计算机网路相关的教材很少,TCP/IP,HTTP 协议非常多,很难找到一个合适的材料去学习。
《计算机网络》自上而下方法是这个方面的经典之作。
1.what is internet?
1.1 nuts and bolts 基本元素
Millions of devices connect in network.
If we let devices connect each other, it 's too complex and unrealistic.
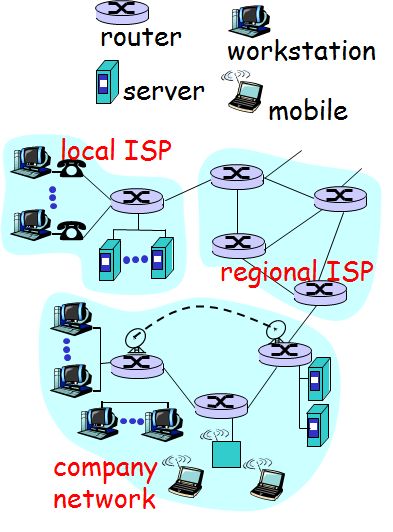
So the real network is like the picture.
pc,mobile ,server are called end-systems or hosts
In today's world, most all devices can access to network. we call it "network apps".
There are many ways for connect in network in today's world.
fiber,copper,radio,satellite ...
The key quota is bandwidth.
routers is the network core.
as you see with below pic, the real network is connect with routers.
when them connect each other, how they communicate each other。
It called "protocols". eg: TCP, IP,HTTP, FTP,UDP etc.
network of networks:
loosely hierarchical----serven or five layer for network。
IP Address:
Because of so many devices, if each devices has been given one ip address, it will not enough for every one.
So, we consider :some of them can get the ip address and others may share this address,or devided them with two region。
public Internet versus & private intranet。
Each router can get one ip address like "112.100.120.224" and every end-system may got one address like "192.168.0.100"
For many protocols, there need one org. to manager these protocols.
RTF:Request for comments
IETF:Internet Engineering Task Force
1.2 A Service View
Web,eMail,game etc. All these are network applications.
communication services:
connectionless:not need connectoion with one line. like Post system. sample say is :UDP
connection-oriented:need connection with line. like call sysntem. sample say is : TCP
For internet: it might be lost, & delay.
connection-oriented:no loss , and delay is control
UDP: quick response DNS
2.What's A protocol?
protocol is like two people talking about.
… specific messages sent
… specific actions taken when messages received, or other events.
protocols define:
format,
order of messages sent and received among network entities,
and actions taken on the transmission/receipt of a message.
2.1 A closer look at network structure
Network edge:
hosts & applications
Network core: routers & network of networks
Access network: between edge & core lines.
They using real line call physical media.
3.Network Edge
End Systems:
run web,email at edge of network.
2 model :
client/server model:
client request, server receive , server is always on.
For lost of client may request,so server should always on.
peer-peer model:
eg. skype. client to client.
min (or no ) use of server, just side to side client.
But for some reason,may contury has forbid these software.
3.1 connection-oriented service
network is lost,delay. but we may want to data not lost.
we want to tansfer data between end systems.
TCP Transmission Control Protocol
The most important protocol in network.
TCP RFC793
1)reliable,in order byte-stream data transfer. For loss problem, it using acknowledgements & retransmissions. Detail will talking about later.
2)flow control: sender and receiver in most case , they will have different bandwidth.So we get the min of the Upper limit of each other.
3)congestion control:sender will put one byte, two byte,exponent. Until, lost packet happen. Then ,it will slow down the packet size.
most using 1/2 of last one.
3.2 connectionless service
data transfer between end systems.
UDP User Datagram Protocol
1)unreliable. may lost data
2)unflow control. so receiver's bandwidth may not enough. normally, it will just pass little data. or transfer video/media data.
3)un congestion control.
fast,using resource small.
TCP:HTTP,FTP,SMTP
UDP:stream media,DNS