C++STL与泛型编程高级 学习笔记(自查用)
https://www.bilibili.com/video/av48068999?p=5
记录一些在里面提到的函数用法例子
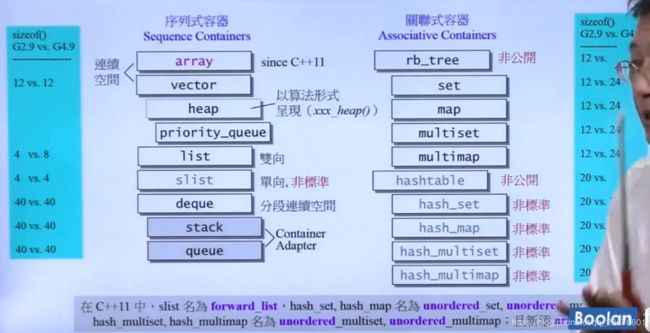
第一讲 容器
- 读取时间
#include -排序(list等不能用std::sort)
array<long, ASIZE> c;
for (long i = 0; i < ASIZE; ++i) {
c[i] = rand() % 65535;
}
qsort(c.data(), ASIZE, sizeof(long), compareLongs);
- 二分查找
#include将数字转化为char,再转换为string
#include在vector中find
auto pItem = find(c.begin(),c.end(),target);
if(pItem !- c.end())
cout<<"find:"<<*pItem<<endl;
else
cout<<"not find"<<endl;
在vector中用二分查找
vector<string> c;
sort(c.begin(),c.end());
int compareStrings(const void* a, const void* b)
{
if (*(string*)a > *(string*)b)
return 1;
else if(*(string*)a < *(string*)b)
return -1;
else
return 0;
}
string* pItem = (string*)bsearch(&target, (c.data()), c.size(), sizeof(string), compareStrings);
if (pItem != NULL)
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found!" << endl;
- bsearch 函数使用说明
void *bsearch(const void *key, const void *base, size_t nitems, size_t size, int (*compar)(const void *, const void *))
key -- 指向要查找的元素的指针,类型转换为 void*。
base -- 指向进行查找的数组的第一个对象的指针,类型转换为 void*。
nitems -- base 所指向的数组中元素的个数。
size -- 数组中每个元素的大小,以字节为单位。
compar -- 用来比较两个元素的函数。
- 某些容器自带sort,例如list ,forward_list,
list<string> c;
c.sort();
- 某些容器自带find,如set,multiset,map,
- multimap,unordered_multiset,unordered_multimao
auto pItem = c.find(target);//更快!!!!!!!!!!
auto pItem = find(c.begin(),c.end(),target);
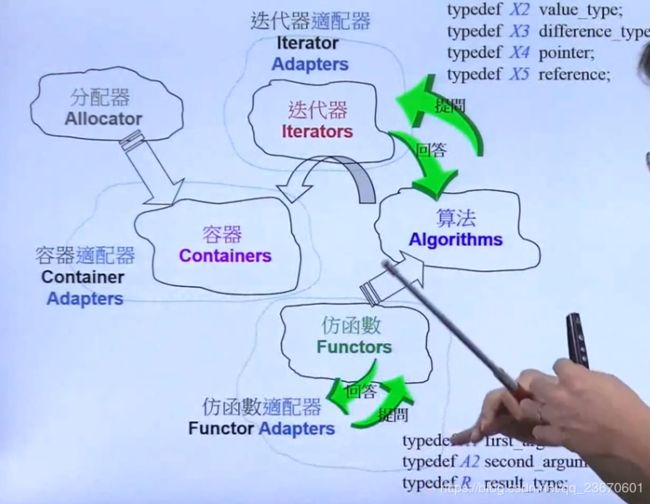
- 分配器allocator
#include第二讲 容器
oop(object-oriented programming )vs GP(generic programming)
面向对象编程与模板编程
GP思维:容器containers和算法algorighms各自管自己,再通过Iterator迭代器联结.
