Huffman编码C语言实现
(1)原理概述
huffamn编码过程实际上是找到一棵最优二叉树的过程;在编码过程中首先要知道各个符号的统计概率,然后找两个最小的合并后的概率再和此前最小的合并,直到到根节点。生成树后就是编码的过程,一般是先左后右为0和1,遍历整个树后再从根节点下来就得到了节点的编码。
流程图如下:
(2)两个关键结构体
1.Huffman节点
typedef struct huffman_node_tag
{
unsigned char isLeaf; //是否为树叶
unsigned long count; //节点代表的符号加权和
struct huffman_node_tag *parent; //父节点指针
union
{
struct
{
struct huffman_node_tag *zero, *one; //子节点指针,分别代表0,1子节点指针
};
unsigned char symbol; //节点代表的符号
};
} huffman_node;2.Huffman码
typedef struct huffman_code_tag
{
unsigned long numbits; //该码所用的比特数
unsigned char *bits; //指向该码比特串的指针
} huffman_code; (3)编码流程
1.读入文件
主函数里面,我们先定义输入输出的文件和表格
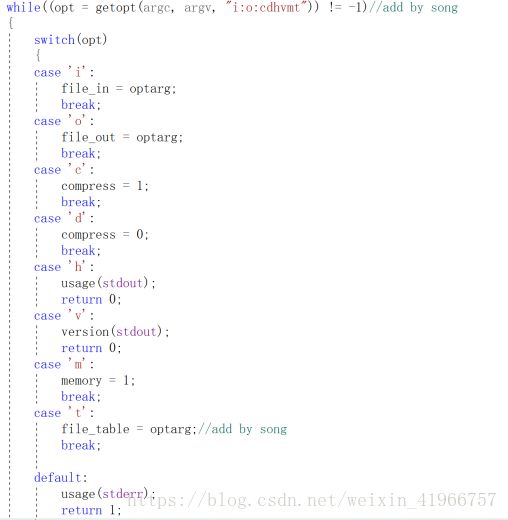
其中opt是用以选择事件的选项,如下所示:
2.统计每个字符的概率
第一次扫描,统计信源字符发生频率(8 比特,共 256 个信源符号)创建一个 256 个元素的指针数组,用以保存 256 个信源符号的频率。其下 标对应相应字符的 ASCII 码
#define MAX_SYMBOLS 256
typedef huffman_node* SymbolFrequencies[MAX_SYMBOLS];
typedef huffman_code* SymbolEncoder[MAX_SYMBOLS];
统计信源符号的频率
static unsigned int
get_symbol_frequencies(SymbolFrequencies *pSF, FILE *in)
{
int c;
unsigned int total_count = 0;
/* Set all frequencies to 0. */
init_frequencies(pSF);
/* Count the frequency of each symbol in the input file. */
while((c = fgetc(in)) != EOF)//读取一个字符
{
unsigned char uc = c;
if(!(*pSF)[uc])//频率统计数组的下标是字符的ascll
(*pSF)[uc] = new_leaf_node(uc);
++(*pSF)[uc]->count;
++total_count;
}
return total_count;
}
按字符概率由小到大将对应结点排序
将所有的节点按照字符概率小到大排序,可使用qsort函数对节点结构体进行排序。排序的依据是SFComp,即根据每个字符发生的概率进行排序。
用qsort编译器函数库自带的快速排序函数排序
qsort((*pSF), MAX_SYMBOLS, sizeof((*pSF)[0]), SFComp);//(数组的起始地址,数组的元素数,每个元素的大小,比较函数的指针)
SFComp的作用:0的时候不排,1的时候排hn1,-1的时候排hn2
/*
* When used by qsort, SFComp sorts the array so that
* the symbol with the lowest frequency is first. Any
* NULL entries will be sorted to the end of the list.
*/
* When used by qsort, SFComp sorts the array so that
* the symbol with the lowest frequency is first. Any
* NULL entries will be sorted to the end of the list.
*/
static int
SFComp(const void *p1, const void *p2)//排序依据
{
const huffman_node *hn1 = *(const huffman_node**)p1;
const huffman_node *hn2 = *(const huffman_node**)p2;
/* Sort all NULLs to the end. */
if(hn1 == NULL && hn2 == NULL)
return 0;
if(hn1 == NULL)
return 1;
if(hn2 == NULL)
return -1;
if(hn1->count > hn2->count)
return 1;
else if(hn1->count < hn2->count)
return -1;
return 0;
}
得到文件出现的字符种类数
for(n = 0; n < MAX_SYMBOLS && (*pSF)[n]; ++n)
; 3.构建Huffman树
/*
* Construct a Huffman tree. This code is based
* on the algorithm given in Managing Gigabytes
* by Ian Witten et al, 2nd edition, page 34.
