Spring源码深度解析(一)容器的基本实现
参考书籍《Spring源码深度解析》
这里写目录标题
- 1. 原理图概要
- 1.1 BeanFactory容器的基础
- 1.2 bean的加载
- 2. 核心类简单介绍
- 2.1 DefaultListableBeanFactory和XmlBeanFactory
- 2.2 XmlBeanDefinitionReader读取资源文件的脉络
- 3. 容器的基础 XmlBeanFactory
- 3.1 分析 XmlBeanFactory的代码实现
- 3.2 配置文件的封装
- 3.3 XmlBeanFactory的构造函数
- 4. 加载bean
- 4.1 获取Document
- 4.2 加载Document
- 4.3 最后的解析及注册BeanDefinitions!!!
1. 原理图概要
1.1 BeanFactory容器的基础
1.2 bean的加载
2. 核心类简单介绍
2.1 DefaultListableBeanFactory和XmlBeanFactory
- DefaultListableBeanFactory是整个bean加载的核心部分是Spring注册及加载bean的默认实现。
- XmlBeanFactory继承自DefaultListableBeanFactory,是对父类的扩展。它们之之间不同的地方在于,XmlBeanFactory使用了自定义的XML读取器XmlBeanDefinitionReader,利用其中的reader属性,对资源文件进行读取和注册。
2.2 XmlBeanDefinitionReader读取资源文件的脉络
- 通过继承自AbstractBeanDefinitionReader中的方法,来使用ResourceLoader将资源文件转换为对应的Resource文件。
- 通过DocumentLoader对Resource文件进行转换,将其转换为Document文件。
- 通过实现接口BeanDefinitionDocumentReader的DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader类对Document进行解析,并使用BeanDefinitionParserDelegate对Element进行解析。
3. 容器的基础 XmlBeanFactory
3.1 分析 XmlBeanFactory的代码实现
让我们先看看如下代码 ↓
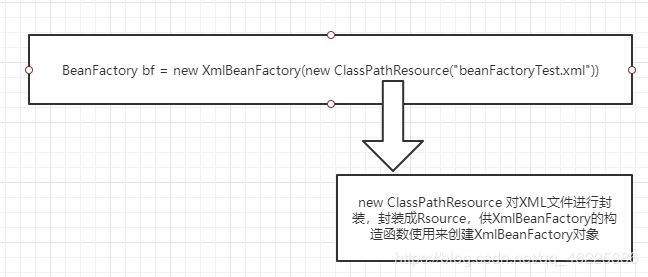
BeanFactory bf = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("beanFactoryTest.xml"));
我们可以看到,其中 new ClassPathResource(“beanFactoryTest.xml”) 调用构造函数,构造了Resource实例对象,那么这个过程是 怎么封装 的呢?下面来解释一下。
3.2 配置文件的封装
Spring对资源文件的封装,实现了自己的独特方式:Resource接口封装底层资源,看下方源代码,我们能发现Resource对不同来源的资源文件都有实现:File,Classpath,URL等
public interface Resource extends InputStreamSource {
//是否存在
boolean exists();
//是否可读
default boolean isReadable() {
return exists();
}
//是否打开
default boolean isOpen() {
return false;
}
default boolean isFile() {
return false;
}
//URL
URL getURL() throws IOException;
//URI
URI getURI() throws IOException;
//File
File getFile() throws IOException;
default ReadableByteChannel readableChannel() throws IOException {
return Channels.newChannel(getInputStream());
}
long contentLength() throws IOException;
long lastModified() throws IOException;
@Nullable
String getFilename();
String getDescription();
}
在日常开发中,常用以下方式来加载文件
Resource resource = new ClassPathResource("beanFacrotyTest.xml");
InputStream inputStream = resource.getInputStream;
我们现在知道了配置文件的封装,那么下面我们可以继续研究XmlBeanFactory的构造了
3.3 XmlBeanFactory的构造函数
上源码!
public class XmlBeanFactory extends DefaultListableBeanFactory {
//这个reader属性是重点!
