[疫情期间复习] mybatis源码分析系列(三) SqlSessionFactory之sql执行流程
上节分析我们已经拿到了sqlsessionFactory工厂
具体怎么执行sql呢 开始分析
通过测试案例 我们看到了 sqlsessionFactory.openSession()
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
//获取环境信息
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
//获取事务管理器
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
//获取执行器
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
看到这就一个小面试题
sql 执行器有几种 ?
分别是什么?
都是什么用途 ?
直接看源码找到答案
public enum ExecutorType {
//默认执行器 简单执行器 每执行一次update或select,就开启一个Statement对象,用完立刻关闭Statement对象
SIMPLE,
//执行器会重用预处理语句
REUSE,
//批量执行器 执行器不仅重用语句还会执行批量更新
BATCH
}
看到这 sqlsession就拿到了
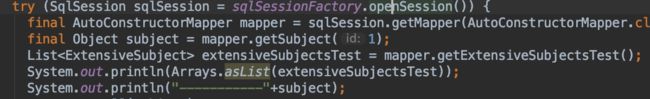
拿到sqlsession就开始执行getMapper分析
抽丝剥茧最后会找到MapperRegistry.class
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
//knownMappers 中获取我们制定的类 knownMappers是时候初始化的呢
//其实是在我们创建sqlSessionFactory的时候做的
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
//MapperProxyFactory.class中的方法
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
可以很清楚的看到最后创建了一个代理类返回。拿到代理类后开始执行sql
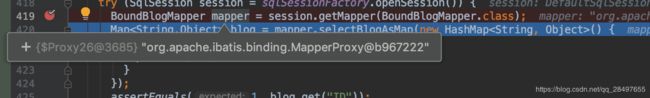
代码跟踪到这里 发现是MapperProxy
@Override
//动态代理执行调用
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
//是否和声明class一致
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else {
//缓存调用
return cachedInvoker(method).invoke(proxy, method, args, sqlSession);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
interface MapperMethodInvoker {
Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, SqlSession sqlSession) throws Throwable;
}
//内部类
private static class PlainMethodInvoker implements MapperMethodInvoker {
private final MapperMethod mapperMethod;
public PlainMethodInvoker(MapperMethod mapperMethod) {
super();
this.mapperMethod = mapperMethod;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, SqlSession sqlSession) throws Throwable {
//执行
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
}
通过上面流程我们 找到MapperMechod.class 看到insert update delete等type类型的处理逻辑
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
....
}
case DELETE: {
.....
}
case SELECT:{
.....
}
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
........
return result;
}
我们以select为例 默认是通过SqlSession的实现类DefaultSqlSession来完成的sql语句处理
![[疫情期间复习] mybatis源码分析系列(三) SqlSessionFactory之sql执行流程_第1张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/d078b95eb2ca4e9d839e4cc8a737c343.jpg)
跟踪其中一个方法会知道CachingExecutor.class的query方法
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
//获取sql语句
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
//生成缓存key 默认情况mybatis是开启一级缓存的
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
//缓存是否存在
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null) {
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
list = delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
return list;
}
}
return delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
@Override
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
//获取config信息
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
//预处理handler
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
//获取数据库连接
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
SimpleStatementHandler.class
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
//获取绑定sql
String sql = boundSql.getSql();
//执行
statement.execute(sql);
//返回数据处理
return resultSetHandler.handleResultSets(statement);
}
![[疫情期间复习] mybatis源码分析系列(三) SqlSessionFactory之sql执行流程_第2张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/35072cfc016e47cfa8ffc3b1a8e56565.jpg)
![[疫情期间复习] mybatis源码分析系列(三) SqlSessionFactory之sql执行流程_第3张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/3b3d0717babf4c67a0ffd13821c35266.jpg)
![[疫情期间复习] mybatis源码分析系列(三) SqlSessionFactory之sql执行流程_第4张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/058c7718b9324590996b97c43facc350.jpg)
![[疫情期间复习] mybatis源码分析系列(三) SqlSessionFactory之sql执行流程_第5张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/c58f0e5eab5d447fba38651406d4d79a.jpg)