使用 D3.js 创建柱状堆积图
柱状堆积图
项目地址
使用 D3.js 创建的图表:
- 使用 D3.js 创建根据值域颜色渐变的地图
- D3.js 中动态计算 x 轴 y 轴的宽度以及偏移量
- 在 Ember.js 项目中由浅入深使用 D3.js 绘制图表
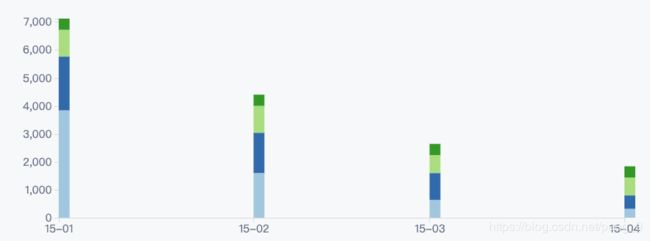
8.1 效果图
可以看到每组数据都进行了叠加。
现在来看一下具体实现:
8.2 实现
堆叠图虽然和柱状图在展示上相差不是很多,但是在实现上差距还是有的。简单的柱状图是使用 svg 中的 rect 元素,根据数据,赋予 rect 相应的宽高来展示数据的差异。但是堆叠图是使用多个 rect 堆叠起,其中的 rect 关系我们是需要计算的。还好在 D3.js 中提供了相关的 API: d3.shape 中的 d3.stack ,对数据进行处理。
本次示例中也是使用的官方示例数据。
8.2.1 坐标轴
坐标轴的生成在之前的文章中也提到不少,这里为了尝试更多的 scale ,使用了在本例中不太合适的 scaleTime 比例尺。
注意 比例尺的选择要根据展示的图的 nature 来选择合适的比例尺,不能只是淡淡因为 x 轴 lable 的数据是什么类型就选择什么类型的比例尺。
看到这里,应该发现我们的展示图上有一些问题:柱状图并不是居中在坐标的 ticks 中,而是有一个 1/2 bandWidth 的偏移。这也是 scaleTime 的原因。
上代码
/** 数据格式
* [
{month: new Date(2015, 0, 1), apples: 3840, bananas: 1920, cherries: 960, dates: 400},
{month: new Date(2015, 1, 1), apples: 1600, bananas: 1440, cherries: 960, dates: 400},
{month: new Date(2015, 2, 1), apples: 640, bananas: 960, cherries: 640, dates: 400},
{month: new Date(2015, 3, 1), apples: 320, bananas: 480, cherries: 640, dates: 400}
]
*/
// ...
const timeDate = data.map(datum => datum.month)
// y 轴 scale
const yScale = scaleLinear()
.domain([0, max(series, d => max(d, d => d[1]))])
.range([this.height - padding.pt - padding.pb, 0]);
const yAxis = axisLeft(yScale)
svg.append('g')
.classed("y-axis", true)
.call(yAxis);
// y轴宽度
const yAxisWidth: number = getYAxisWidth(svg.select('.y-axis'))
svg.select(".y-axis")
.attr("transform", `translate(${padding.pl + yAxisWidth},${padding.pt})`);
// 为了给两端留出空白区域
const phMinDate = timeMonth.offset(min(timeDate),-1);
const phMaxDate = timeMonth.offset(max(timeDate),1);
// x轴scale
const xScale = scaleTime()
.domain([min(timeDate),max(timeDate)])
.range([padding.pl, this.width - padding.pr - yAxisWidth]);
// x轴
const xAxis = axisBottom(xScale)
.ticks(timeMonth.every(1))
.tickFormat(timeFormat('%y-%m'))
svg.append('g')
.classed("x-axis", true)
.attr("transform", `translate(${yAxisWidth},${this.height - padding.pb})`)
.call(xAxis)
// ...
