步步提高网站体验系列之——PWA(Service Worker)
前言
接上篇步步提高网站体验系列之——骨架屏,这次通过Service Worker来实现网站的离线加载。意义就是当个人网站服务暂时挂掉的时候,读者依然可以通过之前的缓存来进行离线访问。
文章目录如下:
- 什么是PWA
- 什么是Service Worker
- Service 生命周期
- 撸起袖子干
什么是 PWA
Progressive Web App, 简称 PWA,是提升 Web App 的体验的一种新方法,能给用户原生应用的体验。
PWA 的主要特点包括下面三点:
可靠 - 即使在不稳定的网络环境下,也能瞬间加载并展现
体验 - 快速响应,并且有平滑的动画响应用户的操作
粘性 - 像设备上的原生应用,具有沉浸式的用户体验,用户可以添加到桌面
PWA 本身强调渐进式,并不要求一次性达到安全、性能和体验上的所有要求。
Service Worker
Service Worker是实现PWA的一个关键部分.
Service workers 本质上充当Web应用程序与浏览器之间的代理服务器,也可以在网络可用时作为浏览器和网络间的代理。它们旨在(除其他之外)使得能够创建有效的离线体验,拦截网络请求并基于网络是否可用以及更新的资源是否驻留在服务器上来采取适当的动作。他们还允许访问推送通知和后台同步API。
了解生命周期是使用service worker的前提。service worker的生命周期很简单,三个关键字:安装(install),激活(activate),废弃(redundant)
离线操作基本上发生在install和activate阶段。
Service Worker 依赖
Service Worker 出于安全性和其实现原理,在使用的时候有一定的前提条件。
- 要求 HTTPS 的环境或localhost
- Service Worker 的缓存机制是依赖 Cache API 实现的
- 依赖 HTML5 fetch API
- 依赖 Promise 实现
兼容性
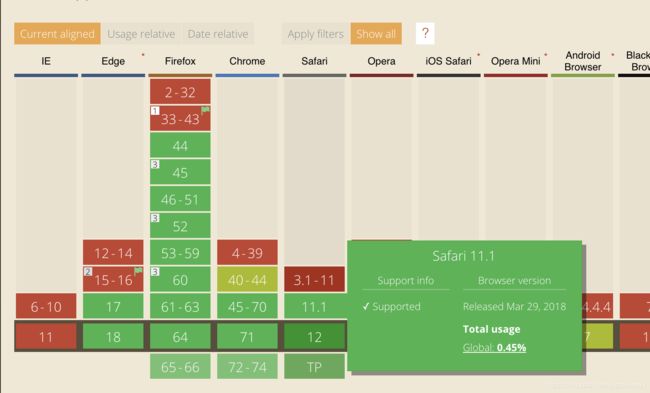
chrome早就兼容了,需要注意的是safari,是从11.1版本即18年4月份才开始支持的。
Edge大概也是从18年4月起开始支持的,不过考虑到Edge马上既要被微软遗弃了,所以爱咋咋地。
撸起袖子干
- 在模版index.html中注册service worker
注:因此项目依赖html-webpack-plugin
<script>
// index.html
if ('serviceWorker' in navigator) {
window.addEventListener('load', function () {
navigator.serviceWorker.register('/sw.js', {scope: '/'})
.then(function (registration) {
// 注册成功
console.log('ServiceWorker registration successful with scope: ', registration.scope)
})
.catch(function (err) {
// 注册失败:(
console.log('ServiceWorker registration failed: ', err)
})
})
}
</script>
- 每次打包时将待注册的sw.js移动到dist目录(即网站根目录)
注:依赖copy-webpack-plugin
const CopyWebpackPlugin = require('copy-webpack-plugin')
const webpackConfig = merge(baseWebpackConfig, {
module: {...},
plugins: [
new CopyWebpackPlugin([
...
// add service worker file to dist
{
from: path.resolve(__dirname, '../src/sw/sw.js'),
to: config.build.assetsRoot,
ignore: ['.*']
},
...
])
]
})
- 缓存策略以及注意的问题
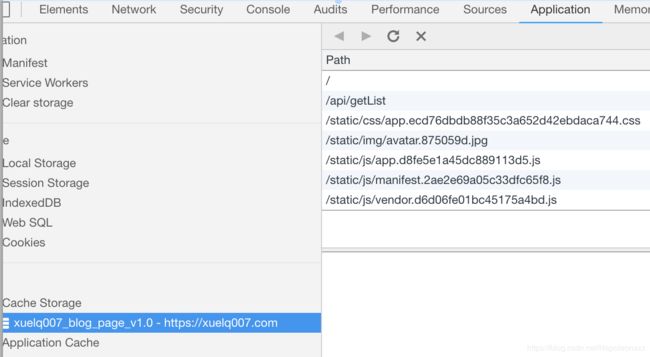
博客网站,是一个标题列表,链接指向csdn博客地址。网站分为游客部分和管理员部分,只针对游客部分做离线缓存(游客部分就是一进网站所看到的)。
这是一个静态网站,由nginx指向vue-cli打包好的dist目录中的index.html。nginx会代理一个名为getList的ajax请求从数据库获取文章列表。
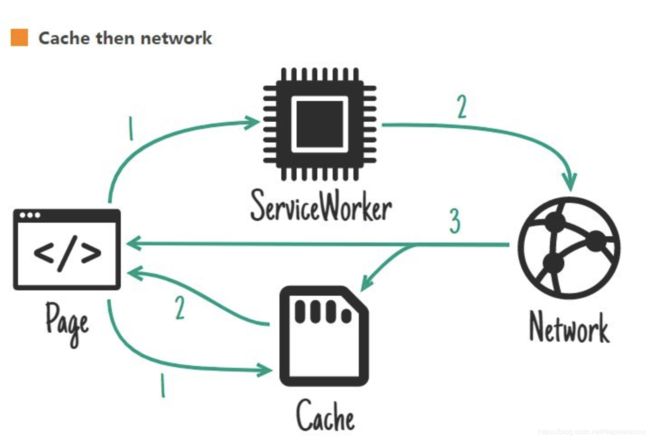
我的缓存策略是: 缓存所有的网络请求结果,包括静态资源以及ajax
第一版sw.js:
'use strict'
const OFFLINE_CACHE_PREFIX = 'xuelq007_blog_page_'
const CACHE_VERSION = 'v1.0'
const OFFLINE_CACHE_NAME = OFFLINE_CACHE_PREFIX + CACHE_VERSION
this.addEventListener('fetch', function (event) {
event.respondWith(
caches.match(event.request).then(function (response) {
// 如果 Service Worker 有自己的返回,就直接返回,减少一次 http 请求
if (response) {
return response
}
// 如果 service worker 没有返回,那就得直接请求真实远程服务
var request = event.request.clone() // 把原始请求拷过来
return fetch(request).then(function (httpRes) {
// http请求的返回已被抓到,可以处置了。
// 请求失败了,直接返回失败的结果就好了。。
if (!httpRes || httpRes.status !== 200) {
return httpRes
}
// 请求成功的话,将请求缓存起来。
var responseClone = httpRes.clone()
caches.open(OFFLINE_CACHE_NAME).then(function (cache) {
cache.put(event.request, responseClone)
})
return httpRes
})
})
)
})
测试中发现了以下严重问题:
- 由于index.html被缓存(请求被拦截),导致浏览器无法从服务端获取改动后的css与js
- 由于getList请求结果被缓存,当数据库发生改变时,最新的文章列表无法获取。
因此在缓存所有请求的基础上,做一些调整:
当service worker拦截到index.html与getList请求时,先请求网络,如果返回status=200,则使用返回结果。如果网站发生异常或服务器挂掉无法访问时,则使用缓存。
注:如果index和getList完全不做离线缓存,那么当服务器挂掉后,网站就无法访问,不符合离线缓存的初衷
第二版sw.js
'use strict'
const OFFLINE_CACHE_PREFIX = 'xuelq007_blog_page_'
const CACHE_VERSION = 'v1.0'
const OFFLINE_CACHE_NAME = OFFLINE_CACHE_PREFIX + CACHE_VERSION
this.addEventListener('fetch', function (event) {
event.respondWith(
caches.match(event.request).then(function (response) {
let isGetListRequest = event.request.url.indexOf('getList') > -1
let isIndexRequest = event.request.referrer === ''
// 如果 Service Worker 有自己的返回,就直接返回,减少一次 http 请求
if (response && !isGetListRequest && !isIndexRequest) {
return response
}
// 如果 service worker 没有返回,那就得直接请求真实远程服务
var request = event.request.clone() // 把原始请求拷过来
return fetch(request).then(function (httpRes) {
// http请求的返回已被抓到,可以处置了。
// 请求失败了,直接返回失败的结果就好了。。
if (!httpRes || httpRes.status !== 200) {
// 如果获取首页或getList网络请求失败,则使用缓存
if (response && (isGetListRequest || isIndexRequest)) {
return response
}
return httpRes
}
// 请求成功的话,将请求缓存起来。
var responseClone = httpRes.clone()
caches.open(OFFLINE_CACHE_NAME).then(function (cache) {
cache.put(event.request, responseClone)
