最短路径之迪杰斯特拉(Dijkstra)算法
定义
迪杰斯特拉算法(Dijkstra)是由荷兰计算机科学家狄克斯特拉于1959 年提出的,因此又叫狄克斯特拉算法。是从一个顶点到其余各顶点的最短路径算法,解决的是有权图中最短路径问题。迪杰斯特拉算法主要特点是以起始点为中心向外层层扩展,直到扩展到终点为止。
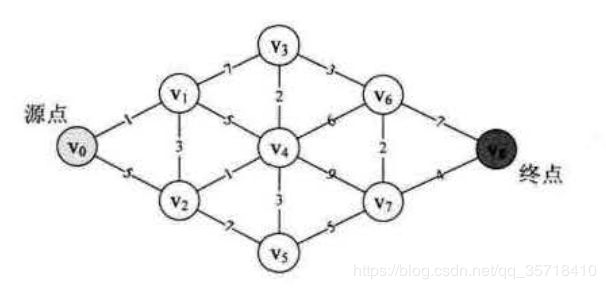
如图所示,我们要求解V0到V8的最小权值及最短路径,这是我们经常碰到的求最小路径问题之一。通过一步就将最短权值和路径求出是不现实的,不过我们可以通过迪杰斯特拉算法,将所有点及个点之间的权值转换为矩阵,也就是二维数组,然后逐步求出最短路径即可。
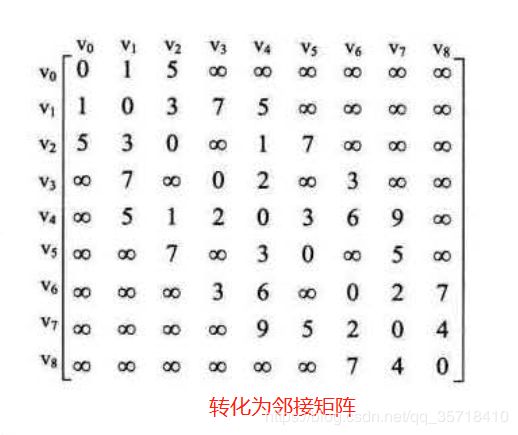
二维矩阵数组如下图:
TS代码如下:
class Dikastra{
private arc:Array<any> = [];
private numVertexes = 0; //顶点数
private vexs:Array<string> = []; //顶点表
private pathmatirx:Array<number> = []; // 用于存储最短路径下标的数组,下标为各个顶点,值为下标顶点的前驱顶点
private shortPathTable:Array<number> = []; //用于存储到各点最短路径的权值和
private final:Array<any> = []; //用于标记V0到V8每个点是否找到了最短路径
/**
* 生成V0 到 V8 顶点
*/
private createVertexs(){
for(let i=0;i<this.numVertexes;i++){
this.vexs.push('V' + i);
}
}
/**
* 初始化状态标记及最短路径表
*/
private initTables(){
this.final.length = this.pathmatirx.length = this.shortPathTable.length = 0;
for (let v = 0; v < this.numVertexes; v++) {
this.final[v] = v === 0 ? 1 : 0; //V0默认是已找到最短路径状态
this.shortPathTable[v] = v === 0 ? 0 : this.arc[0][v]; //V0自己到自己是0
this.pathmatirx[v] = 0;
}
}
/**
* 执行迪杰斯特拉算法
*/
private dijkstra(){
let k:number; //当前找到的最近路线上的最后一个顶点,通过此顶点去找最近路线上的下一个顶点
let min:number; //到当前顶点的最小权值,65535意味着相距无穷大(不挨着初始时距离权值是无穷大)
for (let v = 1; v < this.numVertexes; v++) {
//初始化数据
min = 65535;
for (let w = 0; w < this.numVertexes; w++) {
//寻找离V0最近的顶点
if (!this.final[w] && this.shortPathTable[w] < min) {
k = w;
min = this.shortPathTable[w]; //w 顶点离V0顶点更近
}
}
this.final[k] = 1; //将目前找到的最近的顶点置位1
for (let w = 0; w < this.numVertexes; w++) {
const curPathVal = min + this.arc[k][w];
//修正当前最短路径及距离
if (!this.final[w] && curPathVal < this.shortPathTable[w]) {
//说明找到了更短的路径,修改Pathmatirx[w]和ShortPathTable[w]
this.shortPathTable[w] = curPathVal;
this.pathmatirx[w] = k;
}
}
}
}
/**
* 获取最短距离权值
* @param Vn 终点
* @returns 到终点的距离权值
*/
public getShortPath(Vn:number){
//打印V0-Vn最短路径
console.log(
"%s-%s 最小权值和: %d",
this.vexs[0],
this.vexs[Vn],
this.shortPathTable[Vn]
);
let temp = Vn,
str = "";
while (temp != 0) {
str = "->" + this.vexs[temp] + str;
temp = this.pathmatirx[temp];
}
str = "V0" + str;
console.log("最短路线:" + str);
return this.shortPathTable[Vn];
}
/**
* 设置arc矩阵,重新计算矩阵最短距离权值
*/
public setArc(arc:Array<any>){
this.arc = arc;
this.numVertexes = arc[0].length;
//生成顶点
this.createVertexs();
//初始化最短路径表及是否已找到最短路径关联数组
this.initTables();
//执行迪杰斯特拉算法寻找最短路径
this.dijkstra();
}
}
js版本代码如下:
var Dikastra = /** @class */ (function () {
function Dikastra() {
this.arc = [];
this.numVertexes = 0; //顶点数
this.vexs = []; //顶点表
this.pathmatirx = []; // 用于存储最短路径下标的数组,下标为各个顶点,值为下标顶点的前驱顶点
this.shortPathTable = []; //用于存储到各点最短路径的权值和
this.final = []; //用于标记V0到V8每个点是否找到了最短路径
}
/**
* 生成V0 到 V8 顶点
*/
Dikastra.prototype.createVertexs = function () {