* Note that this implementation uses a simple
* count instead of probability.
*/
for(i = 0; i < n - 1; ++i)
{
/* Set m1 and m2 to the two subsets of least probability. */
m1 = (*pSF)[0];
m2 = (*pSF)[1];//将m1, m2置成前两个树叶节点
/* Replace m1 and m2 with a set {m1, m2} whose probability
* is the sum of that of m1 and m2. */
(*pSF)[0] = m1->parent = m2->parent =
new_nonleaf_node(m1->count + m2->count, m1, m2);//构造m1, m2的父节点,即合并概率
(*pSF)[1] = NULL; //1节点置空
/* Put newSet into the correct count position in pSF. */
qsort((*pSF), n, sizeof((*pSF)[0]), SFComp);//重新排序
}非树叶节点构造:
static huffman_node*
new_nonleaf_node(unsigned long count, huffman_node *zero, huffman_node *one)//新的中间节点
{
huffman_node *p = (huffman_node*)malloc(sizeof(huffman_node));
p->isLeaf = 0;
p->count = count;
p->zero = zero;
p->one = one;
p->parent = 0;
return p;
}4.对码树编码
定义一个指针数组,数组中每个元素是指向码节点的
typedef huffman_code* SymbolEncoder[MAX_SYMBOLS];
pSE = (SymbolEncoder*)malloc(sizeof(SymbolEncoder));
memset(pSE, 0, sizeof(SymbolEncoder)); build_symbol_encoder((*pSF)[0], pSE);
调用build_symbol_encoder
static void
build_symbol_encoder(huffman_node *subtree, SymbolEncoder *pSF)
{
if (subtree == NULL)
return;
if (subtree->isLeaf)
(*pSF)[subtree->symbol] = new_code(subtree);//是树叶就编码
else
{
build_symbol_encoder(subtree->zero, pSF);//从左遍历
build_symbol_encoder(subtree->one, pSF);
}