})
return httpRes
}).catch(function (error) {
// 如果getList网络请求失败,则使用缓存
if (response && (isGetListRequest || isIndexRequest)) {
return response
}
})
})
)
})
基本上完美了,但是还面临一个小问题,如果sw改动后,刷新页面,发现新的sw在等待状态:
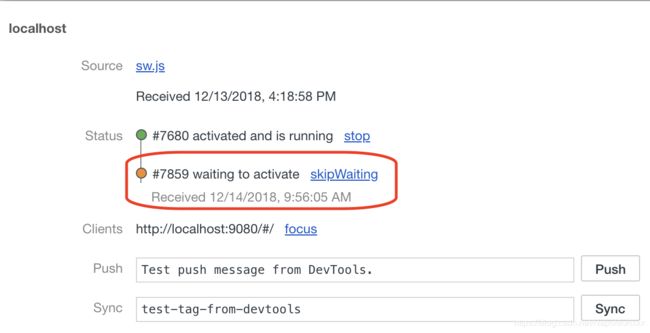
这和service worker的运行机制有关系:更新安装成功后新的sw不会立即进入active状态,需要等待旧版本的Service Worker进/线程终止(如关闭重新打开页面)
但是在生命周期install回调函数中我们可以跳过这个等待,直接安装并进入激活状态
// service worker 安装事件
this.addEventListener('install', function (event) {
event.waitUntil(caches.open(OFFLINE_CACHE_NAME).then(function (cache) {
event.waitUntil(self.skipWaiting())
}))
})
最终版本的sw.js如下:
'use strict'
const OFFLINE_CACHE_PREFIX = 'xuelq007_blog_page_'
const CACHE_VERSION = 'v1.0'
const OFFLINE_CACHE_NAME = OFFLINE_CACHE_PREFIX + CACHE_VERSION
// service worker 安装事件
this.addEventListener('install', function (event) {
event.waitUntil(caches.open(OFFLINE_CACHE_NAME).then(function (cache) {
// event.waitUntil(self.skipWaiting())
}))
})
this.addEventListener('fetch', function (event) {
event.respondWith(
caches.match(event.request).then(function (response) {
let isGetListRequest = event.request.url.indexOf('getList') > -1
let isIndexRequest = event.request.referrer === ''
// 如果 Service Worker 有自己的返回,就直接返回,减少一次 http 请求
if (response && !isGetListRequest && !isIndexRequest) {
return response
}
// 如果 service worker 没有返回,那就得直接请求真实远程服务
var request = event.request.clone() // 把原始请求拷过来
return fetch(request).then(function (httpRes) {
// http请求的返回已被抓到,可以处置了。
// 请求失败了,直接返回失败的结果就好了。。
if (!httpRes || httpRes.status !== 200) {
// 如果获取首页或getList网络请求失败,则使用缓存
if (response && (isGetListRequest || isIndexRequest)) {
return response
}
return httpRes
}
// 请求成功的话,将请求缓存起来。
var responseClone = httpRes.clone()
caches.open(OFFLINE_CACHE_NAME).then(function (cache) {
cache.put(event.request, responseClone)
})
return httpRes
}).catch(function (error) {
// 如果getList网络请求失败,则使用缓存
if (response && (isGetListRequest || isIndexRequest)) {
return response
}
})
})
)
})
运行效果
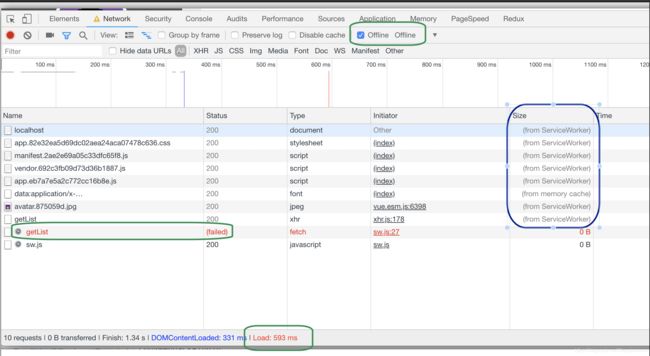
可以看出在断网时offline,通过离线缓存也可以访问网站,并且加载速度只用了593ms
很有意思的小点 : 细心的话会发现两个getList请求,一个旁边有个小齿轮。第一个不带齿轮的getList从size列可以看出是来自serviceWorker,第二个带齿轮的getList是fetch请求网络失败了。
可以说明两点:
- 网络的确断了
- serviceWorker拦截到getList请求,先请求网络,请求失败,然后从离线缓存中读取上次成功的list
尾声–关于service worker生效时间点
写好sw后,第一次打开网址,浏览器会发起请求获取网页内容和sw,同时将sw安装并激活。但是要注意,此时网站资源并没有被缓存(即sw没有拦截请求)。当再次刷新页面时,sw才会开始拦截请求并缓存结果。
第一次运行网站:
再刷新网页: