二叉树先序遍历,中序遍历,后序遍历,层次遍历学习总结及完整C/C++代码
伪代码阐述
先序遍历
先序遍历:先访问根节点, 然后深入左子树,直到不能深入时再深入右子树
由定义可得递归式
void travPre_R(BinNodePosi* x,VISIT& visit){
if(!X) return; //到达叶子节点,开始回归
visit(x->data);//向左子树深入的过程中便开始进行对每个节点的数据进行访问
travPre_R(x->lChild,visit);//深入右子树
travPre_R(x->rChild,visit);//深入右子树
}
例:
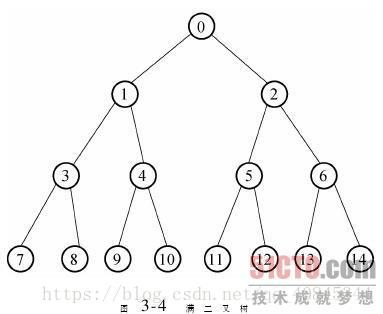
其遍历顺序为: 0-1-3-7-8-4-9-10-2-5-11-12-6-13-14
就上述顺序表明遍历过程总是从根到左,再到右
由消除尾递归的方式可得其迭代式
void travPre_I1(BinNodePosi* x,VISIT& visit){
stacks; //借助辅助栈记录根节点的左右孩子,以便于回溯
if(x) s.push(x);
while(!s.empty()){
visit(s.top()->data);//访问当前节点
s.pop();//删除栈顶
if(x->lChild) s.push(x->rchild);//由于栈的结构,所以让rChild先进,lChild后进即可做到先访问lChild,后rChild
if(x->rChild) s.push(x->lChild);
}
//整个while操作就可以实现向左子树深入的过程,直到没有左子树
}
通过消除尾递归的方式所得到的迭代式不具有普遍性(无法推广到中序,后序,这二者非尾递归),就此通过以下迭代式做阐述
void travPre_I2(BinNodePosi* x,VISIT& visit){
stacks;
while(x){//
visit(x->data);
while(x->lChild){
s.push(x->rChild);//有右孩子存入栈中,以便回溯访问
x=x->lchild;//迭代向左子树进行深入
}
x=s.top();
s.pop();
}
//看似O(n^2),但复杂度低于递归版
}
中序遍历
中序遍历:先查看最左端的叶子节点,然后根节点,最后右子树
得递归式:
void traveIn_R(BinNodePosi* x,VISIT& visit){
if(!x) return;
traveIn_R(x->lChild,visit);//先向左深入直到最左的叶子节点
visit(x->data);
traveIn_R(x->lChild,visit);
}
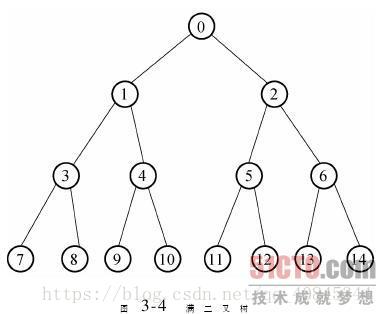
上图的中序遍历顺序:7-3-8-1-9-4-10-0-11-5-12-2-13-6-14
根据先序遍历的迭代可推广到中序遍历
void traveIn_I(BinNodePosi* x,VISIT& visit){
stacks;
while(!s.empty()){
while(x){
s.push(x);
x=x->lChild;//向左子树不断深入
}
x=s.top();
visit(x->data);
x=x->rChild;
s.pop();
}
}
上述过程描述如下:
先将所有最左边的左子树存入栈中,直到到达最左端的叶子节点(如上图的7号位置),当进行完visit操作后,节点转向7号的右子树,没有右子树的情况下将弹出栈内元素,开始回溯,向上回溯至当前节点具有右子树时,将该右子树下的所有左子树入栈,重复上述操作,直到所有节点都遍历.
