffled_Y[:, k * mini_batch_size: (k + 1) * mini_batch_size]
171 mini_batch = (mini_batch_X, mini_batch_Y)
172 mini_batches.append(mini_batch)
173
174 # Handling the end case (last mini-batch < mini_batch_size)
175 if m % mini_batch_size != 0:
176 mini_batch_X = shuffled_X[:, num_complete_minibatches * mini_batch_size: m]
177 mini_batch_Y = shuffled_Y[:, num_complete_minibatches * mini_batch_size: m]
178 mini_batch = (mini_batch_X, mini_batch_Y)
179 mini_batches.append(mini_batch)
180
181 return mini_batches
182
183 def L_layer_model(X, Y, layer_dims, learning_rate, num_iterations, gradient_descent = 'bgd',mini_batch_size = 64):
184 """
185 :param X:
186 :param Y:
187 :param layer_dims:list containing the input size and each layer size
188 :param learning_rate:
189 :param num_iterations:
190 :return:
191 parameters:final parameters:(W,b)
192 """
193 m = Y.shape[1]
194 costs = []
195 # initialize parameters
196 parameters = initialize_parameters(layer_dims)
197 if gradient_descent =='bgd':
198 for i in range(0, num_iterations):
199 #foward propagation
200 AL,caches = forward_propagation(X, parameters)
201 # calculate the cost
202 cost = compute_cost(AL, Y)
203 if i % 1000 == 0:
204 print("Cost after iteration {}: {}".format(i, cost))
205 costs.append(cost)
206 #backward propagation
207 grads = backward_propagation(AL, Y, caches)
208 #update parameters
209 parameters = update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate)
210 elif gradient_descent == 'sgd':
211 np.random.seed(3)
212 # 把数据集打乱,这个很重要
213 permutation = list(np.random.permutation(m))
214 shuffled_X = X[:, permutation]
215 shuffled_Y = Y[:, permutation].reshape((1, m))
216 for i in range(0, num_iterations):
217 for j in range(0, m): # 每次训练一个样本
218 # Forward propagation
219 AL,caches = forward_propagation(shuffled_X[:, j].reshape(-1,1), parameters)
220 # Compute cost
221 cost = compute_cost(AL, shuffled_Y[:, j].reshape(1,1))
222 # Backward propagation
223 grads = backward_propagation(AL, shuffled_Y[:,j].reshape(1,1), caches)
224 # Update parameters.
225 parameters = update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate)
226 if j % 20 == 0:
227 print("example size {}: {}".format(j, cost))
228 costs.append(cost)
229 elif gradient_descent == 'mini-batch':
230 seed = 0
231 for i in range(0, num_iterations):
232 # Define the random minibatches. We increment the seed to reshuffle differently the dataset after each epoch
233 seed = seed + 1
234 minibatches = random_mini_batches(X, Y, mini_batch_size, seed)
235 for minibatch in minibatches:
236 # Select a minibatch
237 (minibatch_X, minibatch_Y) = minibatch
238 # Forward propagation
239 AL, caches = forward_propagation(minibatch_X, parameters)
240 # Compute cost
241 cost = compute_cost(AL, minibatch_Y)
242 # Backward propagation
243 grads = backward_propagation(AL, minibatch_Y, caches)
244 parameters = update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate)
245 if i % 100 == 0:
246 print("Cost after iteration {}: {}".format(i, cost))
247 costs.append(cost)
248 print('length of cost')
249 print(len(costs))
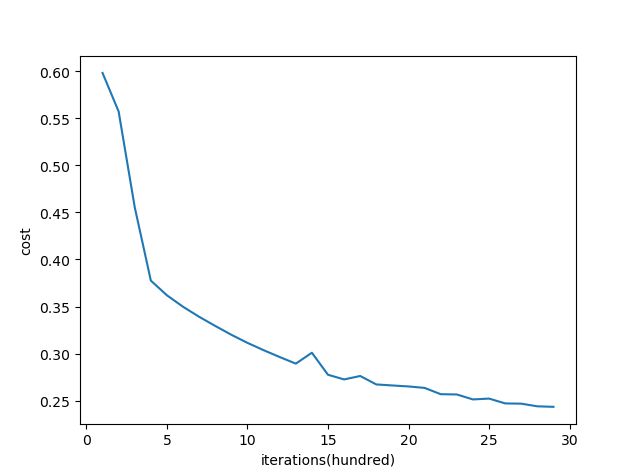
250 plt.clf()
251 plt.plot(costs)
252 plt.xlabel("iterations(hundred)") # 横坐标名字
253 plt.ylabel("cost") # 纵坐标名字
254 plt.show()
255 return parameters
256
257 #predict function
258 def predict(X_test,y_test,parameters):
259 """
260 :param X:
261 :param y:
262 :param parameters:
263 :return:
264 """
265 m = y_test.shape[1]
266 Y_prediction = np.zeros((1, m))
267 prob, caches = forward_propagation(X_test,parameters)
268 for i in range(prob.shape[1]):
269 # Convert probabilities A[0,i] to actual predictions p[0,i]
270 if prob[0, i] > 0.5:
271 Y_prediction[0, i] = 1
272 else:
273 Y_prediction[0, i] = 0
274 accuracy = 1- np.mean(np.abs(Y_prediction - y_test))
275 return accuracy
276 #DNN model
277 def DNN(X_train, y_train, X_test, y_test, layer_dims, learning_rate= 0.0006, num_iterations=30000, gradient_descent = 'bgd',mini_batch_size = 64):
278 parameters = L_layer_model(X_train, y_train, layer_dims, learning_rate, num_iterations,gradient_descent,mini_batch_size)
279 accuracy = predict(X_test,y_test,parameters)
280 return accuracy
281
282 if __name__ == "__main__":
283 X_data, y_data = load_breast_cancer(return_X_y=True)
284 X_train, X_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(X_data, y_data, train_size=0.8,random_state=28)
285 X_train = X_train.T
286 y_train = y_train.reshape(y_train.shape[0], -1).T
287 X_test = X_test.T
288 y_test = y_test.reshape(y_test.shape[0], -1).T
289 #use bgd
290 accuracy = DNN(X_train,y_train,X_test,y_test,[X_train.shape[0],10,5,1])
291 print(accuracy)
292 #use sgd
293 accuracy = DNN(X_train, y_train, X_test, y_test, [X_train.shape[0], 10, 5, 1],num_iterations=5, gradient_descent = 'sgd')
294 print(accuracy)
295 #mini-batch
296 accuracy = DNN(X_train, y_train, X_test, y_test, [X_train.shape[0], 10, 5, 1], num_iterations=10000,gradient_descent='mini-batch')
297 print(accuracy)