所有的算法,其中涉及元素本身的操作就是比大小
例子:比大小
strLonger(const string& s1,const string& s2)
{
return s1.size() < s2.size();
}
cout<<"longest: "<<max(string("zoo"),string("hello",strLonger));//输出hello
基础:
操作符重载 overloaded operators
节选一段list文件中的重载:
template<class _Mylist,
class _Base = _Iterator_base0>
class _List_unchecked_const_iterator
: public _Iterator012<bidirectional_iterator_tag,
typename _Mylist::value_type,
typename _Mylist::difference_type,
typename _Mylist::const_pointer,
typename _Mylist::const_reference,
_Base>
{ // unchecked iterator for nonmutable list
public:
typedef _List_unchecked_const_iterator<_Mylist, _Base> _Myiter;
typedef bidirectional_iterator_tag iterator_category;
typedef typename _Mylist::_Nodeptr _Nodeptr;
typedef typename _Mylist::value_type value_type;
typedef typename _Mylist::difference_type difference_type;
typedef typename _Mylist::const_pointer pointer;
typedef typename _Mylist::const_reference reference;
_List_unchecked_const_iterator()
: _Ptr(0)
{ // construct with null node pointer
}
_List_unchecked_const_iterator(_Nodeptr _Pnode, const _Mylist *_Plist)
: _Ptr(_Pnode)
{ // construct with node pointer _Pnode
this->_Adopt(_Plist);
}
reference operator*() const
{ // return designated value
return (_Mylist::_Myval(_Ptr));
}
pointer operator->() const
{ // return pointer to class object
return (_STD pointer_traits<pointer>::pointer_to(**this));
}
_Myiter& operator++()
{ // preincrement
_Ptr = _Mylist::_Nextnode(_Ptr);
return (*this);
}
_Myiter operator++(int)
{ // postincrement
_Myiter _Tmp = *this;
++*this;
return (_Tmp);
}
_Myiter& operator--()
{ // predecrement
_Ptr = _Mylist::_Prevnode(_Ptr);
return (*this);
}
_Myiter operator--(int)
{ // postdecrement
_Myiter _Tmp = *this;
--*this;
return (_Tmp);
}
bool operator==(const _Myiter& _Right) const
{ // test for iterator equality
return (_Ptr == _Right._Ptr);
}
bool operator!=(const _Myiter& _Right) const
{ // test for iterator inequality
return (!(*this == _Right));
}
_Nodeptr _Mynode() const
{ // return node pointer
return (_Ptr);
}
_Nodeptr _Ptr; // pointer to node
};
- 基础知识:类模板 cass templates
template <typename T>
class complex
//复数类
{
public:
complex(T r = 0, T i = 0): re(r), im (i)
{}
complex& operator +=(const complex&);
T real () const{ return re;}
T imag () const {return im;}
private:
T re,im;
}
/***********使用**********************/
complex<double> c1(2.5,1.5);
- 基础知识:模板函数 function templates
template <class T>
inline
const T& min(const T& a,const T& b)
{
return b < a? b : a;
}
- 基础知识:特化 specialization
对具体模板写对应的特化,如
template<> struct hash<bool>;
template<> struct hash<char>;
template<> struct hash<signed char>;
template<> struct hash<unsigned char>;
template<> struct hash<char8_t>; // C++20
template<> struct hash<char16_t>;
template<> struct hash<char32_t>;
template<> struct hash<wchar_t>;
template<> struct hash<short>;
template<> struct hash<unsigned short>;
template<> struct hash<int>;
template<> struct hash<unsigned int>;
template<> struct hash<long>;
template<> struct hash<long long>;
template<> struct hash<unsigned long>;
template<> struct hash<unsigned long long>;
template<> struct hash<float>;
template<> struct hash<double>;
template<> struct hash<long double>;
template<> struct hash<std::nullptr_t>; // C++17
template< class T > struct hash<T*>;
- 偏特化 partial specialization(个数,范围(是否指针,是否const)两种偏特化方式)
template<class Alloc>
class vector<bool,Alloc>
{
...
