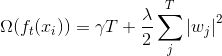《统计学习方法》-李航、《机器学习-西瓜书》-周志华总结+Python代码连载(六)--集成学习_FM/GBDT/Xgboost
一、随机森林/FM(Random Forst)
随机森林是集成学习Bagging流派中一个变体,RF在以决策树为基学习构建Bagging集成的基础上,进一步在决策树的训练过程中引入随机属性选择。传统的决策树在选择划分属性时是在当前节点的属性集合中选择最优的一个;而在RF中,对基决策树的每个结点,先从该结点的属性集合中随机选择一个包含k个属性的子集,然后再从这个子集中选择一个最优属性用于划分。
二、梯度提升决策树/GBDT(Gradient boosting decision tree)
在连载(五)中,知道提升树在每一次优化过程,都是拟合上一次的残差,在GBDT中提出用损失函数的负梯度作为回归问题中的残差近似值。
为什么GBDT中可以用损失函数的负梯度来代替上一步的残差?
设在t次的loss函数为![]() ,该损失函数在
,该损失函数在![]() 泰勒展开:
泰勒展开:
由上式可知,要使得![]() ,可以令
,可以令![]() ,于是可得到GBDT拟合上一步损失函数的负梯度。
,于是可得到GBDT拟合上一步损失函数的负梯度。
算法步骤:
将连载(五)中的计算残差替换成计算上一步的损失函数的负梯度即可。
代码实现:
import numpy as np
import math
# 计算信息熵
def calculate_entropy(y):
log2 = math.log2
unique_labels = np.unique(y)
entropy = 0
for label in unique_labels:
count = len(y[y == label])
p = count / len(y)
entropy += -p * log2(p)
return entropy
# 定义树的节点
class DecisionNode():
def __init__(self, feature_i=None, threshold=None,
value=None, true_branch=None, false_branch=None):
self.feature_i = feature_i
self.threshold = threshold
self.value = value
self.true_branch = true_branch
self.false_branch = false_branch
def divide_on_feature(X, feature_i, threshold):
split_func = None
if isinstance(threshold, int) or isinstance(threshold, float):
split_func = lambda sample: sample[feature_i] >= threshold
else:
split_func = lambda sample: sample[feature_i] == threshold
X_1 = np.array([sample for sample in X if split_func(sample)])
X_2 = np.array([sample for sample in X if not split_func(sample)])
return np.array([X_1, X_2])
# 超类
class DecisionTree(object):
def __init__(self, min_samples_split=2, min_impurity=1e-7,
max_depth=float("inf"), loss=None):
self.root = None #根节点
self.min_samples_split = min_samples_split
self.min_impurity = min_impurity
self.max_depth = max_depth
# 计算值 如果是分类问题就是信息增益,回归问题就基尼指数
self._impurity_calculation = None
self._leaf_value_calculation = None #计算叶子
self.one_dim = None
self.loss = loss
def fit(self, X, y, loss=None):
self.one_dim = len(np.shape(y)) == 1
self.root = self._build_tree(X, y)
self.loss=None
def _build_tree(self, X, y, current_depth=0):
"""
递归求解树
"""
largest_impurity = 0
best_criteria = None
best_sets = None
if len(np.shape(y)) == 1:
y = np.expand_dims(y, axis=1)
Xy = np.concatenate((X, y), axis=1)
n_samples, n_features = np.shape(X)
if n_samples >= self.min_samples_split and current_depth <= self.max_depth:
# 计算每一个特征的增益值
for feature_i in range(n_features):
feature_values = np.expand_dims(X[:, feature_i], axis=1)
unique_values = np.unique(feature_values)
for threshold in unique_values:
Xy1, Xy2 = divide_on_feature(Xy, feature_i, threshold)
if len(Xy1) > 0 and len(Xy2) > 0:
y1 = Xy1[:, n_features:]
y2 = Xy2[:, n_features:]
# 计算增益值
impurity = self._impurity_calculation(y, y1, y2)
if impurity > largest_impurity:
largest_impurity = impurity
best_criteria = {"feature_i": feature_i, "threshold": threshold}
best_sets = {
"leftX": Xy1[:, :n_features],
"lefty": Xy1[:, n_features:],
"rightX": Xy2[:, :n_features],
"righty": Xy2[:, n_features:]
}
if largest_impurity > self.min_impurity:
true_branch = self._build_tree(best_sets["leftX"], best_sets["lefty"], current_depth + 1)
