树莓派应用实例4:环境温湿度测量(改进)
转自:https://blog.csdn.net/weixiazailaide/article/details/52749783
前期准备
环境要求
DHT11,树莓派系统,Python,rpi.gpio等组件
相关软件安装方式见执勤的博客文章:https://blog.csdn.net/fm0517/article/details/80965794
开启i2c,spi,1wire等
一个意外的惊喜
在设置i2c功能时,偶然发现树莓派里有个更强大的功能 Device Tree (DT) ,在/boot/overlays发现了很多外设驱动,于是仔细阅读了README文件,在272行看到了DHT11驱动加载方式,对上章程序进行了简单的修改,使之更加快速准确
修改config.txt后,我是一脸懵逼,去哪找测量结果?☺
然后开始大量查找资料,看输出结果如何查询,费了半天工夫,也没找到相关资料,WTF???
又仔细拜读README文件,没找到任何关于输出结果的介绍,(黑人问号脸 在最后后一行发现个连接,好神奇呀,点开去看,全英语的,U TM DOU I,欺负我英语差。。。
很伤,只能一边翻译一边瞅,瞅完也米看懂啥意思
在我决定放弃的时候,我打算最后博一下,去sys/devices文件下挨个去找,功夫不负有心人,终于找到带有dht11的文件,点进去,挨个打开查看,最后在iio:device0里找到 in_humidityrelative_input和in_temp_input俩个文件,分别对应湿度和温度,但为啥有时打开报错,有时正常呢,心好累
但是iio这个新名词又是什么鬼,求老司机带带我
大家感受下我得之不易的iio文件夹
/sys/devices/platform/dht11@0/iio:device0
├── dev
├── in_humidityrelative_input
├── in_temp_input
├── name
├── of_node -> ../../../../firmware/devicetree/base/dht11@0
├── power
│ ├── autosuspend_delay_ms
│ ├── control
│ ├── runtime_active_time
│ ├── runtime_status
│ └── runtime_suspended_time
├── subsystem -> ../../../../bus/iio
└── uevent
3 directories, 10 files
也感受下不明觉厉的README文件
cat /boot/overlays/readme在config.txt中添加i2c,spi,以及对DHT11的支持
sudo vi /boot/config.txt#开启i2c
dtparam=i2c_arm=on
#开启spi
dtparam=spi=on
#DHT11支持
dtoverlay=dht11温湿度测量
创建temhum2应用
具体方法见之前博客创建raspberrypistate应用的部分
修改settings.py
cd ~/helloworld/helloworld
vi settings.pyINSTALLED_APPS = [
'raspberrypistate.apps.RaspberrypistateConfig',
'temhum2.apps.Temhum2Config', #增加这一行
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
]
修改urls.py
cd ~/helloworld/helloworld
vi urls.pyfrom django.conf.urls import include, url
from django.contrib import admin
from helloworld.view import hello
urlpatterns = [
url(r'^hello/$', hello),
url(r'^raspberrypistate/', include('raspberrypistate.urls',namespace="raspberrypistate")),
url(r'^temhum2/', include('temhum2.urls',namespace="temhum2")), #增加这一行
url(r'^admin/', admin.site.urls),
]
配置tmphum2的views.py
cd ~/helloword/tmphum2
vi views.py# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
from django.http import HttpResponse
from . import temhum2
# Create your views here.
def index(request):
tem=temhum2.getTemHum()
return HttpResponse(tem)
配置tmphum2的urls.py
从其他地方复制过来即可
cp /home/pi/helloworld/temhum/urls.py /home/pi/helloworld/temhum2建立新的程序代码temhum2.py
cd ~/helloword/tmphum2
vi temhum2.py#!/usr/bin/env python
# encoding: utf-8
import commands
#获取温度
def getTemperature():
while True:
res=commands.getoutput("cat /sys/devices/platform/dht11@0/iio:device0/in_temp_input")
if res.isdigit():
return int(res)/1000
#获取湿度
def getHumidity():
while True:
res=commands.getoutput("cat /sys/devices/platform/dht11@0/iio:device0/in_humidityrelative_input")
if res.isdigit():
return int(res)/1000
#温湿度
def getTemHum():
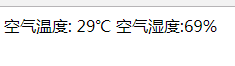
result="空气温度: "+str(getTemperature())+"℃ 空气湿度:"+str(getHumidity())+"%"
return result测试效果
按照惯例重启uwsgi服务
sudo systemctl restart emperor.uwsgi.service在树莓派浏览器输入 http://127.0.0.1/temhum
或者在电脑浏览器输入 http://raspberrypi/temhum
后记
这样写的Python程序简单了许多有木有,我就想玩个树莓派装个B,就又是内核又是驱动的,心好累
界面美化正在学习,求教程,要不几个字太坑爹了
最后附上树莓派官方关于DT介绍的连接和在 www.kernel.org 找到的疑似关于iio的介绍
求老司机出个树莓派使用overlays文件下所有DTB的系列文章,然后再出个DTB编写指南啥的,