}
//对应泛化
template <class T,class Alloc = alloc>
class vector
{...}
- 分配器
- 使用容器的时候会调用分配器来分配内存。
- vc6+中的 allocator 只是通过new和delete来完成allocate()和deallocate(),没有特殊设计。
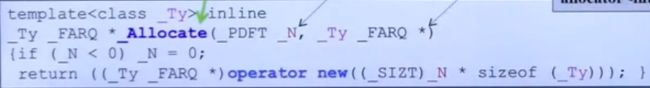
- 举个例子直接调用allocator(一般不直接用)
//分配512ints
int *p = allocator<int>().allocate(512,(int*)0);//创建
allocator<int>().deallocate(p,512);//释放
不做任何处理的分配器会导致在大量malloc的时候产生cookie的额外开销。
G 2.9 stl中对alloc进行了优化:减少malloc的次数。
现在在G4.9中优化方法改名为pool_alloc,使用方法:
vector<string,gnu_cxx::_pool_alloc<string>> vec;
list
G2.9
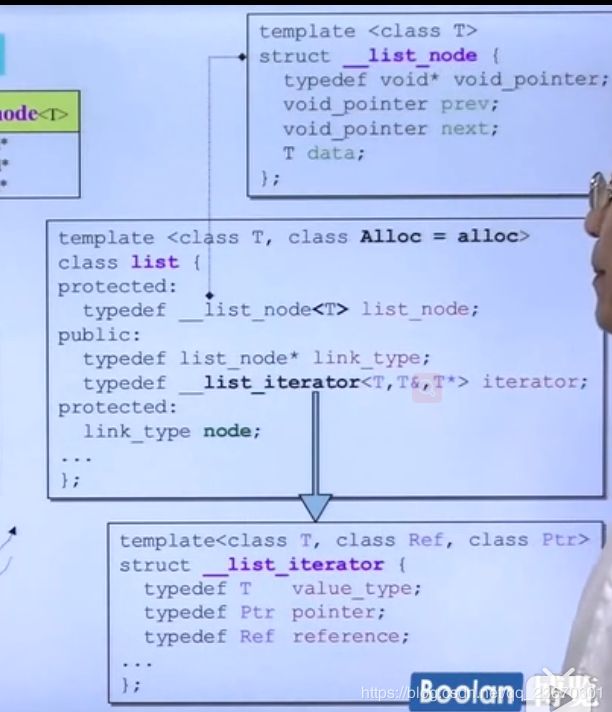
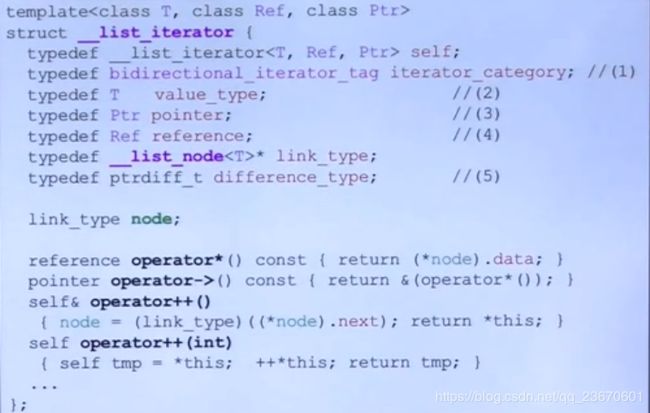
4.9优化

Iterator提供5种associate types:
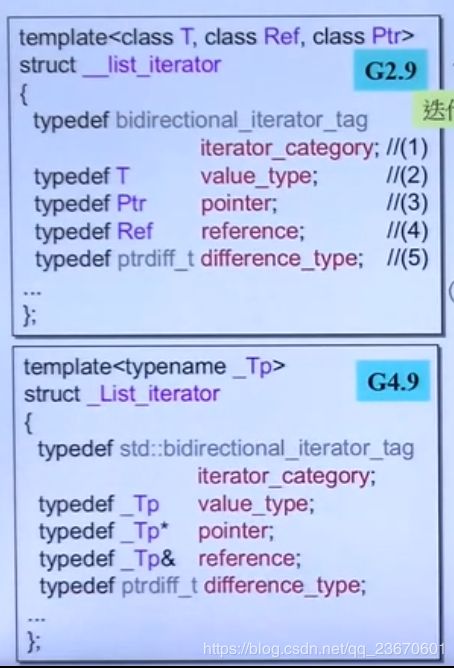
ptrdiff_t指的是两个指针的距离的类型,这就限制了容器的大小。
Vector
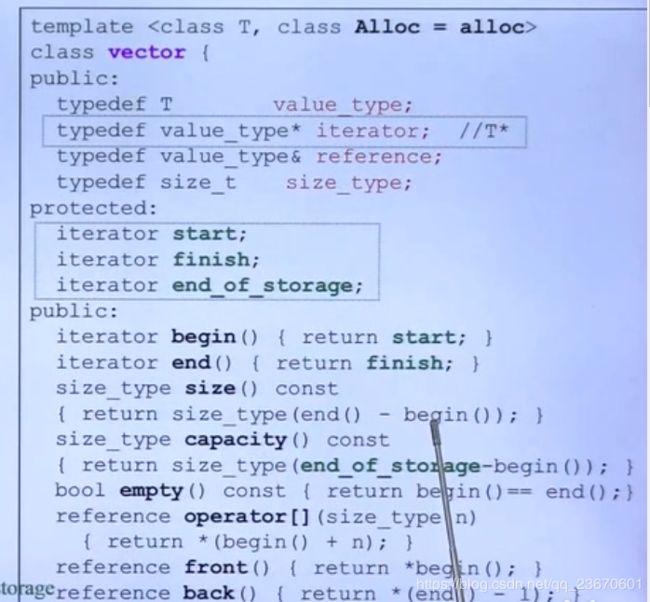
两倍增长:
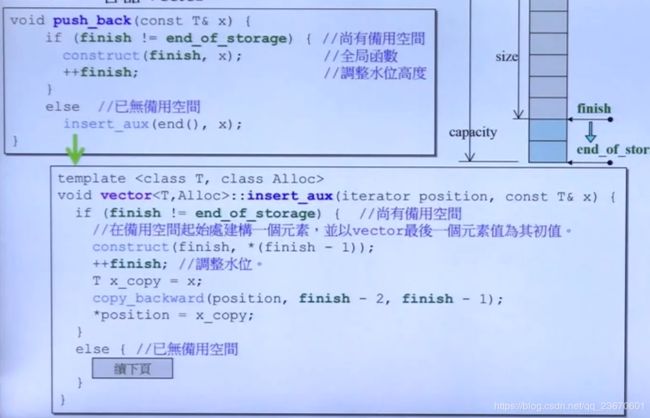
做了两次检测,是因为insert_aux在别处也有被调用,比如insert等调用它。

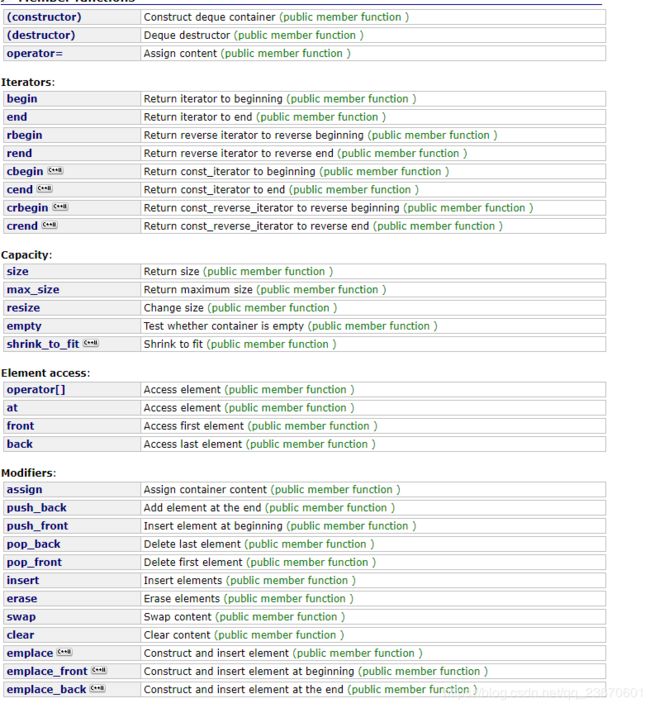
deque
queue和stack
都不提供iterator