false_branch = self._build_tree(best_sets["rightX"], best_sets["righty"], current_depth + 1)
return DecisionNode(feature_i=best_criteria["feature_i"], threshold=best_criteria[
"threshold"], true_branch=true_branch, false_branch=false_branch)
# 计算节点的目标值
leaf_value = self._leaf_value_calculation(y)
return DecisionNode(value=leaf_value)
def predict_value(self, x, tree=None):
"""
预测
"""
if tree is None:
tree = self.root
if tree.value is not None:
return tree.value
feature_value = x[tree.feature_i]
branch = tree.false_branch
if isinstance(feature_value, int) or isinstance(feature_value, float):
if feature_value >= tree.threshold:
branch = tree.true_branch
elif feature_value == tree.threshold:
branch = tree.true_branch
return self.predict_value(x, branch)
def predict(self, X):
y_pred = []
for x in X:
y_pred.append(self.predict_value(x))
return y_pred
def calculate_variance(X):
""" Return the variance of the features in dataset X """
mean = np.ones(np.shape(X)) * X.mean(0)
n_samples = np.shape(X)[0]
variance = (1 / n_samples) * np.diag((X - mean).T.dot(X - mean))
return variance
class RegressionTree(DecisionTree):
def _calculate_variance_reduction(self, y, y1, y2):
var_tot = calculate_variance(y)
var_1 = calculate_variance(y1)
var_2 = calculate_variance(y2)
frac_1 = len(y1) / len(y)
frac_2 = len(y2) / len(y)
# 使用方差缩减
variance_reduction = var_tot - (frac_1 * var_1 + frac_2 * var_2)
return sum(variance_reduction)
def _mean_of_y(self, y):
value = np.mean(y, axis=0)
return value if len(value) > 1 else value[0]
def fit(self, X, y):
self._impurity_calculation = self._calculate_variance_reduction
self._leaf_value_calculation = self._mean_of_y
super(RegressionTree, self).fit(X, y)
class GradientBoosting(object):
def __init__(self, n_estimators, learning_rate, min_samples_split,
min_impurity, max_depth, regression):
self.n_estimators = n_estimators
self.learning_rate = learning_rate
self.min_samples_split = min_samples_split
self.min_impurity = min_impurity
self.max_depth = max_depth
self.regression = regression
self.loss = SquareLoss()
if not self.regression:
self.loss = CrossEntropy()
self.trees = []
for _ in range(n_estimators):
tree = RegressionTree(
min_samples_split=self.min_samples_split,
min_impurity=min_impurity,
max_depth=self.max_depth)
self.trees.append(tree)
def fit(self, X, y):
y_pred = np.full(np.shape(y), np.mean(y, axis=0))
for i in range(self.n_estimators):
gradient = self.loss.gradient(y, y_pred)
self.trees[i].fit(X, gradient)
update = self.trees[i].predict(X)
# Update y prediction
y_pred -= np.multiply(self.learning_rate, update)
def predict(self, X):
y_pred = np.array([])
for tree in self.trees:
update = tree.predict(X)
update = np.multiply(self.learning_rate, update)
y_pred = -update if not y_pred.any() else y_pred - update
if not self.regression:
y_pred = np.exp(y_pred) / np.expand_dims(np.sum(np.exp(y_pred), axis=1), axis=1)
y_pred = np.argmax(y_pred, axis=1)
return y_pred
class Loss(object):
def loss(self, y_true, y_pred):
return NotImplementedError()
def gradient(self, y, y_pred):
raise NotImplementedError()
def acc(self, y, y_pred):
return 0
# 如果是回归模型
class SquareLoss(Loss):
def __init__(self): pass
def loss(self, y, y_pred):
return 0.5 * np.power((y - y_pred), 2)