for (var i = 0; i < this.numVertexes; i++) {
this.vexs.push('V' + i);
}
};
/**
* 初始化状态标记及最短路径表
*/
Dikastra.prototype.initTables = function () {
this.final.length = this.pathmatirx.length = this.shortPathTable.length = 0;
for (var v = 0; v < this.numVertexes; v++) {
this.final[v] = v === 0 ? 1 : 0; //V0默认是已找到最短路径状态
this.shortPathTable[v] = v === 0 ? 0 : this.arc[0][v]; //V0自己到自己是0
this.pathmatirx[v] = 0;
}
};
/**
* 执行迪杰斯特拉算法
*/
Dikastra.prototype.dijkstra = function () {
var k; //当前找到的最近路线上的最后一个顶点,通过此顶点去找最近路线上的下一个顶点
var min; //到当前顶点的最小权值,65535意味着相距无穷大(不挨着初始时距离权值是无穷大)
for (var v = 1; v < this.numVertexes; v++) {
//初始化数据
min = 65535;
for (var w = 0; w < this.numVertexes; w++) {
//寻找离V0最近的顶点
if (!this.final[w] && this.shortPathTable[w] < min) {
k = w;
min = this.shortPathTable[w]; //w 顶点离V0顶点更近
}
}
this.final[k] = 1; //将目前找到的最近的顶点置位1
for (var w = 0; w < this.numVertexes; w++) {
var curPathVal = min + this.arc[k][w];
//修正当前最短路径及距离
if (!this.final[w] && curPathVal < this.shortPathTable[w]) {
//说明找到了更短的路径,修改Pathmatirx[w]和ShortPathTable[w]
this.shortPathTable[w] = curPathVal;
this.pathmatirx[w] = k;
}
}
}
};
/**
* 获取最短距离权值
* @param Vn 终点
* @returns 到终点的距离权值
*/
Dikastra.prototype.getShortPath = function (Vn) {
//打印V0-Vn最短路径
console.log("%s-%s 最小权值和: %d", this.vexs[0], this.vexs[Vn], this.shortPathTable[Vn]);
var temp = Vn, str = "";
while (temp != 0) {
str = "->" + this.vexs[temp] + str;
temp = this.pathmatirx[temp];
}
str = "V0" + str;
console.log("最短路线:" + str);
return this.shortPathTable[Vn];
};
/**
* 设置arc矩阵,重新计算矩阵最短距离权值
*/
Dikastra.prototype.setArc = function (arc) {
this.arc = arc;
this.numVertexes = arc[0].length;
//生成顶点
this.createVertexs();
//初始化最短路径表及是否已找到最短路径关联数组
this.initTables();
//执行迪杰斯特拉算法寻找最短路径
this.dijkstra();
};
return Dikastra;
}());
引入js,然后console打印出测试结果:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body></body>
<script src="./dikastra.js"></script>
<script>
const dikastra = new Dikastra();
//定义图的二维矩阵
const arc1 = [
[0, 1, 5, 65535, 65535, 65535, 65535, 65535, 65535],
[1, 0, 3, 7, 5, 65535, 65535, 65535, 65535],
[5, 3, 0, 65535, 1, 7, 65535, 65535, 65535],
[65535, 7, 65535, 0, 2, 65535, 3, 65535, 65535],
[65535, 5, 1, 2, 0, 3, 6, 9, 65535],
[65535, 65535, 7, 65535, 3, 0, 65535, 5, 65535],
[65535, 65535, 65535, 3, 6, 65535, 0, 2, 7],
[65535, 65535, 65535, 65535, 9, 5, 2, 0, 4],
[65535, 65535, 65535, 65535, 65535, 65535, 7, 4, 0]
];
dikastra.setArc(arc1);
console.log(dikastra.getShortPath(8));
//如果想获取V5到V8的最短权值路径,重新构建V5到V8的矩阵即可
const arc2 = [
[0,65535,5,65535],
[65535,0,2,7],
[5,2,0,4],
[65535,7,4,0]
];
dikastra.setArc(arc2);
console.log(dikastra.getShortPath(3));
</script>
</html>
打印结果如下:

如果想要获取V5到V8的最短路径,只需要构建V5到V8的二维矩阵,然后重新setArc,调用getShortPath方法获取结果即可。