底层可以通过deque或者list封装实现,stack也可以用vector做底层结构
注意使用时pop,push,不带back或者front。
rb_tree
提供两种insert操作,insert_unique()或者insert_equal()
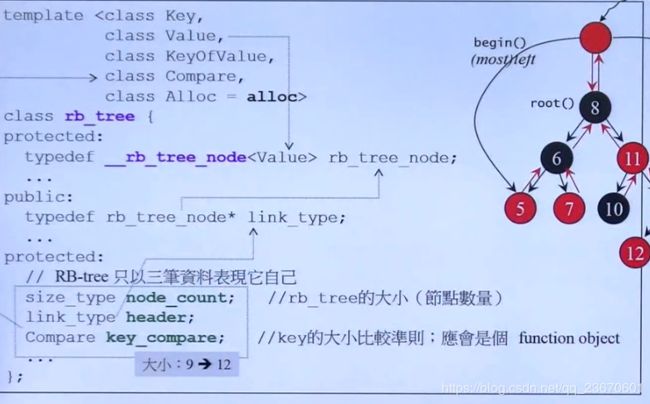
第三讲 算法
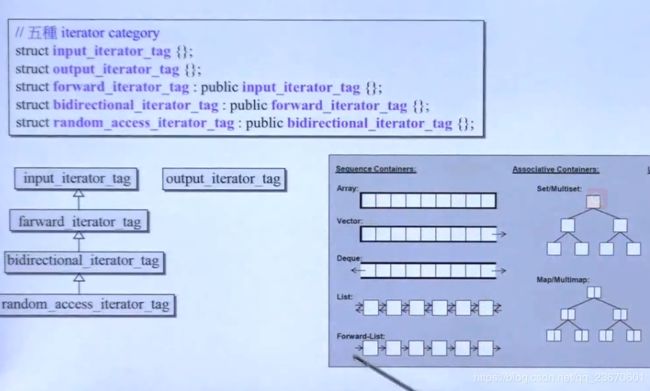
bidirectional 双向
红黑树生成的都是双向迭代器
hash_table生成的容器用单项迭代器
find:

for_each:

count:

sort:

bineary_search:返回真/假
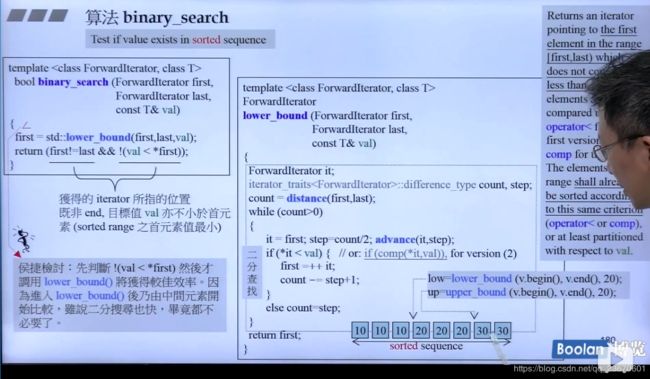
二分查找可以直接用lower_bound:他返回一个在first与last迭代器区间[first,last)内第一个不小于val的元素。
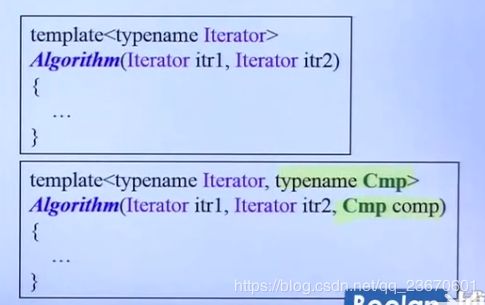
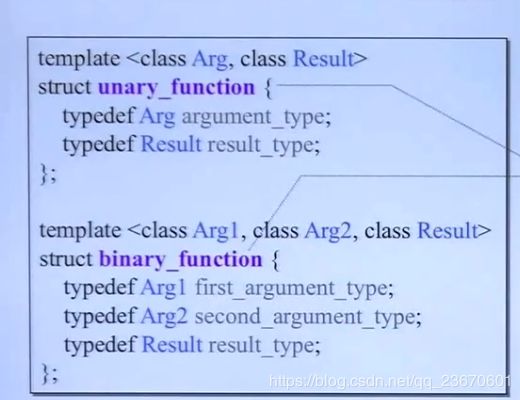
仿函数functors
为算法提供服务,添加一些准则等,比如排序顺序等

仿函数要继承unary单参数或者binary双参数来,以便被适配器后续改造。
适配器adapter
包含: 容器适配器,迭代器适配器,仿函数适配器
容器适配器:
函数适配器:

相当于将第二个参数绑定为固定的,比如less()需要比较两个参数大小,这里就可以把第二个参数绑定为40。但是bind在c++11已经改版了:

函数适配器not1,传递判断条件,取非输出.

新型适配器bind
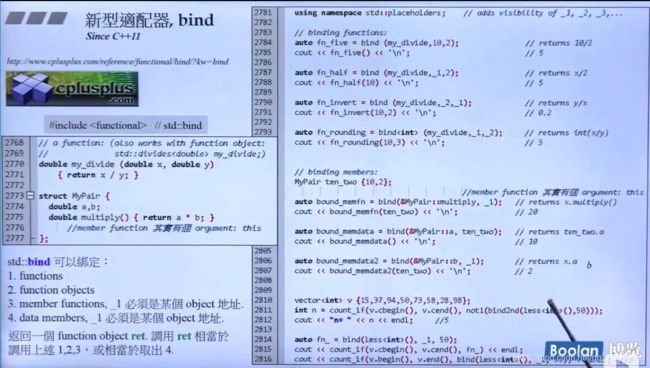
cbegin()表示const型begin迭代器
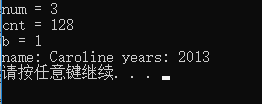
举个例子:
#include 迭代器适配器
X(未知)适配器
ostream_iterator
测试一下:
#include #include第四讲 应用