def gradient(self, y, y_pred):
return -(y - y_pred)
# 如果是分类模型
class CrossEntropy(Loss):
def __init__(self): pass
def loss(self, y, p):
# Avoid division by zero
p = np.clip(p, 1e-15, 1 - 1e-15)
return - y * np.log(p) - (1 - y) * np.log(1 - p)
def acc(self, y, p):
return accuracy_score(np.argmax(y, axis=1), np.argmax(p, axis=1))
def gradient(self, y, p):
# Avoid division by zero
p = np.clip(p, 1e-15, 1 - 1e-15)
return - (y / p) + (1 - y) / (1 - p)
class GradientBoostingRegressor(GradientBoosting):
def __init__(self, n_estimators=200, learning_rate=0.5, min_samples_split=2,
min_var_red=1e-7, max_depth=4, debug=False):
super(GradientBoostingRegressor, self).__init__(n_estimators=n_estimators,
learning_rate=learning_rate,
min_samples_split=min_samples_split,
min_impurity=min_var_red,
max_depth=max_depth,
regression=True)
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# data
def create_data():
iris = load_iris()
df = pd.DataFrame(iris.data, columns=iris.feature_names)
df['label'] = iris.target
df.columns = ['sepal length', 'sepal width', 'petal length', 'petal width', 'label']
data = np.array(df.iloc[:100, [0, 1, -1]])
for i in range(len(data)):
if data[i,-1] == 0:
data[i,-1] = -1
# print(data)
return data[:,:2], data[:,-1]
X, y = create_data()
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2)
plt.scatter(X[:50,0],X[:50,1], label='0')
plt.scatter(X[50:,0],X[50:,1], label='1')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
X = np.arange(10).reshape(10, 1)
y = np.array([1, 1, 1, -1, -1, -1, 1, 1, 1, -1])
X, y = create_data()
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.33)
class Loss(object):
def loss(self, y_true, y_pred):
return NotImplementedError()
def gradient(self, y, y_pred):
raise NotImplementedError()
def acc(self, y, y_pred):
return 0
class SquareLoss(Loss):
def __init__(self): pass
def loss(self, y, y_pred):
return 0.5 * np.power((y - y_pred), 2)
def gradient(self, y, y_pred):
return -(y - y_pred)
model = GradientBoostingRegressor()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
y_pred_line = model.predict(X)
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred)
mse
#分类模型
class GradientBoostingClassifier(GradientBoosting):
def __init__(self, n_estimators=200, learning_rate=.5, min_samples_split=2,
min_info_gain=1e-7, max_depth=2, debug=False):
super(GradientBoostingClassifier, self).__init__(n_estimators=n_estimators,
learning_rate=learning_rate,
min_samples_split=min_samples_split,
min_impurity=min_info_gain,
max_depth=max_depth,
regression=False)
def fit(self, X, y):
y = to_categorical(y)
super(GradientBoostingClassifier, self).fit(X, y)
def to_categorical(x, n_col=None):
""" One-hot encoding of nominal values """
if not n_col:
n_col = np.amax(x) + 1
one_hot = np.zeros((x.shape[0], n_col))
one_hot[np.arange(x.shape[0]), x] = 1
return one_hot
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
data = datasets.load_iris()
X = data.data
y = data.target
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.4)
clf = GradientBoostingClassifier()
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = clf.predict(X_test)
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