遍历过程中无右子树的节点需要做回溯处理
后序遍历
后序遍历: 先依次遍历完左子树,右子树后才访问根节点
得如下递归定义式:
void travePost_R(BinNodePosi* x,VISIT& visit){
if(!x) return;
travePost_R(x->lChild,visit);
travePost_R(x->rChild,visit);
visit(x->data);
}
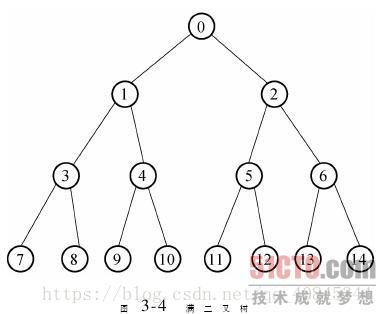
上述图片中的遍历顺序:7-8-3-9-10-4-1-11-12-5-13-14-6-2-0
迭代式如下:
void travePast_I(BinNodePosi* x,VISIT& visit){
stacks;
if(x)
s.push(x);
while(!s.empty()){
if(s.top()!=x->parent){
//s.top()!=x->parent主要用于判断两节点是否属于兄弟节点,例如上图的3,4;使得可以转向4号,将4号下的最左边的左子树及部分右子树进行入栈处理
while(x){
if(x->rChild) s.push(x->rChild);
if(x->lChild) s.push(x->lChild);
x=x->lChild;
//将最左边的左子树,及部分右子树依次存入栈中
}
}
x=s.top();
visit(x->data);
s.pop();
}
}
层次遍历
层次遍历:将二叉树看做金字塔形状,层次遍历做到的就是对每一层中左子树,右子树进行遍历处理,遍历顺序总是"先上后下,先左后右", 该遍历方式在广度优先遍历中也有所应用
由于层次遍历具有顺序性,而非后进先出原则,所以采用queue处理
上图中的遍历顺序:0-1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14
迭代式如下:
void traveLevel_R(BinNodePosi* x,VISIT& visit){
queueq;
if(x) q.push(x);
while(!q.empty()){
x=queue.front();
visit(x->data);
if(x->lChild) q.push(x->lChild);
if(x->rChild) q.push(x->rChild);
}
}
每当一个节点入队时,便让该节点的左右子树入队,由于队列的先进先出的性质,就能使每一层都能依次遍历
来一点小插曲
完全二叉树
在层次遍历中,每一次迭代中都必定有一个节点出队,如果在前n/2次迭代中都有左孩子入队, 且前n/2-1次迭代中都有右孩子入队,那么这棵树就是完全二叉树
拓扑结构特征: 叶子节点只能出现在最底部的两层,且最底层的叶子节点必须位于次叶子节点的左侧
高度h的完全二叉树, 规模介于2h~2(h+1)-1之间
满二叉树
所有叶子节点都位于最底层, 高度为h的满二叉树由2^(h+1)-1个节点组成
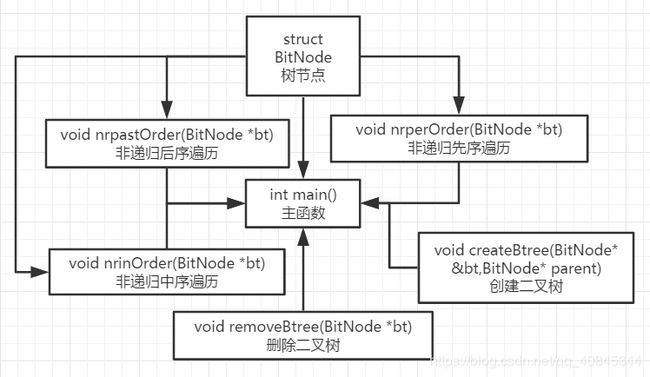
完整详细设计(递归的设计方式很简单将不再阐述)
数据结构定义如下:
二叉树本身主要由结构体完成, 该结构体包含每个节点存储的节点数据value, 以及两个左右指针 lchild 和 rchild和一个父指针 parent , 这两个指针主要用来指向二叉树的左右子树, 通过左右指针, 就能很好的完成二叉树的遍历, 使用父指针也能很好完成节点的记录, 由于采用的非递归的方式遍历树结构, 所以需要使用到辅助数组, 通过数组, 和循环模拟递归遍历的过程。
功能详细设计:
- 二叉树结构:每一个二叉树节点包含数据域以及3个指针(分别指向左子树,右子树,父节点)。
- 创建二叉树: 采用前序遍历的方式创建一棵完整的二叉树, 便于后面的遍历方式的测试,我使用"#"字符代表空。
- 非递归的前序遍历: 前序遍历的方式是先查看当前节点内容然后再查看左子树, 最后查看右子树。所以在非递归遍历中, 就模拟这种遍历方式, 首先存入根节点, 使用循环, 每次将数组最后位置的节点取出, 进行访问, 将访问过的节点的右子树存入数组中, 然后存左子树, 循环终止条件是数组为空, 模拟这种情况, 就能每次做到先访问根, 然后访问左子树, 最后访问右子树
- 非递归中序遍历: 中序遍历是先访问左子树, 再访问根节点, 最后访问右子树, 同样的采用数组模拟这种遍历方式。首先将当前节点的所有依次左子树存入数组中(直到没有左子树),然后取出数组中最后一个位置的节点进行访问,此时再转向右子树(无论右子树是否存在,这里需要利用右子树等于空的条件进行判断下一次循环是否要再将左子树存入数组中),执行完上述操作后,再重复执行,直到所有节点都访问完。
- 非递归后序遍历:后序遍历是先访问左子树,再访问右子树,最后访问根节点,非递归实现:将当前节点的所有左子树依次存入数组中(同时将该节点的右子树存入数组中,便于待会模拟回溯),左右子树存储的条件是:左右节点都访问过才能访问父节点,当栈顶元素与当前元素的父节点是同一个,则说明当前节点存在兄弟节点还没被访问1.整个过程尽量往左子树方向走,如果该节点没有左子树,就往右子树方向走一次,然后重复步骤1,直到节点左右子树都不存在,此时输出该节点存储的数据
写代码容易出现的问题:
正确理解递归遍历的方式, 防止理解错误导致, 不能用栈结构模拟出遍历的过程, 在非递归后序遍历,没用弄清楚循环判断和条件判断,导致在遍历过程中出现错误,最后采用得到方式就是判断栈顶元素与当前节点的父节点是否是同一个,通过这样的方式判断是否输出该节点的父节点内容。
树结构体:
struct BitNode{
BitNode(char c,BitNode *p):data(c),parent(p){}
Type data;
BitNode *parent=NULL,*lchild=NULL,*rchild=NULL;
};
非递归先序遍历:
void nrperOrder(BitNode *bt){//非递归先序遍历
int top=-1;
BitNode *stack[size],*p;
if(bt!=NULL)stack[++top]=bt;
else return;
while(top>-1){
p=stack[top--];
cout<data;
//有右存右,有左存左,先存右再存左
if(p->rchild!=NULL)stack[++top]=p->rchild;
if(p->lchild!=NULL)stack[++top]=p->lchild;
}
}
非递归中序遍历:
void nrinOrder(BitNode *bt){//非递归中序遍历
int top=-1;
BitNode *stack[size],*p=bt;
while(p||top>-1){
if(p){
stack[++top]=p;
p=p->lchild;
}else{
p=stack[top--];
cout<data;
p=p->rchild;
}
}
}
非递归后序遍历:
void nrpastOrder(BitNode *bt){//非递归后序遍历
int top=-1,tag[size];
BitNode *stack[size],*p=bt;
stack[++top]=bt;
while(top>-1){
//左右节点都访问过才能访问parent
//当栈顶元素与当前元素p的parent是一个,则说明p存在兄弟节点还没被访问
if(stack[top]!=p->parent){
p=stack[top];
while(p){
if(p->rchild)stack[++top]=p->rchild;
if(p->lchild)stack[++top]=p->lchild;
if(p->lchild)p=p->lchild;//尽量往左偏移
else if(p->rchild)p=p->rchild;//做不下去,往右走
else p=NULL;//左右都走不下去,p置空
}
}
p=stack[top--];
cout<data;
}
}
求根节点到指定节点的路径:
void path(BitNode *bt,char c,BitNode *parent){
//方法1.先序遍历,找到目标节点,不断返回父节点(即当前节点到根节点路径),中后序遍历一致
//方法2.迭代式查找,找到当前节点然后迭代输出parent
int top=-1;
BitNode *stack[size],*p;
if(bt!=NULL)stack[++top]=bt;
else return;
while(top>-1){
p=stack[top--];
if(p->data==c){
while(p){
cout<data;
p=p->parent;
}
return;
}
if(p->rchild!=NULL)stack[++top]=p->rchild;
if(p->lchild!=NULL)stack[++top]=p->lchild;
}
}
完整函数调用代码如下:
#include
