深入学习java源码之ThreadLocal.get()()与ThreadLocal.initialValue()
深入学习java源码之ThreadLocal.get()()与 ThreadLocal.initialValue()
并发编程ThreadLocal
线程封闭机制强调局部的概念,就是在写代码的时候,尽量使用局部变量代替全局变量(这种叫做栈封闭),如果一定要使用全局变量,而又想让多个线程之间在访问共享变量的时候互不影响,那就使用ThreadLocal
@ThreadSafe
pulic class TestNum{
private int num=0;
public synchronized int getNextNum(){
++num;
return num;
}
public static void main(String [] args){
TestNum tn=new TestNum();
TestClass tc1=new TestClass(tn);
TestClass tc2=new TestClass(tn);
TestClass tc3=new TestClass(tn);
tc1.start();
tc2.start();
tc3.start();
}
class TestClass extends Thread{
private TestNum tn;
public TestClass(TestNum tn){
this.tn=tn;
}
public void run(){
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
System.out.println("thread-"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-"+tn.getNextNum());
}
}
}
} 对于上面的代码,我们使用同步机制的来实现线程安全:tc1-3这三个线程都在访问同一个num空间,并且他们都在干一件事,那就是让这个空间的数字增加,并且能够留下自己的影响(即num++)。此时,输出的结果最大值一定是num=9。
ThreadLocal
用处:保存线程的独立变量。对一个线程类(继承自Thread)
ThreadLocal的作用是提供线程内的局部变量,这种变量在线程的生命周期内起作用,减少同一个线程内多个函数或者组件之间一些公共变量的传递的复杂度。
举个例子,我出门需要先坐公交再做地铁,这里的坐公交和坐地铁就好比是同一个线程内的两个函数,我就是一个线程,我要完成这两个函数都需要同一个东西:公交卡(北京公交和地铁都使用公交卡),那么我为了不向这两个函数都传递公交卡这个变量(相当于不是一直带着公交卡上路),我可以这么做:将公交卡事先交给一个机构,当我需要刷卡的时候再向这个机构要公交卡(当然每次拿的都是同一张公交卡)。这样就能达到只要是我(同一个线程)需要公交卡,何时何地都能向这个机构要的目的。
有人要说了:你可以将公交卡设置为全局变量啊,这样不是也能何时何地都能取公交卡吗?但是如果有很多个人(很多个线程)呢?大家可不能都使用同一张公交卡吧(我们假设公交卡是实名认证的),这样不就乱套了嘛。现在明白了吧?这就是ThreadLocal设计的初衷:提供线程内部的局部变量,在本线程内随时随地可取,隔离其他线程。
当使用ThreadLocal维护变量时,ThreadLocal为每个使用该变量的线程提供独立的变量副本,所以每一个线程都可以独立地改变自己的副本,而不会影响其它线程所对应的副本。常用于用户登录控制,如记录session信息。
@ThreadSafe
pulic class TestNum{
private ThreadLocal num=new ThreadLocal(){
public Integer initialValue(){
return 0;
}
};
public int getNextNum(){
num.set(num.get()+1);
return num.get();
}
public static void main(String [] args){
TestNum tn=new TestNum();
TestClass tc1=new TestClass(tn);
TestClass tc2=new TestClass(tn);
TestClass tc3=new TestClass(tn);
tc1.start();
tc2.start();
tc3.start();
}
class TestClass extends Thread{
private TestNum tn;
public TestClass(TestNum tn){
this.tn=tn;
}
public void run(){
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
System.out.println("thread-"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-"+tn.getNextNum());
}
}
}
} 对于上面的代码,我们使用线程封闭来完成,tc1-3这三个线程访问共享变量在自己栈空间的一个副本,他们都在干自己的事(不是一件事),只不过在干自己的事的过程中使用到了共享变量这个载体,而且他们也不关心最终对共享变量产生了多少影响。此时,输出的结果最大值一定是num=3(每个线程在干自己的事情)。
实现:每个Thread都持有一个TreadLocalMap类型的变量(该类是一个轻量级的Map,功能与map一样,区别是桶里放的是entry而不是entry的链表。功能还是一个map。)以本身为key,以目标为value。
主要方法是get()和set(T a),set之后在map里维护一个threadLocal -> a,get时将a返回。ThreadLocal是一个特殊的容器。
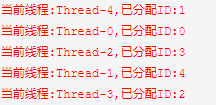
假设我们要为每个线程关联一个唯一的序号,在每个线程周期内,我们需要多次访问这个序号,这时我们就可以使用ThreadLocal了
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
public class ThreadLocalDemo {
public static void main(String []args){
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
final Thread t = new Thread(){
@Override
public void run(){
System.out.println("当前线程:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+",已分配ID:"+ThreadId.get());
}
};
t.start();
}
}
static class ThreadId{
//一个递增的序列,使用AtomicInger原子变量保证线程安全
private static final AtomicInteger nextId = new AtomicInteger(0);
//线程本地变量,为每个线程关联一个唯一的序号
private static final ThreadLocal threadId =
new ThreadLocal() {
@Override
protected Integer initialValue() {
return nextId.getAndIncrement();//相当于nextId++,由于nextId++这种操作是个复合操作而非原子操作,会有线程安全问题(可能在初始化时就获取到相同的ID,所以使用原子变量
}
};
//返回当前线程的唯一的序列,如果第一次get,会先调用initialValue,后面看源码就了解了
public static int get() {
return threadId.get();
}
}
} 执行结果,可以看到每个线程都分配到了一个唯一的ID,同时在此线程范围内的"任何地点",我们都可以通过ThreadId.get()这种方式直接获取。
ThreadLocal,很多地方叫做线程本地变量,也有些地方叫做线程本地存储。ThreadLocal为变量在每个线程中都创建了一个副本,那么每个线程可以访问自己内部的副本变量。
假如每个线程中都有一个connect变量,各个线程之间对connect变量的访问实际上是没有依赖关系的,即一个线程不需要关心其他线程是否对这个connect进行了修改的。ThreadLocal在每个线程中对该变量会创建一个副本,即每个线程内部都会有一个该变量,且在线程内部任何地方都可以使用,线程之间互不影响,这样一来就不存在线程安全问题,也不会严重影响程序执行性能。
但是要注意,虽然ThreadLocal能够解决上面说的问题,但是由于在每个线程中都创建了副本,所以要考虑它对资源的消耗,比如内存的占用会比不使用ThreadLocal要大。
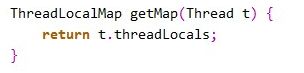
第一句是取得当前线程,然后通过getMap(t)方法获取到一个map,map的类型为ThreadLocalMap。然后接着下面获取到
如果获取成功,则返回value值。
如果map为空,则调用setInitialValue方法返回value。
在getMap中,是调用当期线程t,返回当前线程t中的一个成员变量threadLocals。
成员变量threadLocals是什么:
![]()
实际上就是一个ThreadLocalMap,这个类型是ThreadLocal类的一个内部类
ThreadLocalMap的Entry继承了WeakReference,并且使用ThreadLocal作为键值。
setInitialValue方法的具体实现:
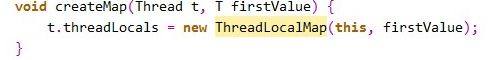
就是如果map不为空,就设置键值对,为空,再创建Map,看一下createMap的实现:
ThreadLocal是如何为每个线程创建变量的副本的:
首先,在每个线程Thread内部有一个ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap类型的成员变量threadLocals,这个threadLocals就是用来存储实际的变量副本的,键值为当前ThreadLocal变量,value为变量副本(即T类型的变量)。
初始时,在Thread里面,threadLocals为空,当通过ThreadLocal变量调用get()方法或者set()方法,就会对Thread类中的threadLocals进行初始化,并且以当前ThreadLocal变量为键值,以ThreadLocal要保存的副本变量为value,存到threadLocals。
然后在当前线程里面,如果要使用副本变量,就可以通过get方法在threadLocals里面查找。
1)实际的通过ThreadLocal创建的副本是存储在每个线程自己的threadLocals中的;
2)为何threadLocals的类型ThreadLocalMap的键值为ThreadLocal对象,因为每个线程中可有多个threadLocal变量,就像上面代码中的longLocal和stringLocal;
3)在进行get之前,必须先set,否则会报空指针异常;
如果想在get之前不需要调用set就能正常访问的话,必须重写initialValue()方法。
如果没有先set的话,即在map中查找不到对应的存储,则会通过调用setInitialValue方法返回i,而在setInitialValue方法中,有一个语句是T value = initialValue(), 而默认情况下,initialValue方法返回的是null。
下面这段代码,即重写了initialValue方法:
在main线程中就可以直接不用先set而直接调用get了。
public class Test {
ThreadLocal longLocal = new ThreadLocal(){
protected Long initialValue() {
return Thread.currentThread().getId();
};
};
ThreadLocal stringLocal = new ThreadLocal(){;
protected String initialValue() {
return Thread.currentThread().getName();
};
};
public void set() {
longLocal.set(Thread.currentThread().getId());
stringLocal.set(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
public long getLong() {
return longLocal.get();
}
public String getString() {
return stringLocal.get();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
final Test test = new Test();
test.set();
System.out.println(test.getLong());
System.out.println(test.getString());
Thread thread1 = new Thread(){
public void run() {
test.set();
System.out.println(test.getLong());
System.out.println(test.getString());
};
};
thread1.start();
thread1.join();
System.out.println(test.getLong());
System.out.println(test.getString());
}
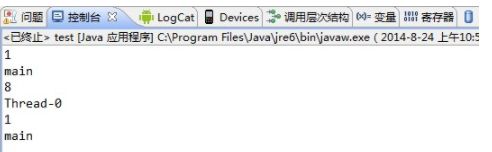
} 从这段代码的输出结果可以看出,在main线程中和thread1线程中,longLocal保存的副本值和stringLocal保存的副本值都不一样。最后一次在main线程再次打印副本值是为了证明在main线程中和thread1线程中的副本值确实是不同的。
总结一下:
1)实际的通过ThreadLocal创建的副本是存储在每个线程自己的threadLocals中的;
2)为何threadLocals的类型ThreadLocalMap的键值为ThreadLocal对象,因为每个线程中可有多个threadLocal变量,就像上面代码中的longLocal和stringLocal;
3)在进行get之前,必须先set,否则会报空指针异常;
ThreadLocal使用场景为 用来解决 数据库连接、Session管理等。
private static ThreadLocal connectionHolder
= new ThreadLocal() {
public Connection initialValue() {
return DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL);
}
};
public static Connection getConnection() {
return connectionHolder.get();
} private static final ThreadLocal threadSession = new ThreadLocal();
public static Session getSession() throws InfrastructureException {
Session s = (Session) threadSession.get();
try {
if (s == null) {
s = getSessionFactory().openSession();
threadSession.set(s);
}
} catch (HibernateException ex) {
throw new InfrastructureException(ex);
}
return s;
}各个线程的value值是相互独立的,本线程的累加操作不会影响到其他线程的值,真正达到了线程内部隔离的效果。
public class TestThreadLocal {
private static final ThreadLocal value = new ThreadLocal() {
@Override
protected Integer initialValue() {
return 0;
}
};
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
new Thread(new MyThread(i)).start();
}
}
static class MyThread implements Runnable {
private int index;
public MyThread(int index) {
this.index = index;
}
public void run() {
System.out.println("线程" + index + "的初始value:" + value.get());
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
value.set(value.get() + i);
}
System.out.println("线程" + index + "的累加value:" + value.get());
}
}
} 执行结果为:
线程0的初始value:0
线程3的初始value:0
线程2的初始value:0
线程2的累加value:45
线程1的初始value:0
线程3的累加value:45
线程0的累加value:45
线程1的累加value:45
线程4的初始value:0
线程4的累加value:45
ThreadLocal实现数据源的切换
public enum DataSourceEnum {
MASTER,SLAVE
}
/**
* 数据源切换类
* 构建一个DataSourceEnum容器,并提供了向其中设置和获取DataSorceEnum的方法
*/
public class DataSourceContextHolder {
private static final ThreadLocal contextHolder = new ThreadLocal(){
protected DataSourceEnum initValue(){
return DataSourceEnum.MASTER;
}
};
public static void setDatabaseType(DataSourceEnum type){
contextHolder.set(type);
}
public static DataSourceEnum getDataSourceType(){
return contextHolder.get();
}
public static void clearDataSourceType(){
contextHolder.remove();
}
} import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.lookup.AbstractRoutingDataSource;
public class DynamicDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
return DataSourceContextHolder.getDataSourceType();
}
}import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceBuilder;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Configuration
public class DataSourceConfig {
@Autowired
private Environment env;
@Bean(name="masterDataSource")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.master")
public DataSource masterDataSource()
{
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean(name="slaveDataSource")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.slave")
public DataSource slaveDataSource()
{
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Primary
@Bean("dataSource")
public DynamicDataSource dataSource(@Qualifier("masterDataSource") DataSource master,
@Qualifier("slaveDataSource") DataSource slave)
{
DynamicDataSource dynamicDataSource = new DynamicDataSource();
Map targetDataSources = new HashMap();
targetDataSources.put(DataSourceEnum.MASTER,master);
targetDataSources.put(DataSourceEnum.SLAVE,slave);
dynamicDataSource.setTargetDataSources(targetDataSources);
dynamicDataSource.setDefaultTargetDataSource(master);
return dynamicDataSource;
}
@Primary
@Bean("sqlSessionFactory")
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(@Qualifier("masterDataSource") DataSource master,
@Qualifier("slaveDataSource") DataSource slave)throws Exception
{
SqlSessionFactoryBean sessionFactoryBean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
sessionFactoryBean.setDataSource(this.dataSource(master,slave));
sessionFactoryBean.setMapperLocations(new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources(env.getProperty("mybatis.mapper-locations")));
return sessionFactoryBean.getObject();
}
@Bean("transactionManager")
public DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager(@Qualifier("dataSource") DynamicDataSource dataSource) throws Exception
{
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
}
}spring:
application:
name: TAG_RULE
datasource:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
#主数据源
master:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://121:33/arcgis?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useOldAliasMetadataBehavior=true
username: arcgis
password: arcgis
#从数据源
slave:
driver-class-name: com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver
url: jdbc:sqlserver://134:33;DatabaseName=arcgis
username: arcgis
password: "%$#@!arcgis"
maximum-pool-size: 100
max-idle: 10
max-wait: 10000
min-idle: 5
initial-size: 5
validation-query: SELECT 1
server:
port: 9001
mybatis:
mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*.xml
logging:
level:
com:
looedu:
mapper: debug业务代码实现数据源的切换
public void synData()
{
try
{
List ruleList = tagRuleMapper.selectAll();
if(CollectionUtils.isEmpty(ruleList))
{
return;
}
DataSourceContextHolder.setDatabaseType(DataSourceEnum.SLAVE);
List valueList = tagValueMapper.queryTagValueList(ruleList);
if(CollectionUtils.isEmpty(valueList))
{
return;
}
DataSourceContextHolder.setDatabaseType(DataSourceEnum.MASTER);
for(TagValue tv:valueList)
{
for(TTagRule rule:ruleList)
{
if(tv.getTagcode().equals(rule.getTagcode()))
{
tv.setTagname(rule.getTagname());
tv.setType(rule.getType());
Date now = new Date();
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
tv.setSynTime(sdf.format(now));
}
}
}
Map param = new HashMap(1);
param.put("list",valueList);
int a = tagValueMapper.insertTagValue(param);
tagValueMapper.deleteRepeatTagValue();
}
catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
return;
}
}
volatile
volatile包含以下语义:
(1)Java 存储模型不会对valatile指令的操作进行重排序:这个保证对volatile变量的操作时按照指令的出现顺序执行的。
(2)volatile变量不会被缓存在寄存器中(只有拥有线程可见)或者其他对CPU不可见的地方,每次总是从主存中读取volatile变量的结果。也就是说对于volatile变量的修改,其它线程总是可见的,并且不是使用自己线程栈内部的变量。也就是在happens-before法则中,对一个valatile变量的写操作后,其后的任何读操作理解可见此写操作的结果。
尽管volatile变量的特性不错,但是volatile并不能保证线程安全的,也就是说volatile字段的操作不是原子性的,volatile变量只能保证可见性(一个线程修改后其它线程能够理解看到此变化后的结果),要想保证原子性,目前为止只能加锁!
使用Volatile的原则:
应用volatile变量的三个原则:
(1)写入变量不依赖此变量的值,或者只有一个线程修改此变量
(2)变量的状态不需要与其它变量共同参与不变约束
(3)访问变量不需要加锁
实际上,这些条件表明,可以被写入 volatile 变量的这些有效值独立于任何程序的状态,包括变量的当前状态。
第一个条件的限制使 volatile 变量不能用作线程安全计数器。虽然增量操作(x++)看上去类似一个单独操作,实际上它是一个由读取-修改-写入操作序列组成的组合操作,必须以原子方式执行,而 volatile 不能提供必须的原子特性。实现正确的操作需要使 x 的值在操作期间保持不变,而 volatile 变量无法实现这点。(然而,如果将值调整为只从单个线程写入,那么可以忽略第一个条件。)
java源码
| Modifier and Type | Method and Description |
|---|---|
T |
get() 返回当前线程的此线程局部变量的副本中的值。 |
protected T |
initialValue() 返回此线程局部变量的当前线程的“初始值”。 |
void |
remove() 删除此线程局部变量的当前线程的值。 |
void |
set(T value) 将当前线程的此线程局部变量的副本设置为指定的值。 |
static |
withInitial(Supplier supplier) 创建线程局部变量。 |
package java.lang;
import java.lang.ref.*;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
import java.util.function.Supplier;
public class ThreadLocal {
private final int threadLocalHashCode = nextHashCode();
private static AtomicInteger nextHashCode =
new AtomicInteger();
private static final int HASH_INCREMENT = 0x61c88647;
private static int nextHashCode() {
return nextHashCode.getAndAdd(HASH_INCREMENT);
}
protected T initialValue() {
return null;
}
public static ThreadLocal withInitial(Supplier supplier) {
return new SuppliedThreadLocal<>(supplier);
}
public ThreadLocal() {
}
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
return setInitialValue();
}
private T setInitialValue() {
T value = initialValue();
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
return value;
}
public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
}
public void remove() {
ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread());
if (m != null)
m.remove(this);
}
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;
}
void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
}
static ThreadLocalMap createInheritedMap(ThreadLocalMap parentMap) {
return new ThreadLocalMap(parentMap);
}
T childValue(T parentValue) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
static final class SuppliedThreadLocal extends ThreadLocal {
private final Supplier supplier;
SuppliedThreadLocal(Supplier supplier) {
this.supplier = Objects.requireNonNull(supplier);
}
@Override
protected T initialValue() {
return supplier.get();
}
}
static class ThreadLocalMap {
static class Entry extends WeakReference> {
/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}
private static final int INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;
private Entry[] table;
/**
* The number of entries in the table.
*/
private int size = 0;
/**
* The next size value at which to resize.
*/
private int threshold; // Default to 0
/**
* Set the resize threshold to maintain at worst a 2/3 load factor.
*/
private void setThreshold(int len) {
threshold = len * 2 / 3;
}
/**
* Increment i modulo len.
*/
private static int nextIndex(int i, int len) {
return ((i + 1 < len) ? i + 1 : 0);
}
/**
* Decrement i modulo len.
*/
private static int prevIndex(int i, int len) {
return ((i - 1 >= 0) ? i - 1 : len - 1);
}
ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocal firstKey, Object firstValue) {
table = new Entry[INITIAL_CAPACITY];
int i = firstKey.threadLocalHashCode & (INITIAL_CAPACITY - 1);
table[i] = new Entry(firstKey, firstValue);
size = 1;
setThreshold(INITIAL_CAPACITY);
}
private ThreadLocalMap(ThreadLocalMap parentMap) {
Entry[] parentTable = parentMap.table;
int len = parentTable.length;
setThreshold(len);
table = new Entry[len];
for (int j = 0; j < len; j++) {
Entry e = parentTable[j];
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
ThreadLocal 一个int可能原子更新的值。 有关原子变量属性的描述,请参阅java.util.concurrent.atomic包规范。 一个AtomicInteger用于诸如原子增量计数器的应用程序中,不能用作Integer的替代品 。 但是,这个类确实扩展了Number以允许通过处理基于数字类的工具和实用程序的统一访问。
| Modifier and Type | Method and Description |
|---|---|
int |
accumulateAndGet(int x, IntBinaryOperator accumulatorFunction) 使用将给定函数应用于当前值和给定值的结果原子更新当前值,返回更新后的值。 |
int |
addAndGet(int delta) 将给定的值原子地添加到当前值。 |
