【OpenCV】OpenCV3的第二天——光流法(Optial Flow)运动目标检测
基于特征点的跟踪算法大致可以分为两个步骤:
1)探测当前帧的特征点;
2)通过当前帧和下一帧灰度比较,估计当前帧特征点在下一帧的位置;
3)过滤位置不变的特征点,余下的点就是目标了。
特征点包括:
1、Harris
2、SURF
3、FAST
4、STAR
5、SIFT
6、ORB
7、MSER
8、GETT
9、Dense
10、SimpleBlob
光流的基本方法:
1、基于梯度
2、基于匹配
3、基于能量
4、基于相位
光流法首先假设的条件:
1、亮度恒定
2、小运动
3、空间一致
使用函数:
goodFeaturesToTrack()——寻找图像中具有大特征的角点
calcOpticalFlowPyrLK()——计算一个稀疏特征集的光流
两篇博客链接:
Opencv学习笔记(九)光流法
http://blog.csdn.net/crzy_sparrow/article/details/7407604
【算法分析】Lucas–Kanade光流算法
http://www.cnblogs.com/gnuhpc/archive/2012/12/04/2802124.htmlOpenCV3编程入门——光流法的代码
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include // Gaussian Blur
#include
#include
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
void duan_OpticalFlow(Mat &frame, Mat & result);
bool addNewPoints();
bool acceptTrackedPoint(int i);
Mat curgray; // 当前图片
Mat pregray; // 预测图片
vector point[2]; // point0为特征点的原来位置,point1为特征点的新位置
vector initPoint; // 初始化跟踪点的位置
vector features; // 检测的特征
int maxCount = 500; // 检测的最大特征数
double qLevel = 0.01; // 特征检测的等级
double minDist = 10.0; // 两特征点之间的最小距离
vector status; // 跟踪特征的状态,特征的流发现为1,否则为0
vector err;
int main()
{
Mat matSrc;
Mat matRst;
VideoCapture cap("Monkey.mp4");
int totalFrameNumber = cap.get(CV_CAP_PROP_FRAME_COUNT);
// perform the tracking process
printf("Start the tracking process, press ESC to quit.\n");
for (int nFrmNum = 0; nFrmNum < totalFrameNumber; nFrmNum++) {
// get frame from the video
cap >> matSrc;
if (!matSrc.empty())
{
duan_OpticalFlow(matSrc, matRst);
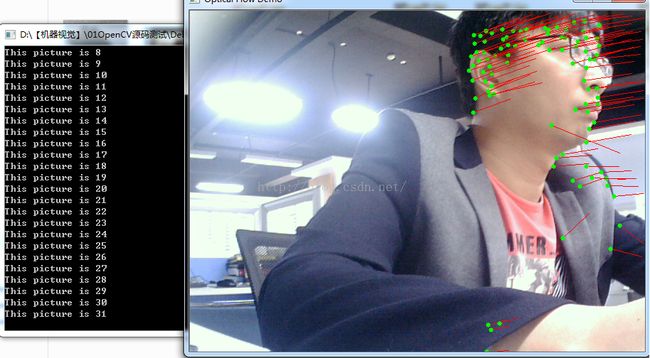
cout << "This picture is " << nFrmNum << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "Error : Get picture is empty!" << endl;
}
if (waitKey(1) == 27) break;
}
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
void duan_OpticalFlow(Mat &frame, Mat & result)
{
cvtColor(frame, curgray, CV_BGR2GRAY);
frame.copyTo(result);
if (addNewPoints())
{
goodFeaturesToTrack(curgray, features, maxCount, qLevel, minDist);
point[0].insert(point[0].end(), features.begin(), features.end());
initPoint.insert(initPoint.end(), features.begin(), features.end());
}
if (pregray.empty())
{
curgray.copyTo(pregray);
}
calcOpticalFlowPyrLK(pregray, curgray, point[0], point[1], status, err);
int k = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i 2);
} ====================OpenCV Source Code===============
enum
{
OPTFLOW_USE_INITIAL_FLOW = CV_LKFLOW_INITIAL_GUESSES,
OPTFLOW_LK_GET_MIN_EIGENVALS = CV_LKFLOW_GET_MIN_EIGENVALS,
OPTFLOW_FARNEBACK_GAUSSIAN = 256
};
//! constructs a pyramid which can be used as input for calcOpticalFlowPyrLK
CV_EXPORTS_W int buildOpticalFlowPyramid(InputArray img, OutputArrayOfArrays pyramid,
Size winSize, int maxLevel, bool withDerivatives = true,
int pyrBorder = BORDER_REFLECT_101, int derivBorder = BORDER_CONSTANT,
bool tryReuseInputImage = true);
//! computes sparse optical flow using multi-scale Lucas-Kanade algorithm
CV_EXPORTS_W void calcOpticalFlowPyrLK( InputArray prevImg, InputArray nextImg,
InputArray prevPts, CV_OUT InputOutputArray nextPts,
OutputArray status, OutputArray err,
Size winSize=Size(21,21), int maxLevel=3,
TermCriteria criteria=TermCriteria(TermCriteria::COUNT+TermCriteria::EPS, 30, 0.01),
int flags=0, double minEigThreshold=1e-4);
//! computes dense optical flow using Farneback algorithm
CV_EXPORTS_W void calcOpticalFlowFarneback( InputArray prev, InputArray next,
CV_OUT InputOutputArray flow, double pyr_scale, int levels, int winsize,
int iterations, int poly_n, double poly_sigma, int flags );
//! estimates the best-fit Euqcidean, similarity, affine or perspective transformation
// that maps one 2D point set to another or one image to another.