}码字位数定义为numbits
倒序:reverse_bits函数
static void
reverse_bits(unsigned char* bits, unsigned long numbits)
{
unsigned long numbytes = numbytes_from_numbits(numbits);//判断码字占用几个字节
unsigned char *tmp =
(unsigned char*)alloca(numbytes);//根据字节数开储存空间
unsigned long curbit;
long curbyte = 0;
memset(tmp, 0, numbytes);
for (curbit = 0; curbit < numbits; ++curbit)
{
unsigned int bitpos = curbit % 8;
if (curbit > 0 && curbit % 8 == 0)//如果一个byte写满了,就跳到下一个byte继续写
//判断当前位是第几位,到下一字节则字节数+1
++curbyte;
tmp[curbyte] |= (get_bit(bits, numbits - curbit - 1) << bitpos);
//从后往前依次取每一位,再移位
}
memcpy(bits, tmp, numbytes);
}判断字节数的函数和去除bits中第i位的函数:
numbytes_from_numbits(unsigned long numbits)
{
return numbits / 8 + (numbits % 8 ? 1 : 0);
}
/*
* get_bit returns the ith bit in the bits array
* in the 0th position of the return value.
*/
static unsigned char
get_bit(unsigned char* bits, unsigned long i)//i/8取整,i%8取余,表示第几个字节的第几位
{
return (bits[i / 8] >> i % 8) & 1;
} 5.将码表输出
写入码表:
static int
write_code_table(FILE* out, SymbolEncoder *se, unsigned int symbol_count)//read
{
unsigned long i, count = 0;
/* Determine the number of entries in se. */
for (i = 0; i < MAX_SYMBOLS; ++i)
{
if ((*se)[i])
++count;
}
/* Write the number of entries in network byte order. */
i = htonl(count);
if (fwrite(&i, sizeof(i), 1, out) != 1)
return 1;
/* Write the number of bytes that will be encoded. */