private final XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(this);
//构造方法
public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource) throws BeansException {
this(resource, null);
}
//构造方法内部再次调用内部构造函数
// parentBeanFactory可以为空
public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource, BeanFactory parentBeanFactory) throws BeansException {
super(parentBeanFactory);
this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
}
}
其中this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource); 是我们要研究的重点,也是之后学习bean加载的切入点 ,我将该方法的源码放在下面。它是资源加载的真正实现,reader属性,即XmlBeanFactory特有的加载资源的方式,就是上文中所说的,XmlBeanFactory区别于DefaultListableBeanFactory的所在。这里我们聊完了BeanFactory容器的基础,下面就要到了 bean加载的过程啦!
public class XmlBeanDefinitionReader extends AbstractBeanDefinitionReader {
//先来到这里,再转到下面的可复用方法loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource)
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
return loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource));
}
public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null");
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource);
}
//记录已经记载的资源
Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get();
if (currentResources == null) {
currentResources = new HashSet<>(4);
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.set(currentResources);
}
if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!");
}
try {
//通过已经封装的encodedResource来再次从中取得inputStream
InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream();
try {
InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream);
if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) {
inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding());
}
//这里就进入了核心部分,我们会在下一节中,重点分析!
return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource());
}
finally {
inputStream.close();
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex);
}
finally {
currentResources.remove(encodedResource);
if (currentResources.isEmpty()) {
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove();
}
}
}
}
4. 加载bean
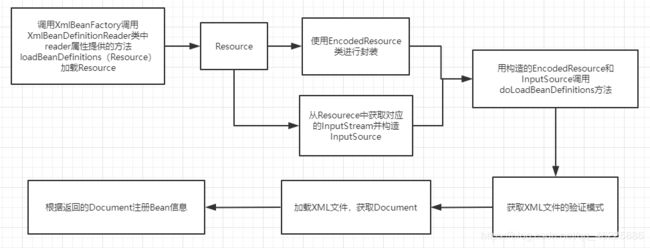
我们可以先对照开篇的原理分析图,对bean加载的过程做一个分解
- 当进入XmlBeanDefinitionReader后,先要对Resource使用EncodedResource类进行封装,即对文件的编码进行处理
- 封装完成后,获取输入流InputSource。
- 用构造的EncodedResource和InputSource为参数调用doLoadBeanDefinitions方法
下面我们来看一下doLoadBeanDefinitions方法的源码,这个方法做了两件重要的事儿,下面都会对这两件事儿进行解释。
1.获取Document对象,其中要获得对XML文件的验证模式
2.返回count用于注册bean信息
4.1 获取Document
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
try {
//加载为Document,下面有该方法的源码
Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource);
//文章最后一部分为registerBeanDefinitions源码的解析
int count = registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Loaded " + count + " bean definitions from " + resource);
}
//返回的count为本次加载BeanDefinition的个数
return count;
}
//下面全是捕获错误,大致浏览以下即可(其实可以不看。。。
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (SAXParseException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Line " + ex.getLineNumber() + " in XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (SAXException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (ParserConfigurationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Parser configuration exception parsing XML from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"IOException parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Unexpected exception parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
}
下面是doLoadDocument方法 的源码,该方法返回Document对象,有必要对其中 getEntityResolver() 和 getValidationModeForResource(resource) 进行解释
protected Document doLoadDocument(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource) throws Exception {
//loadDocument方法在下一节中进行解释
return this.documentLoader.loadDocument(inputSource, getEntityResolver(), this.errorHandler,
getValidationModeForResource(resource), isNamespaceAware());
}
getValidationModeForResource,顾名思义,获得验证模式,究竟是什么验证模式呢?分为以下两种
1.DTD验证模式,这种验证模式简单来说就是拿XML文件与DTD文件来进行比较,看是否符合规范,元素的标签是否使用正确。若使用DTD验证模式,我们则可以在XML文件的头部约束中,看到以下信息,
< !DOCTYPE beans PUBLIC “-//Spring//DTD BEAN 2.0//EN” “http://Springframework.org/dtd/Spring-beans-2.0.dtd”>
2.XSD验证模式,XSD是XML Schema语言,用来验证XML文档是否符合要求。在XML文件头部会有以下约束,xmlns为名称空间,schemaLocation为名称空间的储存位置
xmlns=“http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans”
xsi:schemaLocation=“http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd”>
protected int getValidationModeForResource(Resource resource) {
int validationModeToUse = getValidationMode();
if (validationModeToUse != VALIDATION_AUTO) {
return validationModeToUse;
}
int detectedMode = detectValidationMode(resource);
if (detectedMode != VALIDATION_AUTO) {
return detectedMode;
}
//找不到声明的时候就用XSD,但是现在很少有DTD的验证模式
// Hmm, we didn't get a clear indication... Let's assume XSD,
// since apparently no DTD declaration has been found up until
// detection stopped (before finding the document's root tag).
return VALIDATION_XSD;
}
getEntityResolver() ,EntityResolver参数有什么作用呢?从上方的两种验证模式来看,都有URL地址,默认的验证模式是通过URL地址,去网上寻找DTD或XSD来对XML文件进行验证,但是有了EntityResolver,我们便可以避免通过网络去验证,实现本地验证。
protected EntityResolver getEntityResolver() {
if (this.entityResolver == null) {
// Determine default EntityResolver to use.
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = getResourceLoader();
if (resourceLoader != null) {
this.entityResolver = new ResourceEntityResolver(resourceLoader);
}
else {
this.entityResolver = new DelegatingEntityResolver(getBeanClassLoader());
}
}
return this.entityResolver;
}
4.2 加载Document
下面是loadDocument方法的源码,这一部分完成了创建DocumentBuilderFactory 对象,创建DocumentBuilder,利用DocumentBuilder中的parse方法对inputSource进行解析,返回Document对象
public Document loadDocument(InputSource inputSource, EntityResolver entityResolver,
ErrorHandler errorHandler, int validationMode, boolean namespaceAware) throws Exception {
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = createDocumentBuilderFactory(validationMode, namespaceAware);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Using JAXP provider [" + factory.getClass().getName() + "]");
}
DocumentBuilder builder = createDocumentBuilder(factory, entityResolver, errorHandler);
return builder.parse(inputSource);
}
4.3 最后的解析及注册BeanDefinitions!!!
给我上源码!!!加油儿!胜利在望了!!!
public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
//其中doc为4.1中已经加载出的document对象
//实例化documentReader,BeanDefinitionDocumentReader是一个接口,而它的实例化是通过createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader()完成的
//而DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader implements BeanDefinitionDocumentReader
//它的类型已经是DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader了,下面我们就进入DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader类的源码
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader();
int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount();
documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource));
//此处为4.1源码处的count值,是本次加载中beanDefinition的个数
return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore;
}
public class DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader implements BeanDefinitionDocumentReader {
public void registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext) {
this.readerContext = readerContext;
//下面是doRegisterBeanDefinitions的源码,到这里我们的任务就快要完成啦!!!
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(doc.getDocumentElement());
}
}
//Element类是用来构建XML文件中bean标签的,看到了这个root我们就要到头啦!!!
protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) {
// Any nested elements will cause recursion in this method. In
// order to propagate and preserve default-* attributes correctly,
// keep track of the current (parent) delegate, which may be null. Create
// the new (child) delegate with a reference to the parent for fallback purposes,
// then ultimately reset this.delegate back to its original (parent) reference.
// this behavior emulates a stack of delegates without actually necessitating one.
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate;
this.delegate = createDelegate(getReaderContext(), root, parent);
if (this.delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
//处理profile属性(下面的框框我来简单介绍以下profile),程序会查看beans标签中是否定义了profile属性
//如果有的话,对他进行处理,一般不常用
String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) {
String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(
profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
// We cannot use Profiles.of(...) since profile expressions are not supported
// in XML config. See SPR-12458 for details.
if (!getReaderContext().getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Skipped XML bean definition file due to specified profiles [" + profileSpec +
"] not matching: " + getReaderContext().getResource());
}
return;
}
}
}
//解析前处理,留给子类,方法为空,面向继承设计,反应模板方法模式
preProcessXml(root);
//解析处理源码放在下面,处理完profile就对XML文件进行读取
parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate);
//解析后处理,留给子类,方法为空,面向继承设计,反应模板方法模式
postProcessXml(root);
this.delegate = parent;
}
profile 属性,用于集成到web.xml中,部署两套配置文件来适用于生产环境和开发环境
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
//处理beans
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element) {
Element ele = (Element) node;
//处理bean,默认的标签
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate);
}
else {
//处理bean,自定义的标签
delegate.parseCustomElement(ele);
}
}
}
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(root);
}
}