CV_EXPORTS_W Mat estimateRigidTransform( InputArray src, InputArray dst,
bool fullAffine);
//! computes dense optical flow using Simple Flow algorithm
CV_EXPORTS_W void calcOpticalFlowSF(Mat& from,
Mat& to,
Mat& flow,
int layers,
int averaging_block_size,
int max_flow);
CV_EXPORTS_W void calcOpticalFlowSF(Mat& from,
Mat& to,
Mat& flow,
int layers,
int averaging_block_size,
int max_flow,
double sigma_dist,
double sigma_color,
int postprocess_window,
double sigma_dist_fix,
double sigma_color_fix,
double occ_thr,
int upscale_averaging_radius,
double upscale_sigma_dist,
double upscale_sigma_color,
double speed_up_thr);
class CV_EXPORTS DenseOpticalFlow : public Algorithm
{
public:
virtual void calc(InputArray I0, InputArray I1, InputOutputArray flow) = 0;
virtual void collectGarbage() = 0;
};
// Implementation of the Zach, Pock and Bischof Dual TV-L1 Optical Flow method
//
// see reference:
// [1] C. Zach, T. Pock and H. Bischof, "A Duality Based Approach for Realtime TV-L1 Optical Flow".
// [2] Javier Sanchez, Enric Meinhardt-Llopis and Gabriele Facciolo. "TV-L1 Optical Flow Estimation".
CV_EXPORTS Ptr createOptFlow_DualTVL1(); ==============================================
// Hand01.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include // Gaussian Blur
#include
#include
#include
using namespace cv;
static void convertFlowToImage(const Mat &flow_x, const Mat &flow_y, Mat &img_x, Mat &img_y, double lowerBound, double higherBound) {
#define CAST(v, L, H) ((v) > (H) ? 255 : (v) < (L) ? 0 : cvRound(255*((v) - (L))/((H)-(L))))
for (int i = 0; i < flow_x.rows; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < flow_y.cols; ++j) {
float x = flow_x.at(i, j);
float y = flow_y.at(i, j);
img_x.at(i, j) = CAST(x, lowerBound, higherBound);
img_y.at(i, j) = CAST(y, lowerBound, higherBound);
}
}
#undef CAST
}
static void drawOptFlowMap(const Mat& flow, Mat& cflowmap, int step, double, const Scalar& color)
{
for (int y = 0; y < cflowmap.rows; y += step)
for (int x = 0; x < cflowmap.cols; x += step)
{
const Point2f& fxy = flow.at(y, x);
line(cflowmap, Point(x, y), Point(cvRound(x + fxy.x), cvRound(y + fxy.y)),
color);
circle(cflowmap, Point(x, y), 2, color, -1);
}
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
// IO operation
const char* keys =
{
"{ f | vidFile | ex2.avi | filename of video }"
"{ x | xFlowFile | flow_x | filename of flow x component }"
"{ y | yFlowFile | flow_y | filename of flow x component }"
"{ i | imgFile | flow_i | filename of flow image}"
"{ b | bound | 15 | specify the maximum of optical flow}"
};
//CommandLineParser cmd(argc, argv, keys);
//string vidFile = cmd.get("vidFile");
//string xFlowFile = cmd.get("xFlowFile");
//string yFlowFile = cmd.get("yFlowFile");
//string imgFile = cmd.get("imgFile");
//int bound = cmd.get("bound");
string vidFile = "vidFile";
string xFlowFile = "xFlowFile";
string yFlowFile = "yFlowFile";
string imgFile = "imgFile";
int bound = 80;
namedWindow("video", 1);
namedWindow("imgX", 1);
namedWindow("imgY", 1);
namedWindow("Demo", 1);
//VideoCapture capture(vidFile);
VideoCapture capture("Monkey.mp4");
if (!capture.isOpened()) {
printf("Could not initialize capturing..\n");
return -1;
}
int frame_num = 0;
Mat image, prev_image, prev_grey, grey, frame, flow, cflow;
while (true) {
capture >> frame;
if (frame.empty())
break;
imshow("video", frame);
if (frame_num == 0) {
image.create(frame.size(), CV_8UC3);
grey.create(frame.size(), CV_8UC1);
prev_image.create(frame.size(), CV_8UC3);
prev_grey.create(frame.size(), CV_8UC1);
frame.copyTo(prev_image);
cvtColor(prev_image, prev_grey, CV_BGR2GRAY);
frame_num++;
continue;
}
frame.copyTo(image);
cvtColor(image, grey, CV_BGR2GRAY);
// calcOpticalFlowFarneback(prev_grey,grey,flow,0.5, 3, 15, 3, 5, 1.2, 0 );
calcOpticalFlowFarneback(prev_grey, grey, flow, 0.702, 5, 10, 2, 7, 1.5, cv::OPTFLOW_FARNEBACK_GAUSSIAN);
prev_image.copyTo(cflow);
drawOptFlowMap(flow, cflow, 12, 1.5, Scalar(0, 255, 0));
imshow("cflow", cflow);
Mat flows[2];
split(flow, flows);
Mat imgX(flows[0].size(), CV_8UC1);
Mat imgY(flows[0].size(), CV_8UC1);
convertFlowToImage(flows[0], flows[1], imgX, imgY, -bound, bound);
//char tmp[20];
//sprintf(tmp, "_%04d.jpg", int(frame_num));
//imwrite(xFlowFile + tmp, imgX);
//imwrite(yFlowFile + tmp, imgY);
//imwrite(imgFile + tmp, image);
std::swap(prev_grey, grey);
std::swap(prev_image, image);
frame_num = frame_num + 1;
imshow("imgX", imgX);
imshow("imgY", imgY);
imshow("Demo", image);
if (waitKey(1) == 27) break;
}
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}