06_02_Flink DataStream多流合并算子
在关系型数据库中,最常见的多表关联有笛卡尔积连接,left outer join,rght outer join,full
join,inner join。在Flink中,支持多流关联的有3中算子,如下:
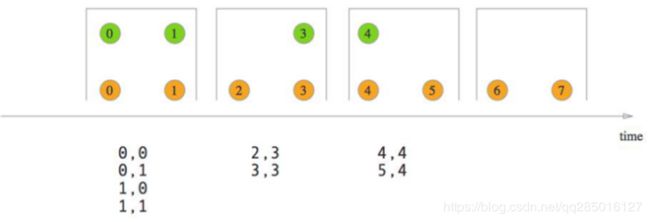
Cogroup
object TestCoGroup {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val env: StreamExecutionEnvironment = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
val stream1: DataStream[(String, String)] = env.readTextFile("C:\\Users\\j\\Desktop\\1.txt")
.map(value => {
val arr: Array[String] = value.split(" ")
(arr(0), arr(1))
})
val stream2: DataStream[(String, String)] = env.readTextFile("C:\\Users\\j\\Desktop\\2.txt")
.map(value => {
val arr: Array[String] = value.split(" ")
(arr(0), arr(1))
})
stream1.coGroup(stream2).where(new Function[(String, String), String] {
override def apply(v1: (String, String)): String = {
v1._1
}
}).equalTo(new Function[(String, String), String] {
override def apply(v1: (String, String)): String = {
v1._1
}
}).window(ProcessingTimeSessionWindows.withGap(Time.seconds(30)))
.trigger(CountTrigger.of(1))
.apply(new CoGroupFunction[(String, String), (String, String), String] {
override def coGroup(first: lang.Iterable[(String, String)], second: lang.Iterable[(String, String)], collector: Collector[String]): Unit = {
import scala.collection.JavaConversions._
val stringBuilder = new StringBuilder("Data in stream1: \n")
for (item <- first) {
stringBuilder.append("" + item._1 + "<=>" + item._2 + "\n")
}
stringBuilder.append("Data in stream2: \n")
import scala.collection.JavaConversions._
for (item <- second) {
stringBuilder.append("" + item._1 + "<=>" + item._2 + "\n")
}
collector.collect(stringBuilder.toString)
}
})
.print()
//这里可以看到,两个流每读取一条数据就会去关联,不管关联是否成功都会发送给下游
//2<=>b null
//null 1<=>c
//1<=>a 1<=>c
env.execute
}
}
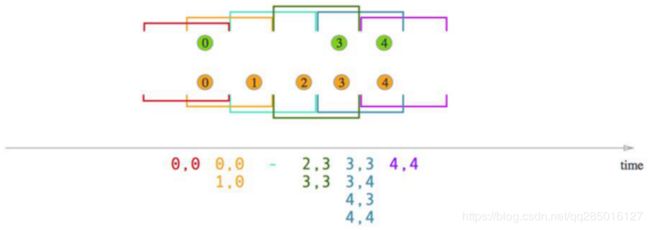
Join
object TestJoin {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val env: StreamExecutionEnvironment = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
val stream1: DataStream[(String, String)] = env.readTextFile("C:\\Users\\j\\Desktop\\1.txt")
.map(value => {
val arr: Array[String] = value.split(" ")
(arr(0), arr(1))
})
val stream2: DataStream[(String, String)] = env.readTextFile("C:\\Users\\j\\Desktop\\2.txt")
.map(value => {
val arr: Array[String] = value.split(" ")
(arr(0), arr(1))
})
stream1.join(stream2)
.where(item=>item._1)
.equalTo(item=>item._1)
.window(ProcessingTimeSessionWindows.withGap(Time.seconds(30)))
.trigger(CountTrigger.of(1))
.apply(new FlatJoinFunction[(String, String), (String, String), String] {
override def join(in1: (String, String), in2: (String, String), collector: Collector[String]): Unit = {
collector.collect("in1:"+in1._1+":"+in1._2+"<<<>>>"+"in2:"+in2._1+":"+in2._2)
}
})
.print()
//只有匹配key成功的数据才能发送到下游
//in1:1:a<<<>>>in2:1:c
env.execute
}
}
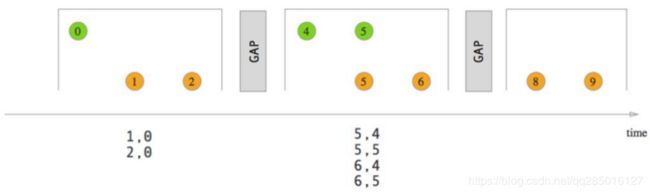
Interval Join
KeyedStream,KeyedStream → DataStream
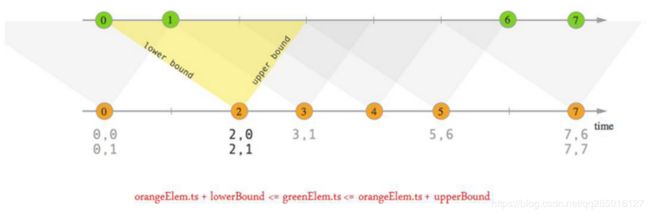
• 在给定的周期内,按照指定的key对两个KeyedStream进行join操作,把符合join条件的两个event 拉到一起,然后怎么处理由用户你来定义。
• key1 == key2 && e1.timestamp + lowerBound <= e2.timestamp <= e1.timestamp + upperBound
• 场景:把一定时间范围内相关的分组数据拉成一个宽表
object TestIntervalJoin {
//定义样例类
case class Transcript(var id: String, var name: String, var subject: String, var score: Int, var time: Long)
case class Student(var id: String, var name: String, var clazz: String, var time: Long)
@throws[Exception]
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
//获取执行环境并指定Time
val env: StreamExecutionEnvironment = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
env.setStreamTimeCharacteristic(TimeCharacteristic.EventTime)
//初始化DataStream
val TRANSCRIPTS: Array[Transcript] = Array[Transcript](
Transcript("1", "张三", "语文", 100, System.currentTimeMillis),
Transcript("2", "李四", "语文", 78, System.currentTimeMillis),
Transcript("3", "王五", "语文", 99, System.currentTimeMillis),
Transcript("4", "赵六", "语文", 81, System.currentTimeMillis),
Transcript("5", "钱七", "语文", 59, System.currentTimeMillis),
Transcript("6", "马二", "语文", 97, System.currentTimeMillis))
val STUDENTS: Array[Student] = Array[Student](
Student("1", "张三", "class1", System.currentTimeMillis),
Student("2", "李四", "class1", System.currentTimeMillis),
Student("3", "王五", "class1", System.currentTimeMillis),
Student("4", "赵六", "class2", System.currentTimeMillis),
Student("5", "钱七", "class2", System.currentTimeMillis),
Student("6", "马二", "class2", System.currentTimeMillis))
// TRANSCRIPTS: _* 可以将数组转换成可变参数
val input1: DataStream[Transcript] = env.fromElements(TRANSCRIPTS: _*).assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(new AscendingTimestampExtractor[Transcript] {
override def extractAscendingTimestamp(t: Transcript): Long = t.time
})
val input2: DataStream[Student] = env.fromElements(STUDENTS: _*).assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(new AscendingTimestampExtractor[Student] {
override def extractAscendingTimestamp(t: Student): Long = t.time
})
//对数据进行分组
val keyedStream: KeyedStream[Transcript, String] = input1.keyBy(new KeySelector[Transcript, String]() {
@throws[Exception]
override def getKey(value: Transcript): String = value.id
})
val otherKeyedStream: KeyedStream[Student, String] = input2.keyBy(new KeySelector[Student, String]() {
@throws[Exception]
override def getKey(value: Student): String = value.id
})
//e1.timestamp + lowerBound <= e2.timestamp <= e1.timestamp + upperBound
// key1 == key2 && leftTs - 2 < rightTs < leftTs + 2
keyedStream.intervalJoin(otherKeyedStream)
.between(Time.milliseconds(-2), Time.milliseconds(2))
.upperBoundExclusive
.lowerBoundExclusive
.process(new ProcessJoinFunction[Transcript, Student, (String, String, String, String, Integer)]() {
@throws[Exception]
override def processElement(transcript: Transcript, student: Student, ctx: ProcessJoinFunction[Transcript, Student, (String, String, String, String, Integer)]#Context, out: Collector[(String, String, String, String, Integer)]): Unit = {
out.collect((transcript.id, transcript.name, student.clazz, transcript.subject, transcript.score))
}
}).print
env.execute
//2> (3,王五,class1,语文,99)
//1> (2,李四,class1,语文,78)
//1> (4,赵六,class2,语文,81)
//1> (6,马二,class2,语文,97)
//3> (5,钱七,class2,语文,59)
}
}
connect & union(合并流)
connect之后生成ConnectedStreams,会对两个流的数据应用不同的处理方法,并且双流
之间可以共享状态(比如计数)。这在第一个流的输入会影响第二个流 时, 会非常有用; union
合并多个流,新的流包含所有流的数据。
• union是DataStream* → DataStream
• connect只能连接两个流,而union可以连接多于两个流
• connect连接的两个流类型可以不一致,而union连接的流的类型必须一致
object TestConnect {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val env: StreamExecutionEnvironment = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
val someStream: DataStream[Long] = env.generateSequence(0, 10)
val otherStream: DataStream[String] = env.fromElements(WORDS: _*)
val connectedStreams: ConnectedStreams[Long, String] = someStream.connect(otherStream)
//将第一个流从数字转换成字符串,与第二个流进行合并,合并后两个流的类型都是字符串
val result: DataStream[Object] = connectedStreams.flatMap((value1: Long, collector1) => {
collector1.collect(value1.toString)
}, (value2, collector2) => {
collector2.collect(value2)
})
result.print
env.execute
}
val WORDS: Array[String] = Array[String]("And thus the native hue of resolution", "Is sicklied o'er with the pale cast of thought;", "And enterprises of great pith and moment,", "With this regard, their currents turn awry,", "And lose the name of action.--Soft you now!", "The fair Ophelia!--Nymph, in thy orisons", "Be all my sins remember'd.")
}
CoMap,CoFlatMap
跟map and flatMap类似,只不过作用在ConnectedStreams上
• ConnectedStreams → DataStream
split & select (拆分流)
• split
DataStream → SplitStream
按照指定标准将指定的DataStream拆分成多个流用SplitStream来表示
• select
SplitStream → DataStream
跟split搭配使用,从SplitStream中选择一个或多个流
object TestSplitAndSelect {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val env: StreamExecutionEnvironment = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment
val input: DataStream[Long] = env.generateSequence(0, 10)
// TraversableOnce代表函数需返回一个Scala集合
val splitStream: SplitStream[Long] = input.split(item=>{
val output = ArrayBuffer[String]()
if (item % 2 == 0) output.append("even")
else output.append("odd")
output
})
splitStream.print(); //返回0-10所有流数据
val even: DataStream[Long] = splitStream.select("even")
val odd: DataStream[Long] = splitStream.select("odd") //返回1,3,5,7,9
val all: DataStream[Long] = splitStream.select("even", "odd")
//even.print();
//odd.print
//all.print();
env.execute
}
}