symbol_count = htonl(symbol_count);
if (fwrite(&symbol_count, sizeof(symbol_count), 1, out) != 1)
return 1;
/* Write the entries. */
for (i = 0; i < MAX_SYMBOLS; ++i)
{
huffman_code *p = (*se)[i];
if (p)
{
unsigned int numbytes;
/* Write the 1 byte symbol. */
fputc((unsigned char)i, out);
/* Write the 1 byte code bit length. */
fputc(p->numbits, out);
/* Write the code bytes. */
numbytes = numbytes_from_numbits(p->numbits);
if (fwrite(p->bits, 1, numbytes, out) != numbytes)
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}对文件编码:
static int
do_file_encode(FILE* in, FILE* out, SymbolEncoder *se)
{
unsigned char curbyte = 0;
unsigned char curbit = 0;
int c;
while ((c = fgetc(in)) != EOF)
{
unsigned char uc = (unsigned char)c;
huffman_code *code = (*se)[uc];
unsigned long i;
for (i = 0; i < code->numbits; ++i)
{
/* Add the current bit to curbyte. */
curbyte |= get_bit(code->bits, i) << curbit;
/* If this byte is filled up then write it
* out and reset the curbit and curbyte. */
if (++curbit == 8)
{
fputc(curbyte, out);
curbyte = 0;
curbit = 0;
}
}
}命令参数的设定:
-i是输入文件,-o是输出文件,-c是压缩,-t是输出的频率/码长/码字表
本次实验错误:
错误1:开始命令参数设到环境变量了导致调试时exe一直运行
错误2:PDB不兼容,在文件夹里删了PDB再次生成就可以
实验结果:
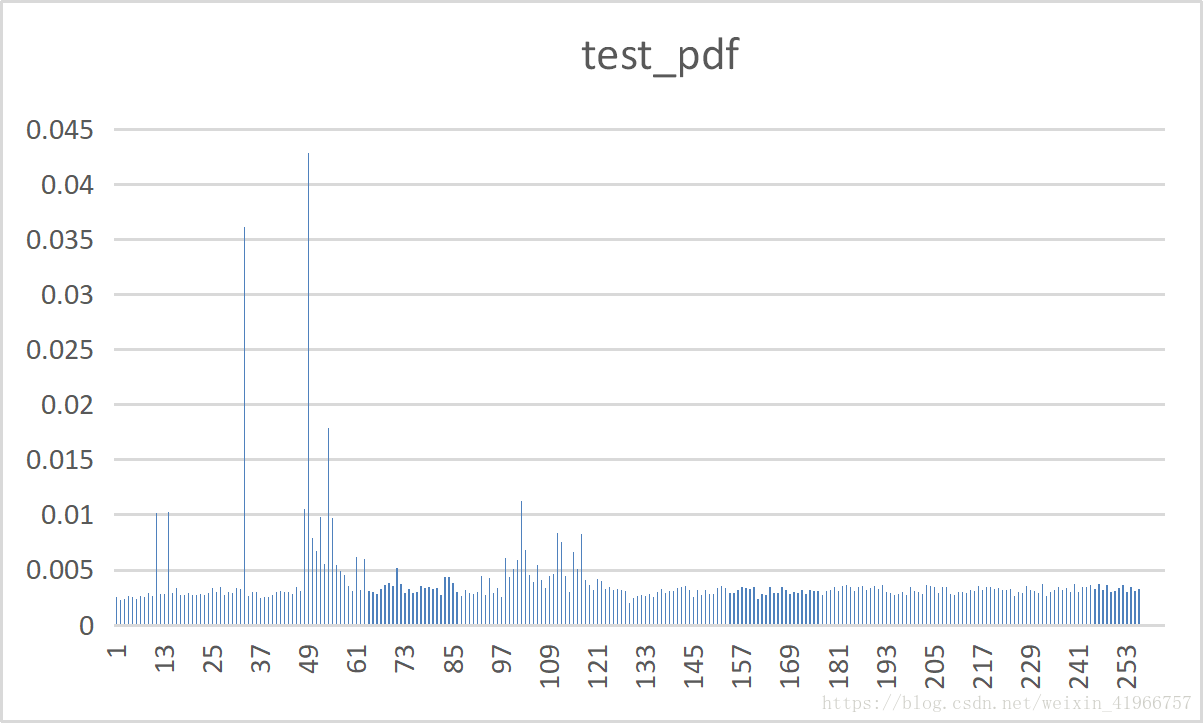
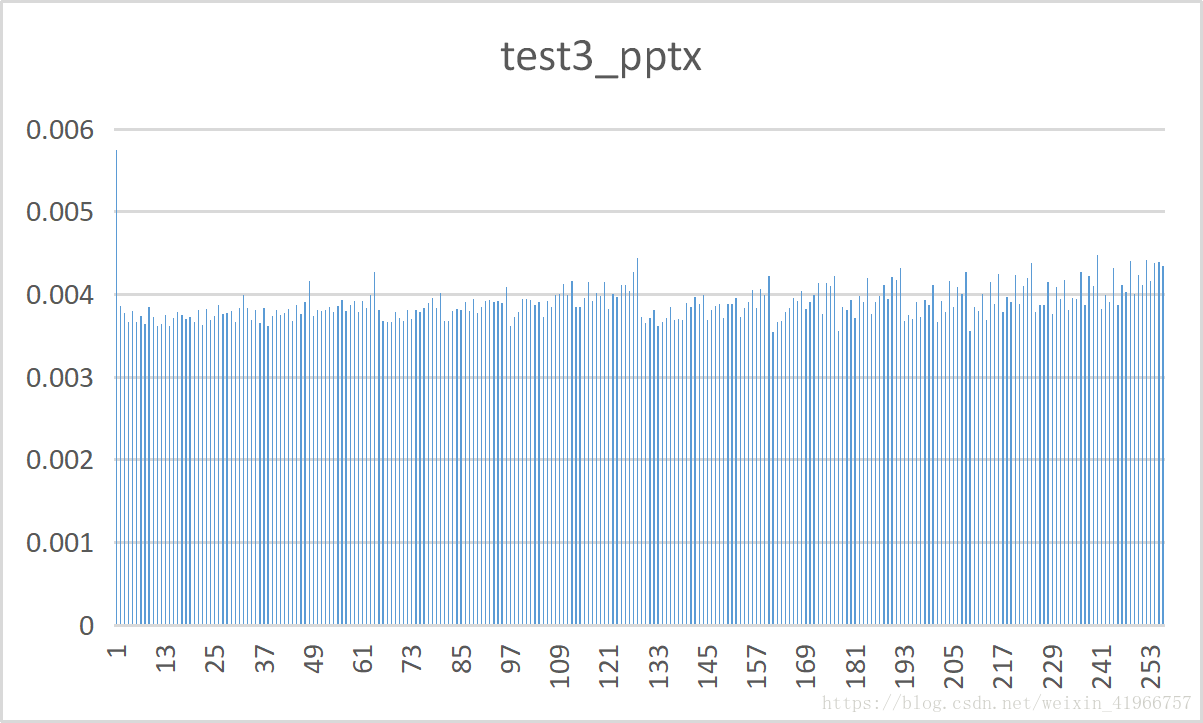
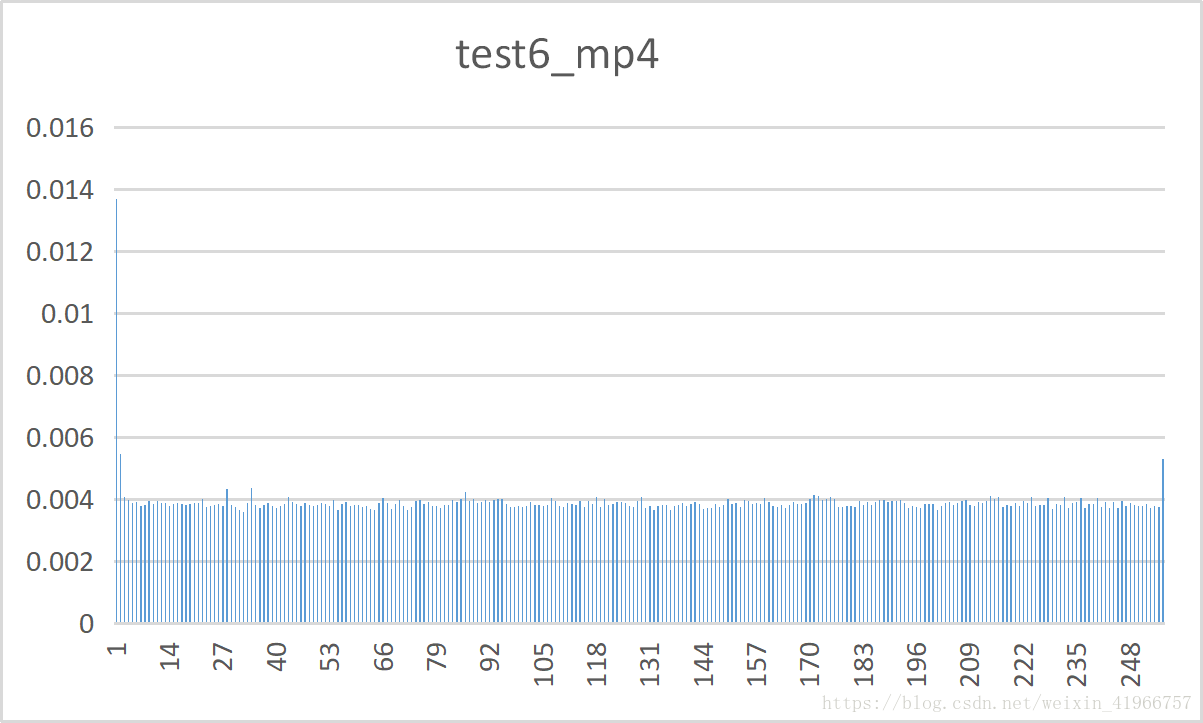
10种测试文件的频率分布表: