实验5 遗传算法求解tsp问题
传送门(所有的实验都使用python实现)
实验1 BP神经网络实验
实验2 som网实验
实验3 hopfield实现八皇后问题
实验4 模糊搜索算法预测薄冰厚度
实验5 遗传算法求解tsp问题
实验6 蚁群算法求解tsp问题
实验7 粒子群优化算法求解tsp问题
实验8 分布估计算法求解背包问题
实验9 模拟退火算法求解背包问题
实验10 禁忌搜索算法求解tsp问题
一、实验目的
理解并使用遗传算法
二、实验内容
实现基于遗传算法的旅行商路线寻找
三、实验环境
使用Python3.0 在 eclipse进行编辑
四、实验步骤
1、输入介绍:
城市总数目为30,每个城市的坐标以(x,y)表示,x,y的取值均为0~30的随机数。
2、初始群体设定:
随机产生n条长度为m的数组。n代表个体数目,m代表城市个数。在本次实验中设定n=10,m=30。且同一个体中的m个数互不相同,因为每个城市只经过一次。
4、适应度计算
根据两点之间的距离公式可得n与m的距离
![]()
将城市之间的相邻距离相加,总和越小的个体适应度越高。
5、选择算子
采用最优保存策略,最优的个体直接覆盖最差个体,且这两个个体不参与交叉变异运算。
6.交叉算子
采用有序交叉法,产生新个体。
7.变异
对于变异的个体,在序列上随机出a,b两点,并将两点之间的序列倒置。
8.终止条件
分别进行100,500,2000,10000次进化后终止。
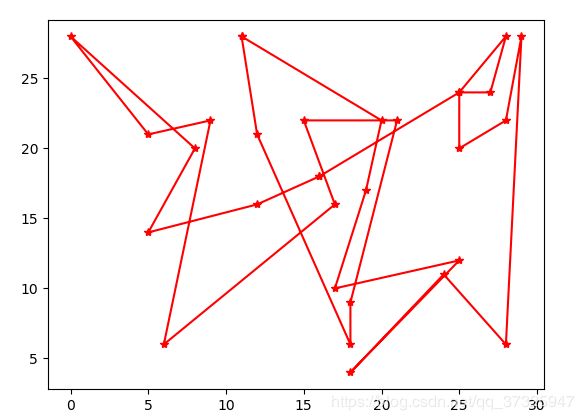
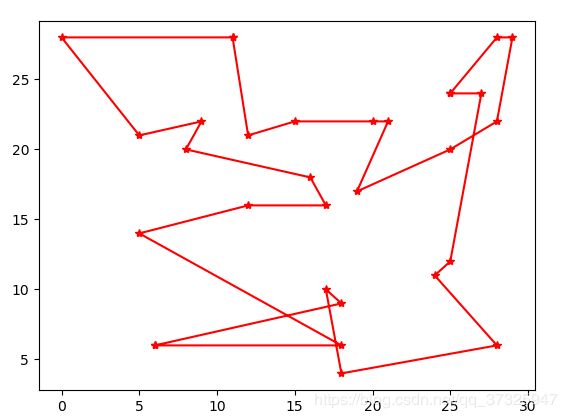
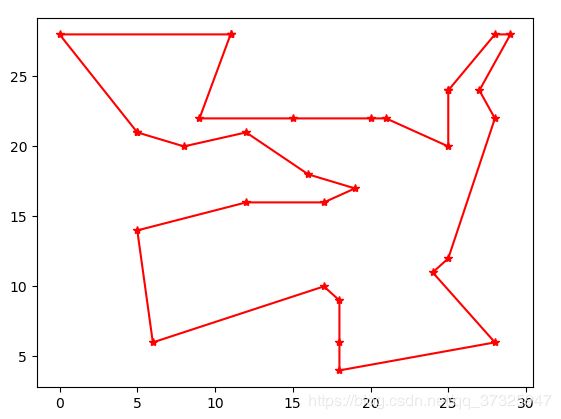
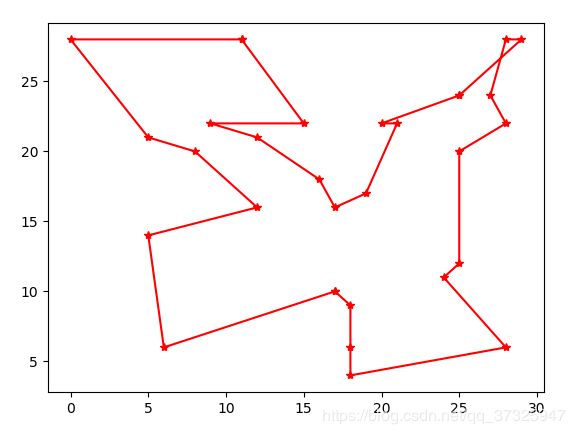
运行截图:
100次进化:总距离:240.883
500次进化总距离:172.05
2000次进化总距离:143.708
10000次进化总距离:142.136
五、总结
种群的初始个体数目设置的越多,产生的个体种类就越多,进而在比较少的进化次数中就能找到较优解,但是单次进化的时间会变长。此外变异因子不同值也会影响进化的进程。在本次实验中可以看到刚开始最优解变化很快,到2000次时开始趋于稳定。
Python源码
#coding:gbk
import random
import math
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
global n,m,pc,pm,best;
pc = 0.9;pm=0.2; #pc为交配概率 pm为变异概率
best = 10000; #best记录最优距离,初始化无限大
n=10;m=30; #n:样本个数 m:城市个数
dna = [[0]*(m) for i in range(n)] #开辟n*m的数组
value = [0.0]*n; #value数组记录个体适应度
way =[0]*m; #way数组记录最优解路线
class no: #该类表示每个点的坐标
def __init__(self,x,y):
self.x=x;
self.y=y;
p=[];
def draw(t): #该函数用于描绘路线图
x=[0]*(m+1);y=[0]*(m+1);
for i in range(m):
x[i] =p[t[i]].x;
y[i] =p[t[i]].y;
x[m] =p[t[0]].x;
y[m] =p[t[0]].y;
plt.plot(x,y,color='r',marker='*' );
plt.show();
def variation(x): # 变异操作函数
x1 = [0]*m;
for i in range(m):
x1[i] = x[i];
a =random.randint(0,m-1); #随机出两个点进行倒置
b = random.randint(0,m-1);
if(a > b): a,b=b,a;
le = b-a+1;
for i in range(le):
x[a+i]=x1[b-i];
def mycol(): #城市坐标输入
p.append(no( 8 , 20 ));
p.append(no( 28 , 6 )); p.append(no( 27 , 24 )); p.append(no( 25 , 20 )); p.append(no( 5 , 14 )); p.append(no( 18 , 4 )); p.append(no( 21 , 22 ));
p.append(no( 19 , 17 )); p.append(no( 28 , 22 )); p.append(no( 16 , 18 )); p.append(no( 28 , 28 )); p.append(no( 11 , 28 )); p.append(no( 29 , 28 ));
p.append(no( 15 , 22 )); p.append(no( 25 , 24 )); p.append(no( 9 , 22 )); p.append(no( 17 , 16 )); p.append(no( 12 , 16 )); p.append(no( 5 , 21 ));
p.append(no( 6 , 6 )); p.append(no( 12 , 21 )); p.append(no( 11 , 28 )); p.append(no( 20 , 22 )); p.append(no( 17 , 10 )); p.append(no( 18 , 6 ));
p.append(no( 18 , 9 )); p.append(no( 25 , 24 )); p.append(no( 24 , 11 )); p.append(no( 25 , 12 )); p.append(no( 0 , 28 ));
def init(): #初始化函数 随机产生初始个体
vis = [0]*m;
num=0;
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
vis[j] = 0;
for j in range(m):
num = random.randint(0,m-1);
while(vis[num] == 1):
num = random.randint(0,m-1);
vis[num]=1;dna[i][j]=num;
def get_value(t): #适应度计算
ans = 0.0;
for i in range(1,m): #两点距离公式
ans += math.sqrt((p[t[i]].x-p[t[i-1]].x) *(p[t[i]].x-p[t[i-1]].x) +(p[t[i]].y-p[t[i-1]].y) *(p[t[i]].y-p[t[i-1]].y));
ans += math.sqrt((p[t[0]].x-p[t[m-1]].x) * (p[t[0]].x-p[t[m-1]].x) +(p[t[0]].y-p[t[m-1]].y) *(p[t[0]].y-p[t[m-1]].y));
return ans;
def find(x,a,b,num): #交叉算子运算时判断是否出现重复的城市id
for i in range(a,b+1):
if(num[i] == x):
return i;
return -1;
def swap(x, y): #有序交叉法
x1 = [0]*m; y1 = [0]*m;
for i in range(m):
x1[i]=x[i];y1[i]=y[i];
a = random.randint(0,m-1); #随机产生两个点
b = random.randint(0,m-1);
if(a > b): a,b=b,a;
for i in range(a): #交叉运算
x1[i]=y[i];y1[i]=x[i];
for i in range(b+1,m):
x1[i]=y[i];y1[i]=x[i];
ob = 0;
for i in range(m): #判断交叉的合法性并进行维护,直到交叉成功
if(i>= a and i<= b):
continue;
ob = find(x1[i],a,b,x1);
while(ob != -1):
x1[i] = y1[ob];
ob = find(x1[i],a,b,x1);
for i in range(m): #操作同上,维护另一新个体的交叉合法性。
if(i>= a and i<= b):
continue;
ob = find(y1[i],a,b,y1);
while(ob != -1):
y1[i] = x1[ob];
ob = find(y1[i],a,b,y1);
for i in range(m):
x[i]=x1[i];y[i]=y1[i];
def slove(): #总执行函数
global best; #记录最短距离
for i in range(n):
value[i]=get_value(dna[i]);
max_id = value.index(max(value)); #最优解与最差解个体的id被记录
min_id = value.index(min(value));
if(value[min_id] < best):
best = value[min_id];
for i in range(m):
way[i] = dna[min_id][i];
value[max_id] = value[min_id]; #最优解覆盖最差解
fa = -1;
for i in range(m):
dna[max_id][i]=dna[min_id][i];
for i in range(n): #开始交配
if(random.random()> pc or i == max_id or i == min_id):
continue;
if(fa == -1):
fa = i;
else :
swap(dna[fa], dna[i]);
fa = -1;
for i in range(n): #变异运算
if(random.random()> pm or i == max_id or i == min_id):
continue;
variation(dna[i]);
mycol(); #数据输入
init(); #群体初始化
for i in range(1000): #控制进化次数
slove();
draw(way); #画图描绘路线
print(round(best,3)); #打印距离
print(way); #打印路线,以序列表示