accuracy三、Xgboost
xgboost的目标函数: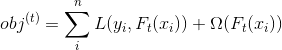 ,相比较于GBDT来说,目标函数添加正则化部分。
,相比较于GBDT来说,目标函数添加正则化部分。
将目标函数![]() 在
在![]() 泰勒展开:
泰勒展开:
使用贪心策略求解上述式子。
代码实现:
import numpy as np
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score,mean_squared_error
# 定义Sigmoid函数用来做对数几率回归
class Sigmoid():
def __call__(self, x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
def gradient(self, x):
return self.__call__(x) * (1 - self.__call__(x))
class LogisticLoss():
def __init__(self):
sigmoid = Sigmoid()
self.log_func = sigmoid
self.log_grad = sigmoid.gradient
def loss(self, y, y_pred):
y_pred = np.clip(y_pred, 1e-15, 1 - 1e-15)
p = self.log_func(y_pred)
return y * np.log(p) + (1 - y) * np.log(1 - p)
# gradient w.r.t y_pred
def gradient(self, y, y_pred):
p = self.log_func(y_pred)
return -(y - p)
# w.r.t y_pred
def hess(self, y, y_pred):
p = self.log_func(y_pred)
return p * (1 - p)
def to_categorical(x, n_col=None):
""" One-hot encoding of nominal values """
if not n_col:
n_col = np.amax(x) + 1
one_hot = np.zeros((x.shape[0], n_col))
one_hot[np.arange(x.shape[0]), x] = 1
return one_hot
def divide_on_feature(X, feature_i, threshold):
""" Divide dataset based on if sample value on feature index is larger than
the given threshold """
split_func = None
if isinstance(threshold, int) or isinstance(threshold, float):
split_func = lambda sample: sample[feature_i] >= threshold
else:
split_func = lambda sample: sample[feature_i] == threshold
X_1 = np.array([sample for sample in X if split_func(sample)])
X_2 = np.array([sample for sample in X if not split_func(sample)])
return np.array([X_1, X_2])
class DecisionNode():
"""Class that represents a decision node or leaf in the decision tree
Parameters:
-----------
feature_i: int
Feature index which we want to use as the threshold measure.
threshold: float
The value that we will compare feature values at feature_i against to
determine the prediction.
value: float
The class prediction if classification tree, or float value if regression tree.
true_branch: DecisionNode
Next decision node for samples where features value met the threshold.
false_branch: DecisionNode
Next decision node for samples where features value did not meet the threshold.
"""
def __init__(self, feature_i=None, threshold=None,
value=None, true_branch=None, false_branch=None):
self.feature_i = feature_i # Index for the feature that is tested
self.threshold = threshold # Threshold value for feature
self.value = value # Value if the node is a leaf in the tree
self.true_branch = true_branch # 'Left' subtree
self.false_branch = false_branch # 'Right' subtree
# Super class of RegressionTree and ClassificationTree
class DecisionTree(object):
"""Super class of RegressionTree and ClassificationTree.
Parameters:
-----------
min_samples_split: int
The minimum number of samples needed to make a split when building a tree.
min_impurity: float
The minimum impurity required to split the tree further.
max_depth: int
The maximum depth of a tree.
loss: function
Loss function that is used for Gradient Boosting models to calculate impurity.
"""
def __init__(self, min_samples_split=2, min_impurity=1e-7,
max_depth=float("inf"), loss=None):
self.root = None # Root node in dec. tree
# Minimum n of samples to justify split
self.min_samples_split = min_samples_split
# The minimum impurity to justify split
self.min_impurity = min_impurity
# The maximum depth to grow the tree to
self.max_depth = max_depth
# Function to calculate impurity (classif.=>info gain, regr=>variance reduct.)
self._impurity_calculation = None
# Function to determine prediction of y at leaf
self._leaf_value_calculation = None
# If y is one-hot encoded (multi-dim) or not (one-dim)
self.one_dim = None
# If Gradient Boost
self.loss = loss
def fit(self, X, y, loss=None):
""" Build decision tree """
self.one_dim = len(np.shape(y)) == 1
self.root = self._build_tree(X, y)
self.loss=None
def _build_tree(self, X, y, current_depth=0):
""" Recursive method which builds out the decision tree and splits X and respective y
on the feature of X which (based on impurity) best separates the data"""
largest_impurity = 0
best_criteria = None # Feature index and threshold
best_sets = None # Subsets of the data
# Check if expansion of y is needed
if len(np.shape(y)) == 1:
y = np.expand_dims(y, axis=1)
# Add y as last column of X
Xy = np.concatenate((X, y), axis=1)
n_samples, n_features = np.shape(X)
if n_samples >= self.min_samples_split and current_depth <= self.max_depth:
# Calculate the impurity for each feature
for feature_i in range(n_features):
# All values of feature_i
feature_values = np.expand_dims(X[:, feature_i], axis=1)
unique_values = np.unique(feature_values)
# Iterate through all unique values of feature column i and
# calculate the impurity
for threshold in unique_values:
# Divide X and y depending on if the feature value of X at index feature_i
# meets the threshold
Xy1, Xy2 = divide_on_feature(Xy, feature_i, threshold)
if len(Xy1) > 0 and len(Xy2) > 0:
# Select the y-values of the two sets
y1 = Xy1[:, n_features:]
y2 = Xy2[:, n_features:]
# Calculate impurity
impurity = self._impurity_calculation(y, y1, y2)
# If this threshold resulted in a higher information gain than previously
# recorded save the threshold value and the feature
# index
if impurity > largest_impurity:
largest_impurity = impurity
best_criteria = {"feature_i": feature_i, "threshold": threshold}
best_sets = {
"leftX": Xy1[:, :n_features], # X of left subtree
"lefty": Xy1[:, n_features:], # y of left subtree
"rightX": Xy2[:, :n_features], # X of right subtree
"righty": Xy2[:, n_features:] # y of right subtree
}
if largest_impurity > self.min_impurity:
# Build subtrees for the right and left branches
true_branch = self._build_tree(best_sets["leftX"], best_sets["lefty"], current_depth + 1)
false_branch = self._build_tree(best_sets["rightX"], best_sets["righty"], current_depth + 1)
return DecisionNode(feature_i=best_criteria["feature_i"], threshold=best_criteria[
"threshold"], true_branch=true_branch, false_branch=false_branch)
# We're at leaf => determine value
leaf_value = self._leaf_value_calculation(y)
return DecisionNode(value=leaf_value)
def predict_value(self, x, tree=None):
""" Do a recursive search down the tree and make a prediction of the data sample by the
value of the leaf that we end up at """
if tree is None:
tree = self.root
# If we have a value (i.e we're at a leaf) => return value as the prediction
if tree.value is not None:
return tree.value
# Choose the feature that we will test
feature_value = x[tree.feature_i]
# Determine if we will follow left or right branch
branch = tree.false_branch
if isinstance(feature_value, int) or isinstance(feature_value, float):
if feature_value >= tree.threshold:
branch = tree.true_branch
elif feature_value == tree.threshold:
branch = tree.true_branch
# Test subtree
return self.predict_value(x, branch)
def predict(self, X):
""" Classify samples one by one and return the set of labels """
y_pred = []
for x in X:
y_pred.append(self.predict_value(x))
return y_pred
def print_tree(self, tree=None, indent=" "):
""" Recursively print the decision tree """
if not tree:
tree = self.root
# If we're at leaf => print the label
if tree.value is not None:
print (tree.value)
# Go deeper down the tree
else:
# Print test
print ("%s:%s? " % (tree.feature_i, tree.threshold))
# Print the true scenario
print ("%sT->" % (indent), end="")
self.print_tree(tree.true_branch, indent + indent)
# Print the false scenario
print ("%sF->" % (indent), end="")
self.print_tree(tree.false_branch, indent + indent)
class XGBoostRegressionTree(DecisionTree):
"""
Regression tree for XGBoost
- Reference -
http://xgboost.readthedocs.io/en/latest/model.html
"""
def _split(self, y):
""" y contains y_true in left half of the middle column and
y_pred in the right half. Split and return the two matrices """
col = int(np.shape(y)[1]/2)
y, y_pred = y[:, :col], y[:, col:]
return y, y_pred
def _gain(self, y, y_pred):
nominator = np.power((y * self.loss.gradient(y, y_pred)).sum(), 2)
denominator = self.loss.hess(y, y_pred).sum()
return 0.5 * (nominator / denominator)
def _gain_by_taylor(self, y, y1, y2):
# Split
y, y_pred = self._split(y)
y1, y1_pred = self._split(y1)
y2, y2_pred = self._split(y2)
true_gain = self._gain(y1, y1_pred)
false_gain = self._gain(y2, y2_pred)
gain = self._gain(y, y_pred)
return true_gain + false_gain - gain
def _approximate_update(self, y):
# y split into y, y_pred
y, y_pred = self._split(y)
# Newton's Method
gradient = np.sum(y * self.loss.gradient(y, y_pred), axis=0)
hessian = np.sum(self.loss.hess(y, y_pred), axis=0)
update_approximation = gradient / hessian
return update_approximation
def fit(self, X, y):
self._impurity_calculation = self._gain_by_taylor
self._leaf_value_calculation = self._approximate_update
super(XGBoostRegressionTree, self).fit(X, y)
class XGBoost(object):
"""The XGBoost classifier.