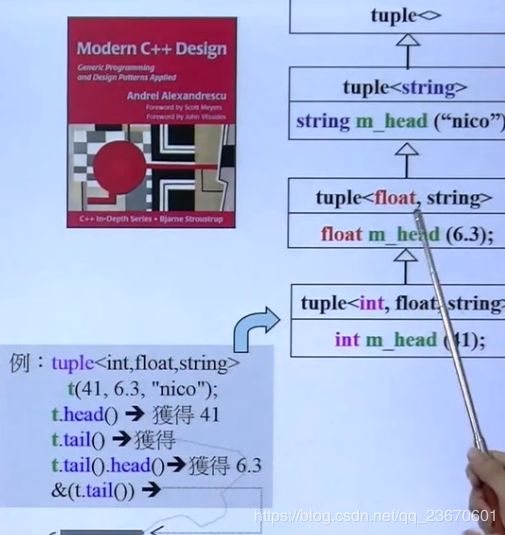
tuple元组
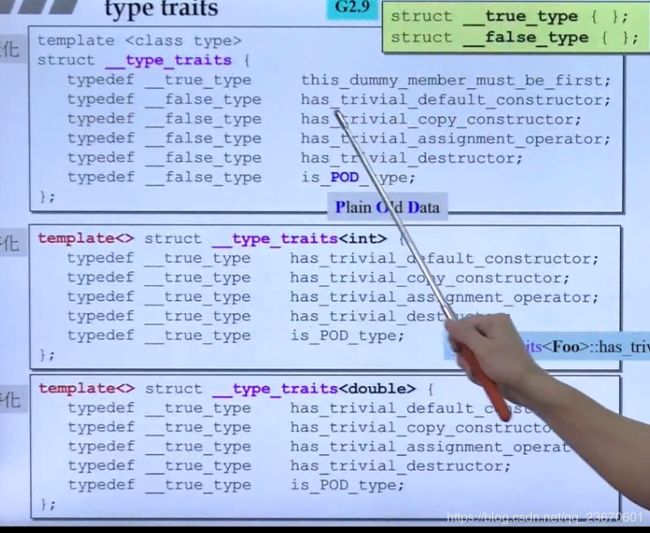
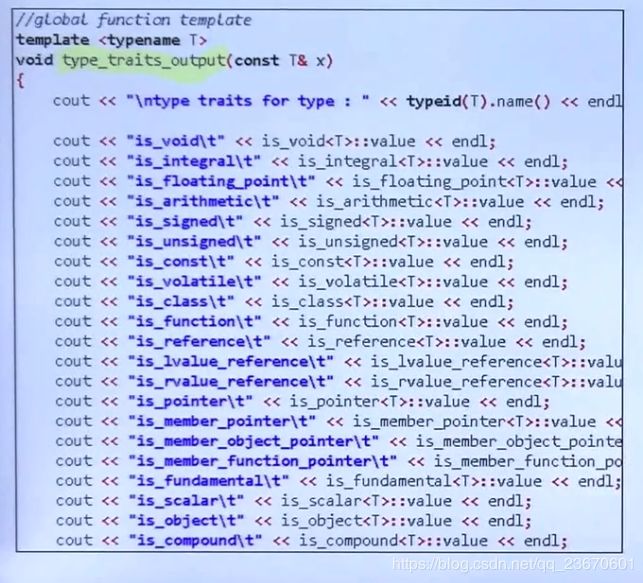
#include type traits 类型萃取
#include 用法:判断From类型是否可以转为To类型*/
cout << is_convertible<Parent*, Child*>::value << endl; //false
cout << is_convertible<Child*, Parent*>::value << endl; //true
cout << is_convertible<Parent*, Alone*>::value << endl; //false
return 0;
}
cout
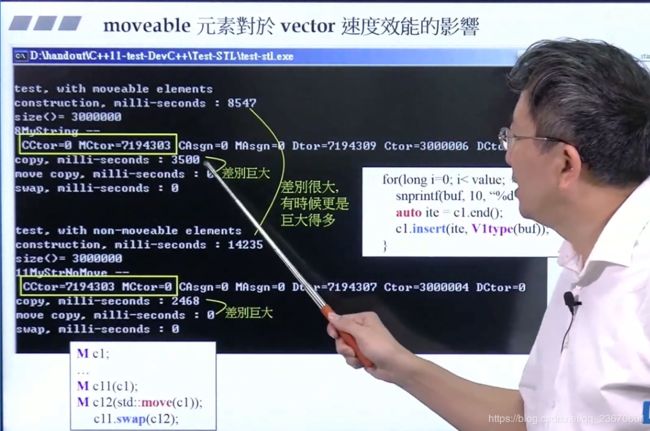
moveable对效率的影响
完结撒花~~