其中使用的 utils 函数 - getYAxisWidth 在 项目 可查看。
这个示例展示了 scaleTime 的用法以及对时间的进一步格式化:
// x轴
const xAxis = axisBottom(xScale)
.ticks(timeMonth.every(1))
.tickFormat(timeFormat('%y-%m'))
当 timeMonth.every 的参数值为 3 的时候,我们就可以得到按季度分隔的时间轴了。
这时我们可以看到:
8.2.2 数据展示
要展示 stack 数据,需要对原始数据进行预处理。D3.js 提供 d3.stack 处理函数:
const stackIns = stack()
.keys(Object.keys(data[0]).slice(1))
.order(stackOrderNone)
.offset(stackOffsetNone);
const series = stackIns(data);
现在,我们得到的 series 即时我们要绘制的堆叠图的能够识别的数据:
svg.selectAll('g.stack')
.data(series)
.join(
enter => enter.append('g'),
update => update,
exit => exit.remove()
)
.classed('stack', true)
.attr('fill', (d:any,i:number)=>schemePaired[i])
.attr('transform',`translate(${yAxisWidth},${padding.pt})`)
.selectAll('rect')
.data(d => d)
.join(
enter => enter.append('rect'),
update => update,
exit => exit.remove()
)
.attr('x', (d: any) => xScale(d.data.month))
.attr('y', (d: any) => yScale(d[1]))
.attr('height', (d: any) => yScale(d[0]) - yScale(d[1]))
.attr('width', 14)
这样像图 8.1 的效果就出来了。现在来看一下完整的代码:
// bp-stack.ts
import Component from '@glimmer/component';
import { action } from '@ember/object';
import Layout from 'ember-d3-demo/utils/d3/layout';
import { scaleTime, scaleLinear } from 'd3-scale';
import { axisBottom, axisLeft } from 'd3-axis';
import { min, max } from 'd3-array';
import { timeMonth } from 'd3-time';
import { timeFormat } from 'd3-time-format';
import { stack, stackOrderNone, stackOffsetNone } from 'd3-shape';
import { getYAxisWidth } from 'ember-d3-demo/utils/d3/yAxisWidth';
import { schemePaired} from 'd3-scale-chromatic';
interface D3BpStackArgs {
data: any[];
/** 数据格式
* [
{month: new Date(2015, 0, 1), apples: 3840, bananas: 1920, cherries: 960, dates: 400},
{month: new Date(2015, 1, 1), apples: 1600, bananas: 1440, cherries: 960, dates: 400},
{month: new Date(2015, 2, 1), apples: 640, bananas: 960, cherries: 640, dates: 400},
{month: new Date(2015, 3, 1), apples: 320, bananas: 480, cherries: 640, dates: 400}
]
*/
width: number;
height: number;
}
export default class D3BpStack extends Component<D3BpStackArgs> {
constainer: any = null
width: number = this.args.width
height: number = this.args.height
@action
initChart() {
const data = this.args.data
let layout = new Layout('.bp-stack')
let { width, height } = this
if (width) {
layout.setWidth(width)
} else {
width = layout.getWidth()
}
if (height) {
layout.setHeight(height)
} else {
height = layout.getHeight()
}
const container = layout.getContainer()
this.width = layout.getWidth()
this.height = layout.getHeight()
this.constainer = container
const padding = layout.getPadding()
// 生成 svg
let svg = container.append('svg')
.attr("width", width)
.attr("height", height);
const stackIns = stack()
.keys(Object.keys(data[0]).slice(1))
.order(stackOrderNone)
.offset(stackOffsetNone);
const series = stackIns(data);
const timeDate = data.map(datum => datum.month)
// y 轴 scale
const yScale = scaleLinear()
.domain([0, max(series, d => max(d, d => d[1]))])
.range([this.height - padding.pt - padding.pb, 0]);
const yAxis = axisLeft(yScale)
svg.append('g')
.classed("y-axis", true)
.call(yAxis);
// y轴宽度
const yAxisWidth: number = getYAxisWidth(svg.select('.y-axis'))
svg.select(".y-axis")
.attr("transform", `translate(${padding.pl + yAxisWidth},${padding.pt})`);
// 为了给两端留出空白区域
const phMinDate = timeMonth.offset(min(timeDate),-1);
const phMaxDate = timeMonth.offset(max(timeDate),1);
// x轴scale
const xScale = scaleTime()
.domain([min(timeDate),max(timeDate)])
.range([padding.pl, this.width - padding.pr - yAxisWidth]);
// x轴
const xAxis = axisBottom(xScale)
.ticks(timeMonth.every(1))
.tickFormat(timeFormat('%y-%m'))
svg.append('g')
.classed("x-axis", true)
.attr("transform", `translate(${yAxisWidth},${this.height - padding.pb})`)
.call(xAxis)
svg.selectAll('g.stack')
.data(series)
.join(
enter => enter.append('g'),
update => update,
exit => exit.remove()
)
.classed('stack', true)
.attr('fill', (d:any,i:number)=>schemePaired[i])
.attr('transform',`translate(${yAxisWidth},${padding.pt})`)
.selectAll('rect')
.data(d => d)
.join(
enter => enter.append('rect'),
update => update,
exit => exit.remove()
)
.attr('x', (d: any) => xScale(d.data.month))
.attr('y', (d: any) => yScale(d[1]))
.attr('height', (d: any) => yScale(d[0]) - yScale(d[1]))
.attr('width', 14)
}
}
{{!-- bp-stack.hbs --}}
<div class="bp-stack" {{did-insert this.initChart}}></div>