使用YOLOv3(YOLOv3-tiny)训练自己的数据(1)
数据准备
图像xml+txt数据集的制作:
参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/Patrick_Lxc/article/details/80615433
中的test.py与voc_annotation.py
https://blog.csdn.net/lilai619/article/details/79695109
中的voc_label.py
文件夹安排:
- data
- - Annotations
- - Images
- - labels(存放坐标的txt文件)
- - xml(存放坐标的xml文件)
- - .names
- - 2007_train.txt
- - 2007_test.txt
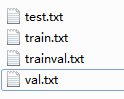
- - ImageSets
- - -Main
- - - - train.txt
- - - - test.txt
- - - - trainval.txt
- - - - val.txt
1、
从链接中下载exe文件,对图像进行Label。得到xml文件。
注意:
exe文件的路径不要有中文,否则无法打开exe文件。
2、运行test.py文件
import os
import random
trainval_percent = 0.1
train_percent = 0.9
xmlfilepath = 'Annotations/xml'
txtsavepath = 'ImageSets\Main'
total_xml = os.listdir(xmlfilepath)
num = len(total_xml)
list = range(num)
tv = int(num * trainval_percent)
tr = int(tv * train_percent)
trainval = random.sample(list, tv)
train = random.sample(trainval, tr)
ftrainval = open('ImageSets/Main/trainval.txt', 'w')
ftest = open('ImageSets/Main/test.txt', 'w')
ftrain = open('ImageSets/Main/train.txt', 'w')
fval = open('ImageSets/Main/val.txt', 'w')
for i in list:
name = total_xml[i][:-4] + '\n'
if i in trainval:
ftrainval.write(name)
if i in train:
ftest.write(name)
else:
fval.write(name)
else:
ftrain.write(name)
ftrainval.close()
ftrain.close()
fval.close()
ftest.close()
---------------------
作者:Patrick_Lxc
来源:CSDN
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/Patrick_Lxc/article/details/80615433
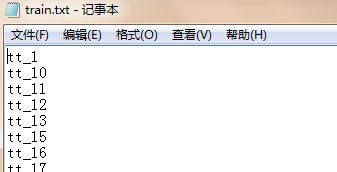
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请附上博文链接!在ImageSets/Main中得到以下四个文件,文件内容是图像的文件名
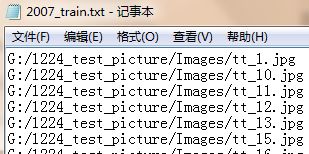
3、运行voc_annotation.py文件得到训练集、测试集、验证集的图片路径
按照需要修改classes = [ ]的内容、修改in_file,image_ids,list_file.write的路径
文件内容是图片的路径:
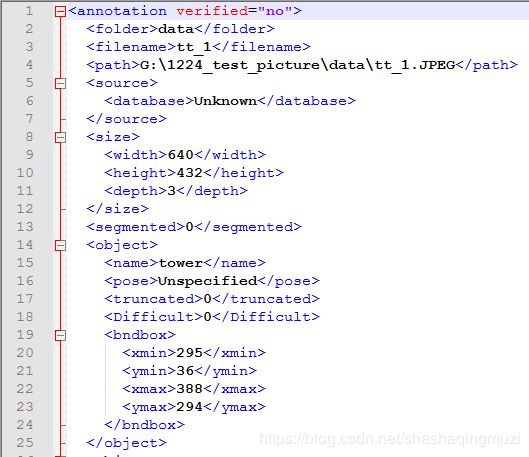
4、使用voc_label.py将Annotations文件夹下的xml文件转化为labels文件夹下的txt格式
可以参考以下代码:
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import pickle
import os
from os import listdir, getcwd
from os.path import join
sets=[('2007', 'train'), ('2007', 'val'), ('2007', 'test')]
classes = ["tower", "tree"]
def convert(size, box):
dw = 1./(size[0])
dh = 1./(size[1])
x = (box[0] + box[1])/2.0 - 1
y = (box[2] + box[3])/2.0 - 1
w = box[1] - box[0]
h = box[3] - box[2]
x = x*dw
w = w*dw
y = y*dh
h = h*dh
return (x,y,w,h)
def convert_annotation(image_id):
in_file = open('Annotations/%s.xml'%(image_id))
out_file = open('labels/%s.txt'%(image_id), 'w')
tree=ET.parse(in_file)
root = tree.getroot()
size = root.find('size')
w = int(size.find('width').text)
h = int(size.find('height').text)
for obj in root.iter('object'):
difficult = obj.find('Difficult').text
cls = obj.find('name').text
if cls not in classes or int(difficult)==1:
continue
cls_id = classes.index(cls)
xmlbox = obj.find('bndbox')
b = (float(xmlbox.find('xmin').text), float(xmlbox.find('xmax').text), float(xmlbox.find('ymin').text), float(xmlbox.find('ymax').text))
bb = convert((w,h), b)
out_file.write(str(cls_id) + " " + " ".join([str(a) for a in bb]) + '\n')
wd = getcwd()
for year, image_set in sets:
if not os.path.exists('labels/'):
os.makedirs('labels/')
image_ids = open('ImageSets/Main/%s.txt'%(image_set)).read().strip().split()
list_file = open('%s_%s.txt'%(year, image_set), 'w')
for image_id in image_ids:
list_file.write('JPEGImages/%s.jpg\n'%(image_id))
convert_annotation(image_id)
list_file.close()
# os.system("cat 2007_train.txt 2007_val.txt 2012_train.txt 2012_val.txt > train.txt")
# os.system("cat 2007_train.txt 2007_val.txt 2007_test.txt 2012_train.txt 2012_val.txt > train.all.txt")
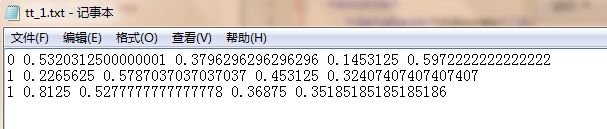
运行结果如下:
xml文件
转化为txt文件:
5、修改文件参数
修改data/voc.names 为自己的类别
修改cfg/voc.data 中classes train valid 等信息
修改yolov3-tiny.cfg文件