#define Type char
#define size 20
using namespace std;
struct BitNode{
BitNode(char c,BitNode *p):data(c),parent(p){}
Type data;
BitNode *parent=NULL,*lchild=NULL,*rchild=NULL;
};
void createBtree(BitNode* &bt,BitNode* parent){//创建二叉树
char c;
if((cin>>c)&&(c!='#')&&(c!='\n')){
bt=new BitNode(c,parent);
parent=bt;
createBtree(bt->lchild,parent);
createBtree(bt->rchild,parent);
}
}
void nrperOrder(BitNode *bt){//非递归先序遍历
int top=-1;
BitNode *stack[size],*p;
if(bt!=NULL)stack[++top]=bt;
else return;
while(top>-1){
p=stack[top--];
cout<data;
//有右存右,有左存左,先存右再存左
if(p->rchild!=NULL)stack[++top]=p->rchild;
if(p->lchild!=NULL)stack[++top]=p->lchild;
}
}
void nrinOrder(BitNode *bt){//非递归中序遍历
int top=-1;
BitNode *stack[size],*p=bt;
while(p||top>-1){
if(p){
stack[++top]=p;
p=p->lchild;
}else{
p=stack[top--];
cout<data;
p=p->rchild;
}
}
}
void nrpastOrder(BitNode *bt){//非递归后序遍历
int top=-1,tag[size];
BitNode *stack[size],*p=bt;
stack[++top]=bt;
while(top>-1){
//左右节点都访问过才能访问parent
//当栈顶元素与当前元素p的parent是一个,则说明p存在兄弟节点还没被访问
if(stack[top]!=p->parent){
p=stack[top];
while(p){
if(p->rchild)stack[++top]=p->rchild;
if(p->lchild)stack[++top]=p->lchild;
if(p->lchild)p=p->lchild;//尽量往左偏移
else if(p->rchild)p=p->rchild;//做不下去,往右走
else p=NULL;//左右都走不下去,p置空
}
}
p=stack[top--];
cout<data;
}
}
void path(BitNode *bt,char c,BitNode *parent){
//方法1.先序遍历,找到目标节点,不断返回父节点(即当前节点到根节点路径),中后序遍历一致
//方法2.迭代式查找,找到当前节点然后迭代输出parent
int top=-1;
BitNode *stack[size],*p;
if(bt!=NULL)stack[++top]=bt;
else return;
while(top>-1){
p=stack[top--];
if(p->data==c){
while(p){
cout<data;
p=p->parent;
}
return;
}
if(p->rchild!=NULL)stack[++top]=p->rchild;
if(p->lchild!=NULL)stack[++top]=p->lchild;
}
}
void removeBtree(BitNode *bt){
if(bt){
removeBtree(bt->lchild);
removeBtree(bt->rchild);
delete bt;
}
}
int main(){//ABD#GJ#K###EH###C#F#I##
BitNode *bt;
char c;
int count=0;
cout<<"创建二叉树:";createBtree(bt,NULL);
cout<<"非递归前序遍历:";nrperOrder(bt);cout<>c; path(bt,c,NULL);cout<