boolean |
compareAndSet(int expect, int update) 如果当前值 |
int |
decrementAndGet() 原子减1当前值。 |
double |
doubleValue() 返回此值 |
float |
floatValue() 返回此值 |
int |
get() 获取当前值。 |
int |
getAndAccumulate(int x, IntBinaryOperator accumulatorFunction) 使用给定函数应用给当前值和给定值的结果原子更新当前值,返回上一个值。 |
int |
getAndAdd(int delta) 将给定的值原子地添加到当前值。 |
int |
getAndDecrement() 原子减1当前值。 |
int |
getAndIncrement() 原子上增加一个当前值。 |
int |
getAndSet(int newValue) 将原子设置为给定值并返回旧值。 |
int |
getAndUpdate(IntUnaryOperator updateFunction) 用应用给定函数的结果原子更新当前值,返回上一个值。 |
int |
incrementAndGet() 原子上增加一个当前值。 |
int |
intValue() 将 |
void |
lazySet(int newValue) 最终设定为给定值。 |
long |
longValue() 返回此值 |
void |
set(int newValue) 设置为给定值。 |
String |
toString() 返回当前值的String表示形式。 |
int |
updateAndGet(IntUnaryOperator updateFunction) 使用给定函数的结果原子更新当前值,返回更新的值。 |
boolean |
weakCompareAndSet(int expect, int update) 如果当前值 |
package java.util.concurrent.atomic;
import java.util.function.IntUnaryOperator;
import java.util.function.IntBinaryOperator;
import sun.misc.Unsafe;
public class AtomicInteger extends Number implements java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 6214790243416807050L;
// setup to use Unsafe.compareAndSwapInt for updates
private static final Unsafe unsafe = Unsafe.getUnsafe();
private static final long valueOffset;
static {
try {
valueOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset
(AtomicInteger.class.getDeclaredField("value"));
} catch (Exception ex) { throw new Error(ex); }
}
private volatile int value;
public AtomicInteger(int initialValue) {
value = initialValue;
}
public AtomicInteger() {
}
public final int get() {
return value;
}
public final void set(int newValue) {
value = newValue;
}
public final void lazySet(int newValue) {
unsafe.putOrderedInt(this, valueOffset, newValue);
}
public final int getAndSet(int newValue) {
return unsafe.getAndSetInt(this, valueOffset, newValue);
}
public final boolean compareAndSet(int expect, int update) {
return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this, valueOffset, expect, update);
}
public final boolean weakCompareAndSet(int expect, int update) {
return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this, valueOffset, expect, update);
}
public final int getAndIncrement() {
return unsafe.getAndAddInt(this, valueOffset, 1);
}
public final int getAndDecrement() {
return unsafe.getAndAddInt(this, valueOffset, -1);
}
public final int getAndAdd(int delta) {
return unsafe.getAndAddInt(this, valueOffset, delta);
}
public final int incrementAndGet() {
return unsafe.getAndAddInt(this, valueOffset, 1) + 1;
}
public final int decrementAndGet() {
return unsafe.getAndAddInt(this, valueOffset, -1) - 1;
}
public final int addAndGet(int delta) {
return unsafe.getAndAddInt(this, valueOffset, delta) + delta;
}
public final int getAndUpdate(IntUnaryOperator updateFunction) {
int prev, next;
do {
prev = get();
next = updateFunction.applyAsInt(prev);
} while (!compareAndSet(prev, next));
return prev;
}
public final int updateAndGet(IntUnaryOperator updateFunction) {
int prev, next;
do {
prev = get();
next = updateFunction.applyAsInt(prev);
} while (!compareAndSet(prev, next));
return next;
}
public final int getAndAccumulate(int x,
IntBinaryOperator accumulatorFunction) {
int prev, next;
do {
prev = get();
next = accumulatorFunction.applyAsInt(prev, x);
} while (!compareAndSet(prev, next));
return prev;
}
public final int accumulateAndGet(int x,
IntBinaryOperator accumulatorFunction) {
int prev, next;
do {
prev = get();
next = accumulatorFunction.applyAsInt(prev, x);
} while (!compareAndSet(prev, next));
return next;
}
public String toString() {
return Integer.toString(get());
}
public int intValue() {
return get();
}
public long longValue() {
return (long)get();
}
public float floatValue() {
return (float)get();
}
public double doubleValue() {
return (double)get();
}
}