Reference: http://xgboost.readthedocs.io/en/latest/model.html
Parameters:
-----------
n_estimators: int
The number of classification trees that are used.
learning_rate: float
The step length that will be taken when following the negative gradient during
training.
min_samples_split: int
The minimum number of samples needed to make a split when building a tree.
min_impurity: float
The minimum impurity required to split the tree further.
max_depth: int
The maximum depth of a tree.
"""
def __init__(self, n_estimators=200, learning_rate=0.001, min_samples_split=2,
min_impurity=1e-7, max_depth=2):
self.n_estimators = n_estimators # Number of trees
self.learning_rate = learning_rate # Step size for weight update
self.min_samples_split = min_samples_split # The minimum n of sampels to justify split
self.min_impurity = min_impurity # Minimum variance reduction to continue
self.max_depth = max_depth # Maximum depth for tree
# Log loss for classification
self.loss = LogisticLoss()
# Initialize regression trees
self.trees = []
for _ in range(n_estimators):
tree = XGBoostRegressionTree(
min_samples_split=self.min_samples_split,
min_impurity=min_impurity,
max_depth=self.max_depth,
loss=self.loss)
self.trees.append(tree)
def fit(self, X, y):
y = to_categorical(y)
y_pred = np.zeros(np.shape(y))
for i in range(self.n_estimators):
tree = self.trees[i]
y_and_pred = np.concatenate((y, y_pred), axis=1)
tree.fit(X, y_and_pred)
update_pred = tree.predict(X)
y_pred -= np.multiply(self.learning_rate, update_pred)
def predict(self, X):
y_pred = None
# Make predictions
for tree in self.trees:
# Estimate gradient and update prediction
update_pred = tree.predict(X)
if y_pred is None:
y_pred = np.zeros_like(update_pred)
y_pred -= np.multiply(self.learning_rate, update_pred)
# Turn into probability distribution (Softmax)
y_pred = np.exp(y_pred) / np.sum(np.exp(y_pred), axis=1, keepdims=True)
# Set label to the value that maximizes probability
y_pred = np.argmax(y_pred, axis=1)
return y_pred
data = datasets.load_iris()
X = data.data
y = data.target
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.5)
clf = XGBoost()
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = clf.predict(X_test)
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test,y_pred)
accuracy连载GitHub同步更新:https://github.com/wenhan123/ML-Python-
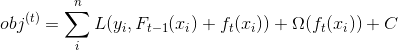
![obj^{(t)}=\sum_i^n[L(y_i,F_{t-1}(x_i))+\frac{\partial L(y_i,F_{t-1}(x_i))}{\partial F_t(x_i)}f_t(x_i)+\frac{\partial^2 L(y_i,F_{t-1}(x_i))}{\partial F_t(x_i)^2)}f_t^2(x_i]+\Omega (f_t(x_i))+C](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/2f22eda814f846518cd6cbf77a49e472.gif)